- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
public interface ICommand
{
event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged;
bool CanExecute(object parameter);
void Execute(object parameter);
}
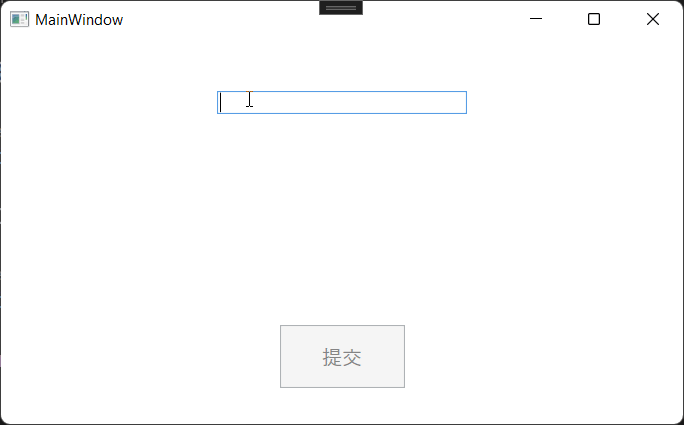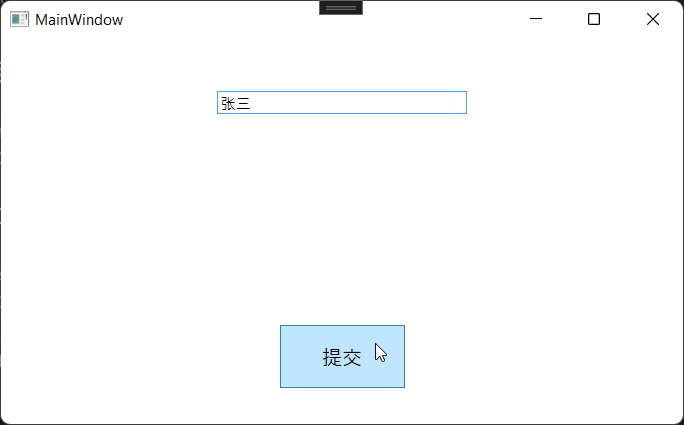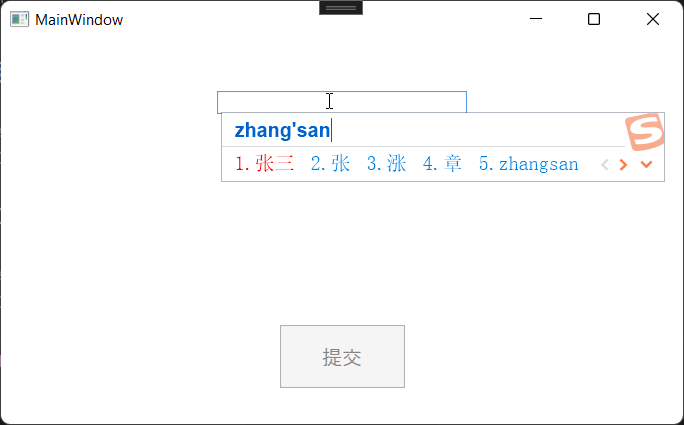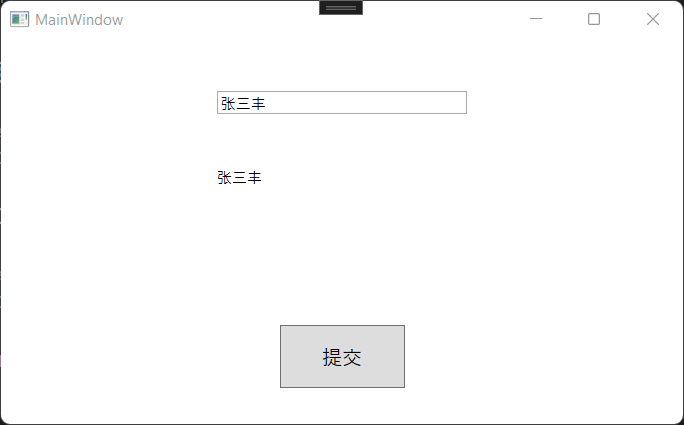
在整个MVVM架构中该接口起着非常重要的作用,我们来看一下该接口成员,CanExecuteChanged事件触发通知UI界面做出响应,比如按钮禁用或启用,表示CanExecute该接口返回一个bool值,表示是否执行命令,返回true,命令执行,false命令不执行。我们通过一个简单的例子实现命令绑定,需求比较简单:我们定义一个输入框,如果为空状态,提交按钮禁用,如果有值,按钮启用,点击提交,并将值显示到页面。
public class DelegateCommand : ICommand
{
private Action _execute;
private Func<bool> _canExecute;
public DelegateCommand(Action executeMethod)
{
_execute = executeMethod;
}
public DelegateCommand(Action executeMethod, Func<bool> canExecute)
: this(executeMethod)
{
this._canExecute = canExecute;
}
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
{
return _canExecute();
}
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged
{
add
{
CommandManager.RequerySuggested += value;
}
remove
{
CommandManager.RequerySuggested -= value;
}
}
public void Execute(object parameter)
{
_execute();
}
}
接下来我们定义一个ViewMode类,命名为SampleViewModel实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口 public class SampleViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
private void NotifyPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] String propertyName = "")
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
private string name = String.Empty;
public string Name
{
get
{
return name;
}
set
{
if (value != this.name)
{
this.name = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
private string displayName = string.Empty;
public string DisplayName
{
get { return displayName; }
set
{
if (value != this.displayName)
{
displayName = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
ICommand delegateCommand;
public ICommand DelegateCommand
{
get
{
if (delegateCommand == null)
{
delegateCommand = new DelegateCommand(Execute, CanExecute);
}
return delegateCommand;
}
}
public void Execute()
{
DisplayName = Name;
}
public bool CanExecute()
{
return !string.IsNullOrEmpty(Name);
}
}
XMLA页面定义:<Window x:Class="Example_21.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:Example_21"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
<RowDefinition></RowDefinition>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<TextBox Grid.Row="0" Name="txtBox" Width="200" Text="{Binding Path=Name,UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Width="200" Text="{Binding Path=DisplayName}"></TextBlock>
<Button Grid.Row="2" x:Uid="btnSend" x:Name="btnSend" FontSize="16" Content="提交" Width="100" Height="50"
Margin="0,0,0,5" Command="{Binding DelegateCommand}" >
</Button>
</Grid>
</Window>
MainWindow.xaml.cs 文件 public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
this.DataContext = new SampleViewModel();
}
}
从上面的例子可以看出我们可以使用控件的Command属性来绑定要执行的命令,我们还可以设置CommandParameter来传递参数,可以把UI上数据传递到后台,WPF整个框架是基于数据驱动,我们可以做到把UI层完全剥离出来,所以说WPF是一个前端和后台可以完全分离的框架。其实走到这里结合我们WPF-18 INotifyPropertyChanged 接口我们有点看到了MVVM开发模式的影子。