- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
<beans>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
<!-- 其他配置 -->
</beans>
然后,我们可以创建一个切面类来实现日志记录:@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggingAspect.class);
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.*.*(..))")
public void logMethod() {}
@Before("logMethod()")
public void logMethodEntry(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
LOGGER.info("Entering method: {} with arguments: {}", joinPoint.getSignature().getName(), Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "logMethod()", returning = "result")
public void logMethodExit(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
LOGGER.info("Exiting method: {} with result: {}", joinPoint.getSignature().getName(), result);
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们定义了一个切点 logMethod(),它匹配所有 com.example 包下的方法。然后,我们使用 @Before 和 @AfterReturning 注解来分别记录方法的入参和返回值。在 JoinPoint 对象中,我们可以获取方法的签名和参数。@Service
public class MyService {
@LogMethod
public void doSomething(String arg1, int arg2) {
// 方法实现
}
}
这样,每次调用 doSomething 方法时,日志切面都会记录方法的入参和返回值。对于 Spring Boot 项目,实现日志切面的方法与普通的 Spring 项目类似。只需要在 Spring Boot 的配置类上添加 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解即可启用 AOP。@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {
// 其他配置
}
然后,我们可以创建一个切面类来实现日志记录:@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggingAspect.class);
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.*.*(..))")
public void logMethod() {}
@Before("logMethod()")
public void logMethodEntry(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
LOGGER.info("Entering method: {} with arguments: {}", joinPoint.getSignature().getName(), Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "logMethod()", returning = "result")
public void logMethodExit(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
LOGGER.info("Exiting method: {} with result: {}", joinPoint.getSignature().getName(), result);
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们定义了一个切点 logMethod(),它匹配所有 com.example 包下的方法。然后,我们使用 @Before 和 @AfterReturning 注解来分别记录方法的入参和返回值。在 JoinPoint 对象中,我们可以获取方法的签名和参数。@Service
public class MyService {
@LogMethod
public void doSomething(String arg1, int arg2) {
// 方法实现
}
}
这样,每次调用 doSomething 方法时,日志切面都会记录方法的入参和返回值。<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
然后,我们可以创建一个切面类来实现日志记录:@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggingAspect.class);
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.*.*(..))")
public void logMethod() {}
@Before("logMethod()")
public void logMethodEntry(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
LOGGER.info("Entering method: {} with arguments: {}", joinPoint.getSignature().getName(), Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
@(pointcut = "logMethod()", returning = "result")
public void logMethodExit(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
LOGGER.info("Exiting method: {} with result: {}", joinPoint.getSignature().getName(), result);
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们定义了一个切点 logMethod(),它匹配所有 com.example 包下的方法。然后,我们使用 @Before 和 @AfterReturning 注解来分别记录方法的入参和返回值。在 JoinPoint 对象中,我们可以获取方法的签名和参数。@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {
// 其他配置
}
这样,我们就可以在需要记录日志的方法上添加 @LogMethod 注解用日志:@Service
public class MyService {
@LogMethod
public void doSomething(String arg1, int arg2) {
// 方法实现
}
}
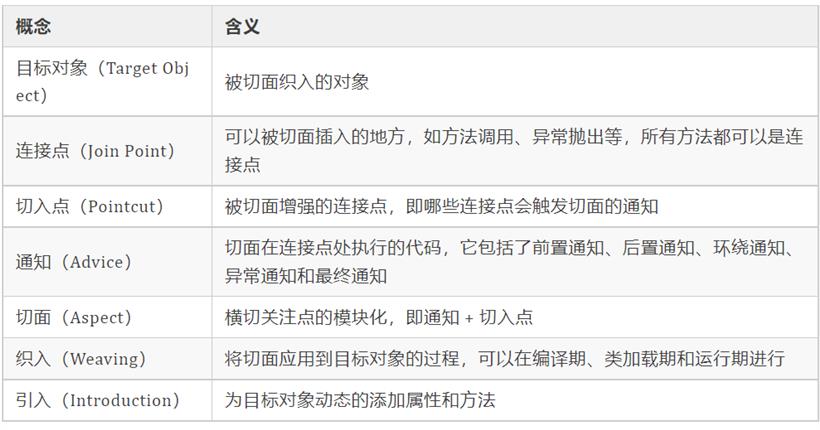
这样,每次调用 doSomething 方法时,日志切面都会记录方法的入参和返回值。织入(Weaving):将切面应用到目标对象并创建新的代理对象的过程。
提高代码的可读性和可理解性,将关注点的代码集中在一起,使得代码更加清晰和易于理解。