-
2.3 Web RESTFul HelloWorld
-
本节介绍使用 Kotlin 结合 SpringBoot 开发一个RESTFul版本的 Hello.World。
1.新建gradle,kotlin工程:
打开IDEA的File > New > Project , 如下图

按照界面操作,输入相应的工程名等信息,即可新建一个使用Gradle构建的标准Kotlin工程。
1.build.gradle 基本配置
IDEA自动生成的Gradle配置文件如下:
group 'com.easy.kotlin' version '1.0-SNAPSHOT' buildscript { ext.kotlin_version = '1.1.2-2' repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { // Kotlin Gradle插件 classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:$kotlin_version" } } apply plugin: 'java' apply plugin: 'kotlin' sourceCompatibility = 1.8 targetCompatibility = 1.8 repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { compile "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jre8:$kotlin_version" testCompile group: 'junit', name: 'junit', version: '4.12' }从上面的配置文件我们可以看出,IDEA已经自动把Gradle 构建Kotlin工程插件 kotlin-gradle-plugin,以及Kotlin标准库kotlin-stdlib添加到配置文件中了。
配置SpringBoot相关内容
下面我们来配置SpringBoot相关内容。首先在构建脚本里面添加ext变量springBootVersion。
ext.kotlin_version = '1.1.2-2' ext.springboot_version = '1.5.2.RELEASE'
然后在构建依赖里添加spring-boot-gradle-plugin
buildscript { ... dependencies { // Kotlin Gradle插件 classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:$kotlin_version" // SpringBoot Gradle插件 classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:$springboot_version") // Kotlin整合SpringBoot的默认无参构造函数,默认把所有的类设置open类插件 classpath("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-noarg:$kotlin_version") classpath("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-allopen:$kotlin_version") } }配置无参(no-arg)、全开放(allopen)插件
其中,org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-noarg是无参(no-arg)编译器插件,它为具有特定注解的类生成一个额外的零参数构造函数。 这个生成的构造函数是合成的,因此不能从 Java 或 Kotlin 中直接调用,但可以使用反射调用。 这样我们就可以使用 Java Persistence API(JPA)实例化 data 类。
其中,org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-allopen 是全开放编译器插件。我们使用Kotlin 调用Java的Spring AOP框架和库,需要类为 open(可被继承实现),而Kotlin 类和函数都是默认 final 的,这样我们需要为每个类和函数前面加上open修饰符。
这样的代码写起来,可费事了。还好,我们有all-open 编译器插件。它会适配 Kotlin 以满足这些框架的需求,并使用指定的注解标注类而其成员无需显式使用 open 关键字打开。 例如,当我们使用 Spring 时,就不需要打开所有的类,跟我们在Java中写代码一样,只需要用相应的注解标注即可,如 @Configuration 或 @Service。
完整的build.gradle配置文件如下:
group 'com.easy.kotlin' version '1.0-SNAPSHOT' buildscript { ext.kotlin_version = '1.1.2-2' ext.springboot_version = '1.5.2.RELEASE' repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { // Kotlin Gradle插件 classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:$kotlin_version" // SpringBoot Gradle插件 classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:$springboot_version") // Kotlin整合SpringBoot的默认无参构造函数,默认把所有的类设置open类插件 // 无参(no-arg)编译器插件为具有特定注解的类生成一个额外的零参数构造函数。 这个生成的构造函数是合成的,因此不能从 Java 或 Kotlin 中直接调用,但可以使用反射调用。 这允许 Java Persistence API(JPA)实例化 data 类,虽然它从 Kotlin 或 Java 的角度看没有无参构造函数 classpath("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-noarg:$kotlin_version") // 全开放插件(kotlin-allopen) classpath("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-allopen:$kotlin_version") } } apply plugin: 'java' apply plugin: 'kotlin' //Kotlin整合SpringBoot需要的spring,jpa,org.springframework.boot插件 //Kotlin-spring 编译器插件,它根据 Spring 的要求自动配置全开放插件。 apply plugin: 'kotlin-spring' //该插件指定 @Entity 和 @Embeddable 注解作为应该为一个类生成无参构造函数的标记。 apply plugin: 'kotlin-jpa' apply plugin: 'org.springframework.boot' sourceCompatibility = 1.8 targetCompatibility = 1.8 repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { compile "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jre8:$kotlin_version" testCompile group: 'junit', name: 'junit', version: '4.12' compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web") testCompile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test") compile("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa") compile('mysql:mysql-connector-java:5.1.13') }配置application.properties
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/easykotlin spring.datasource.username = root spring.datasource.password = root#spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver# Specify the DBMS spring.jpa.database = MYSQL# Keep the connection alive if idle for a long time (needed in production) spring.datasource.testWhileIdle = true spring.datasource.validationQuery = SELECT 1# Show or not log for each sql query spring.jpa.show-sql = true# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, update) spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update# Naming strategy spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy = org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy# The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect server.port=8000
整体工程架构
UNIX操作系统说,“一切都是文件”。所以,我们 的所有的源代码、字节码、工程资源文件等等,一切都是文件。文件里面存的是字符串(01也当做是字符)。各种框架、库、编译器,解释器,都是对这些字符串流进行过滤,最后映射成01机器码(或者CPU微指令码等),最终落地到硬件上的高低电平。
整体工程目录如下:
. ├── README.md ├── build │ └── kotlin-build │ └── caches │ └── version.txt ├── build.gradle ├── easykotlin.sql ├── settings.gradle └── src ├── main │ ├── java │ ├── kotlin │ │ └── com │ │ └── easy │ │ └── kotlin │ │ ├── Application.kt │ │ ├── controller │ │ │ ├── HelloWorldController.kt │ │ │ └── PeopleController.kt │ │ ├── entity │ │ │ └── People.kt │ │ ├── repository │ │ │ └── PeopleRepository.kt │ │ └── service │ │ └── PeopleService.kt │ └── resources │ ├── application.properties │ └── banner.txt └── test ├── java ├── kotlin └── resources 19 directories, 13 files一切尽在不言中,静静地看工程文件结构。
直接写个HelloWorldController
package com.easy.kotlin.controller import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController @RestController class HelloWorldController { @GetMapping(value = *arrayOf("/helloworld", "/")) fun helloworld(): Any { return "Hello,World!" } }我们再写个访问数据库的标准四层代码
写领域模型类People
package com.easy.kotlin.entity import java.util.* import javax.persistence.Entity import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue import javax.persistence.GenerationType import javax.persistence.Id /** * Created by jack on 2017/6/6. */ @Entity class People( @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) val id: Long?, val firstName: String?, val lastName: String?, val gender: String?, val age: Int?, val gmtCreated: Date, val gmtModified: Date ) { override fun toString(): String { return "People(id=$id, firstName='$firstName', lastName='$lastName', gender='$gender', age=$age, gmtCreated=$gmtCreated, gmtModified=$gmtModified)" } }写PeopleRepository
package com.easy.kotlin.repository import com.easy.kotlin.entity.People import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository interface PeopleRepository : CrudRepository<People, Long> { fun findByLastName(lastName: String): List<People>? }写PeopleService
package com.easy.kotlin.service import com.easy.kotlin.entity.People import com.easy.kotlin.repository.PeopleRepository import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired import org.springframework.stereotype.Service @Service class PeopleService : PeopleRepository { @Autowired val peopleRepository: PeopleRepository? = null override fun findByLastName(lastName: String): List<People>? { return peopleRepository?.findByLastName(lastName) } override fun <S : People?> save(entity: S): S? { return peopleRepository?.save(entity) } override fun <S : People?> save(entities: MutableIterable<S>?): MutableIterable<S>? { return peopleRepository?.save(entities) } override fun delete(entities: MutableIterable<People>?) { } override fun delete(entity: People?) { } override fun delete(id: Long?) { } override fun findAll(ids: MutableIterable<Long>?): MutableIterable<People>? { return peopleRepository?.findAll(ids) } override fun findAll(): MutableIterable<People>? { return peopleRepository?.findAll() } override fun exists(id: Long?): Boolean { return peopleRepository?.exists(id)!! } override fun count(): Long { return peopleRepository?.count()!! } override fun findOne(id: Long?): People? { return peopleRepository?.findOne(id) } override fun deleteAll() { } }写PeopleController
package com.easy.kotlin.controller import com.easy.kotlin.service.PeopleService import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody @Controller class PeopleController { @Autowired val peopleService: PeopleService? = null @GetMapping(value = "/hello") @ResponseBody fun hello(@RequestParam(value = "lastName") lastName: String): Any { val peoples = peopleService?.findByLastName(lastName) val map = HashMap<Any, Any>() map.put("hello", peoples!!) return map } }运行测试
点击Gradle的bootRun , 如下图
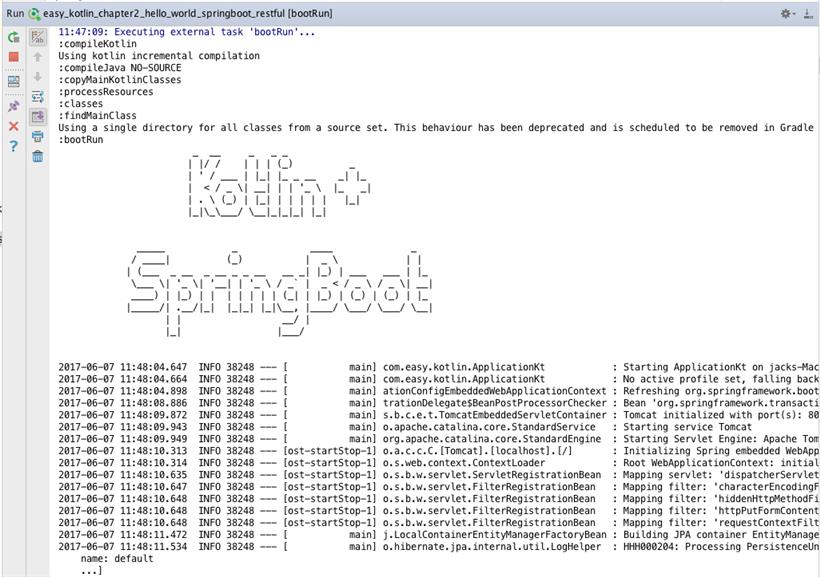
如果没有异常,启动成功,我们将看到以下输出:
打开浏览器,访问请求:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/
输出响应:
Hello,World!
访问
http://127.0.0.1:8000/hello?lastName=chen
// 20170607115700 // http://127.0.0.1:8000/hello?lastName=chen { "hello": [ { "id": 1, "firstName": "Jason", "lastName": "Chen", "gender": "Male", "age": 28, "gmtCreated": 1496768497000, "gmtModified": 1496768497000 }, { "id": 3, "firstName": "Corey", "lastName": "Chen", "gender": "Female", "age": 20, "gmtCreated": 1496768497000, "gmtModified": 1496768497000 } ... ] }本节示例工程源代码:
https://github.com/EasyKotlin/easy_kotlin_chapter2_hello_world_springboot_restful
- 留下你的读书笔记
- 你还没登录,点击这里
-
用户笔记留言

