-
3.1 观察者模式
-
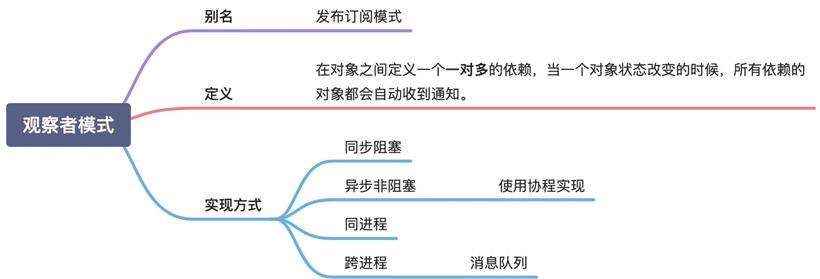
代码实现
基础实现
Code
package observer import "fmt" // ISubject subject type ISubject interface { Register(observer IObserver) Remove(observer IObserver) Notify(msg string) } // IObserver 观察者 type IObserver interface { Update(msg string) } // Subject Subject type Subject struct { observers[] IObserver } // Register 注册 func(sub * Subject) Register(observer IObserver) { sub.observers = append(sub.observers, observer) } // Remove 移除观察者 func(sub * Subject) Remove(observer IObserver) { for i, ob: = range sub.observers { if ob == observer { sub.observers = append(sub.observers[: i], sub.observers[i + 1: ]...) } } } // Notify 通知 func(sub * Subject) Notify(msg string) { for _, o: = range sub.observers { o.Update(msg) } } // Observer1 Observer1 type Observer1 struct {} // Update 实现观察者接口 func(Observer1) Update(msg string) { fmt.Printf("Observer1: %s", msg) } // Observer2 Observer2 type Observer2 struct {} // Update 实现观察者接口 func(Observer2) Update(msg string) { fmt.Printf("Observer2: %s", msg) }单元测试
package observer import "testing" func TestSubject_Notify(t * testing.T) { sub: = & Subject {} sub.Register( & Observer1 {}) sub.Register( & Observer2 {}) sub.Notify("hi") }使用 Golang 实现 EventBus
我们实现一个支持以下功能的事件总线:
1.异步不阻塞
2.支持任意参数值
Code
package eventbus import ( "fmt" "reflect" "sync" ) // Bus Bus type Bus interface { Subscribe(topic string, handler interface {}) error Publish(topic string, args...interface {}) } // AsyncEventBus 异步事件总线 type AsyncEventBus struct { handlers map[string][] reflect.Value lock sync.Mutex } // NewAsyncEventBus new func NewAsyncEventBus() * AsyncEventBus { return &AsyncEventBus { handlers: map[string][] reflect.Value {}, lock: sync.Mutex {}, } } // Subscribe 订阅 func(bus * AsyncEventBus) Subscribe(topic string, f interface {}) error { bus.lock.Lock() defer bus.lock.Unlock() v: = reflect.ValueOf(f) if v.Type().Kind() != reflect.Func { return fmt.Errorf("handler is not a function") } handler, ok: = bus.handlers[topic] if !ok { handler = [] reflect.Value {} } handler = append(handler, v) bus.handlers[topic] = handler return nil } // Publish 发布 // 这里异步执行,并且不会等待返回结果 func(bus * AsyncEventBus) Publish(topic string, args...interface {}) { handlers, ok: = bus.handlers[topic] if !ok { fmt.Println("not found handlers in topic:", topic) return } params: = make([] reflect.Value, len(args)) for i, arg: = range args { params[i] = reflect.ValueOf(arg) } for i: = range handlers { go handlers[i].Call(params) } }单元测试
package eventbus import ( "fmt" "testing" "time" ) func sub1(msg1, msg2 string) { time.Sleep(1 * time.Microsecond) fmt.Printf("sub1, %s %s\n", msg1, msg2) } func sub2(msg1, msg2 string) { fmt.Printf("sub2, %s %s\n", msg1, msg2) } func TestAsyncEventBus_Publish(t * testing.T) { bus: = NewAsyncEventBus() bus.Subscribe("topic:1", sub1) bus.Subscribe("topic:1", sub2) bus.Publish("topic:1", "test1", "test2") bus.Publish("topic:1", "testA", "testB") time.Sleep(1 * time.Second) }结果
=== RUN TestAsyncEventBus_Publish sub2, testA testB sub2, test1 test2 sub1, testA testB sub1, test1 test2 -- -PASS: TestAsyncEventBus_Publish(1.01 s)
- 留下你的读书笔记
- 你还没登录,点击这里
-
用户笔记留言

