- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
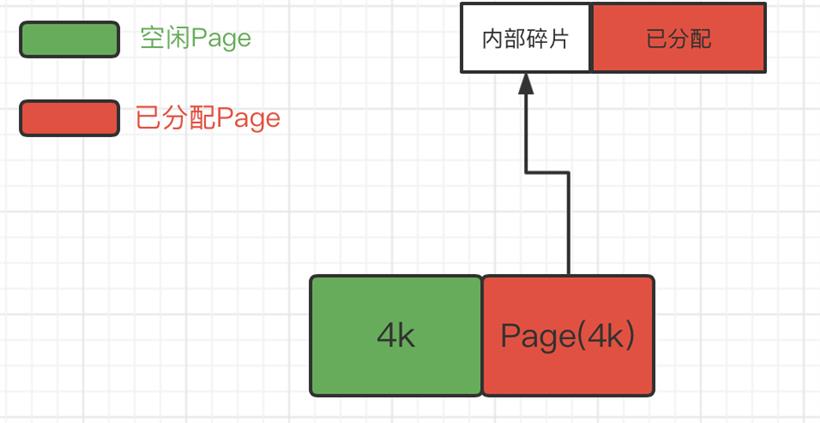
2.减少内存碎片,包括内部碎片和外部碎片,提升内存的有效利用率。


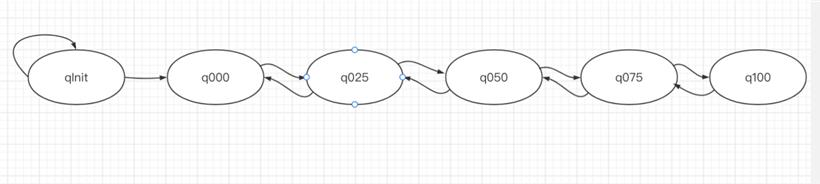
// 堆代码 duidaima.com // 内存使用率为100%的Chunk q100 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, null, 100, Integer.MAX_VALUE, chunkSize); // 内存使用率为75~100%的Chunk q075 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q100, 75, 100, chunkSize); // 内存使用率为50~100%的Chunk q050 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q075, 50, 100, chunkSize); // 内存使用率为25~75%的Chunk q025 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q050, 25, 75, chunkSize); // 内存使用率为1~50%的Chunk q000 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q025, 1, 50, chunkSize); // 内存使用率为0~25%的Chunk qInit = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q000, Integer.MIN_VALUE, 25, chunkSize); q100.prevList(q075); q075.prevList(q050); q050.prevList(q025); q025.prevList(q000); q000.prevList(null); qInit.prevList(qInit);六种类型的 PoolChunkList 除了 qInit,它们都形成了双向链表。
private void allocateNormal(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {
// 1.尝试从现有的 Chunk 进行分配
if (q050.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)
|| q025.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)
|| q000.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)
|| qInit.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)
|| q075.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
return;
}
// Add a new chunk 2.尝试创建一个 Chuank 进行内存分配
PoolChunk<T> c = newChunk(pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize);
boolean success = c.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
assert success;
// 4.将 PoolChunk 添加到 PoolChunkList 中
qInit.add(c);
}
boolean allocate(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {
final long handle;
// >= pageSize 通过位运算是否大于 512k
if ((normCapacity & subpageOverflowMask) != 0) {
handle = allocateRun(normCapacity);
} else {
handle = allocateSubpage(normCapacity);
}
if (handle < 0) {
return false;
}
ByteBuffer nioBuffer = cachedNioBuffers != null ? cachedNioBuffers.pollLast() : null;
// 3.初始化 PooledByteBuf
initBuf(buf, nioBuffer, handle, reqCapacity);
return true;
}
分配内存时为什么选择从 q050 开始?1、qinit 的 Chunk 利用率低,但不会被回收。
2、q075 和 q100 由于内存利用率太高,导致内存分配的成功率大大降低,因此放到最后。
3、q050 保存的是内存利用率 50%~100% 的 Chunk,这应该是个折中的选择。这样能保证 Chunk 的利用率都会保持在一个较高水平提高整个应用的内存利用率,并且内存利用率在 50%~100% 的 Chunk 内存分配的成功率有保障。
4、当应用在实际运行过程中碰到访问高峰,这时需要分配的内存是平时的好几倍需要创建好几倍的 Chunk,如果先从 q000 开始,这些在高峰期创建的 Chunk 被回收的概率会大大降低,延缓了内存的回收进度,造成内存使用的浪费。
final class PoolChunkList<T> implements PoolChunkListMetric {
private static final Iterator<PoolChunkMetric> EMPTY_METRICS = Collections.<PoolChunkMetric>emptyList().iterator();
private final PoolArena<T> arena;
// 下一个PoolChunkList(使用率更高的)
private final PoolChunkList<T> nextList;
// 最低使用率,低于该值,会移除该chunk,放到preList中
private final int minUsage;
// 最高使用率,高于该值,会移除该chunk,放到nextList中
private final int maxUsage;
// 最大可分配的内存大小,就是用minUsage计算的
private final int maxCapacity;
private PoolChunk<T> head;
// This is only update once when create the linked
// like list of PoolChunkList in PoolArena constructor.
// 前一个PoolChunkList(使用率更低的)
private PoolChunkList<T> prevList;
每个 PoolChunkList 都有内存使用率的上下限:minUsage 和 maxUsage,当 PoolChunk 进行内存分配后,如果使用率超过 maxUsage,那么 PoolChunk 会从当前 PoolChunkList 中删除,并移动到下一个 PoolChunkList;同理,PoolChunk 中的内存发生释放后,使用率小于 minUsage,那么 PoolChunk 会从当前 PoolChunkList 中移除,移动到前一个 PoolChunk List。final class PoolChunk<T> implements PoolChunkMetric {
final PoolArena<T> arena;
// 存储的数据
final T memory;
// 满二叉树中的节点是否被分配,数组大小为 4096
private final byte[] memoryMap;
// 满二叉树中的节点高度,数组大小为 4096
private final byte[] depthMap;
// PoolChunk 中管理的 2048 个 8K 内存块
private final PoolSubpage<T>[] subpages;
// 剩余的内存大小
private int freeBytes;
PoolChunkList<T> parent;
PoolChunk<T> prev;
PoolChunk<T> next;
// 省略其他代码
}
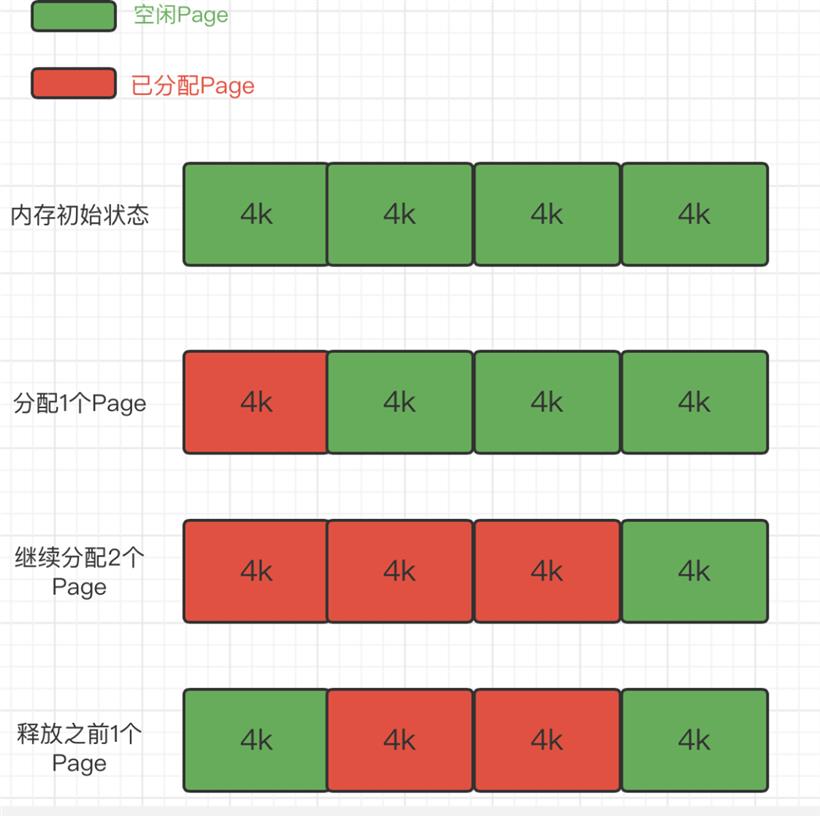
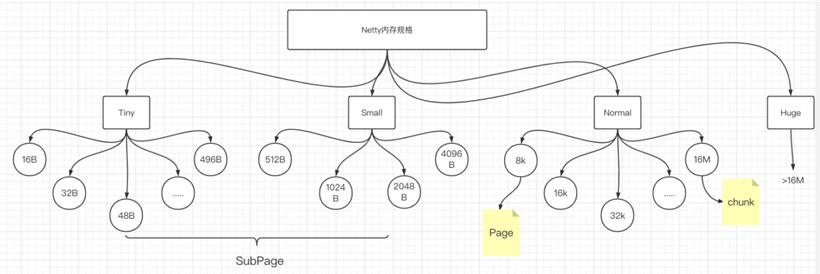
PoolChunk 我们可以理解为 Page(8K) 的集合 ,Page 只是一种抽象的概念,实际在 Netty 中 Page 指的是 PoolChunk 所管理的子内存块,每个子内存块采用 PoolSubpage 表示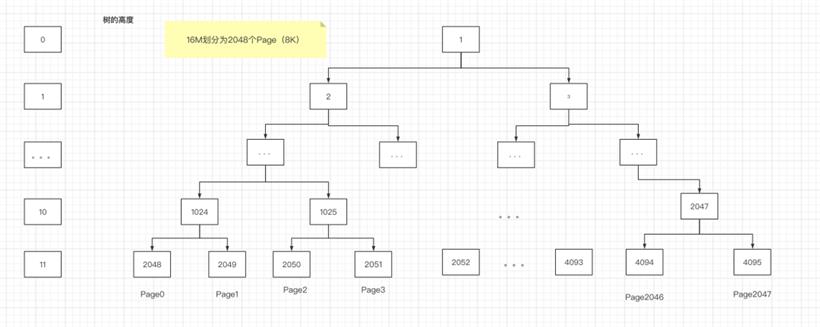
maxOrder = 11;
maxSubpageAllocs = 1 << maxOrder;
// Generate the memory map.
memoryMap = new byte[maxSubpageAllocs << 1];
depthMap = new byte[memoryMap.length];
int memoryMapIndex = 1;
// move down the tree one level at a time
for (int d = 0; d <= maxOrder; ++ d) {
int depth = 1 << d;
for (int p = 0; p < depth; ++ p) {
// in each level traverse left to right and set value to the depth of subtree
memoryMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d;
depthMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d;
memoryMapIndex ++;
}
}
deptMap 用于存放节点所对应的高度。例如第 2048 个节点 depthMap[1025] = 10 。private long allocateSubpage(int normCapacity) {
// Obtain the head of the PoolSubPage pool that is owned by the PoolArena and synchronize on it.
// This is need as we may add it back and so alter the linked-list structure.
PoolSubpage<T> head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(normCapacity);
// subpages are only be allocated from pages i.e., leaves
int d = maxOrder;
synchronized (head) {
int id = allocateNode(d);
if (id < 0) {
return id;
}
final PoolSubpage<T>[] subpages = this.subpages;
final int pageSize = this.pageSize;
freeBytes -= pageSize;
int subpageIdx = subpageIdx(id);
PoolSubpage<T> subpage = subpages[subpageIdx];
if (subpage == null) {
subpage = new PoolSubpage<T>(head, this, id, runOffset(id), pageSize, normCapacity);
subpages[subpageIdx] = subpage;
} else {
subpage.init(head, normCapacity);
}
return subpage.allocate();
}
}
PoolSubpage<T> findSubpagePoolHead(int elemSize) {
int tableIdx;
PoolSubpage<T>[] table;
// < 512
if (isTiny(elemSize)) {
tableIdx = elemSize >>> 4;
table = tinySubpagePools;
} else {
tableIdx = 0;
elemSize >>>= 10;
while (elemSize != 0) {
elemSize >>>= 1;
tableIdx ++;
}
table = smallSubpagePools;
}
return table[tableIdx];
}
根据代码可以看出,小内存分配的场景下,会首先找到对应的 PoolArena,然后根据计算出对应的TinySubpagePools 或者 SmallSubpagePools 数组对应的下标,如果对应数组元素所包含的 PoolSubpage 链表不存在任何节点,那么将创建新的 PoolSubpage 加入链表中。final class PoolSubpage<T> implements PoolSubpageMetric {
final PoolChunk<T> chunk;
// 对应满二叉树节点的下标
private final int memoryMapIdx;
// PoolSubpage 在 PoolChunk 中 memory 的偏移量
private final int runOffset;
// 记录每个小内存块的状态
private final long[] bitmap;
// 与 PoolArena 中 tinySubpagePools 或 smallSubpagePools 中元素连接成双向链表
PoolSubpage<T> prev;
PoolSubpage<T> next;
// 每个小内存块的大小
int elemSize;
// 最多可以存放多少小内存块:8K/elemSize
private int maxNumElems;
// 可用于分配的内存块个数
private int numAvail;
// 省略其他代码
}
PoolSubpage 是通过位图 bitmap 来记录子内存是否已经被使用,bit 的取值为 0 或 1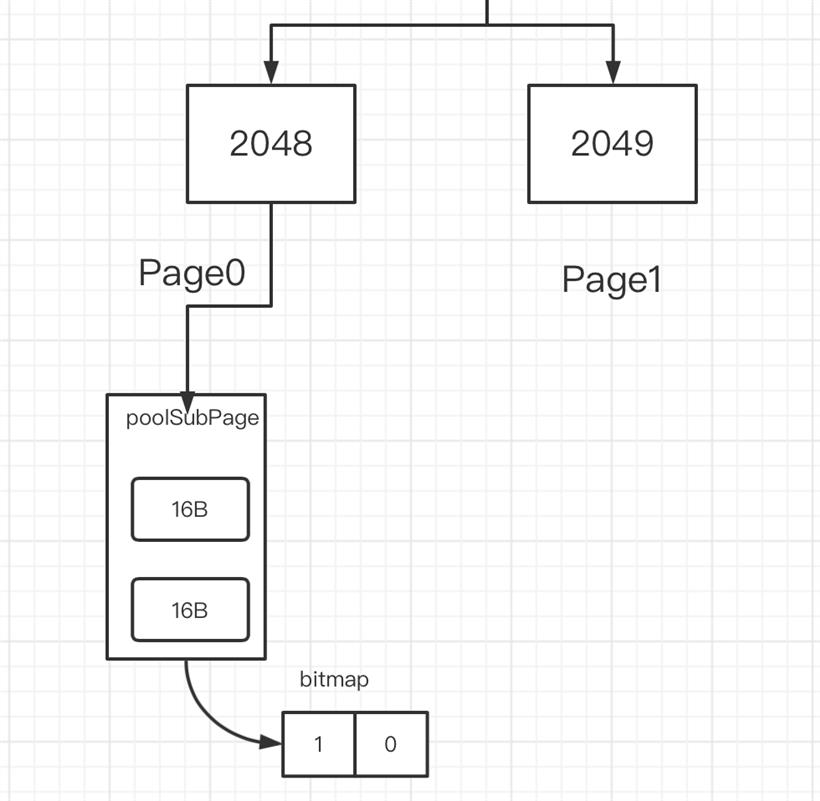
private long allocateRun(int normCapacity) {
// 根据分配内存大小计算树对应的节点高度 maxOrder 为二叉树的最大高度 11. , pageShifts 默认为13
int d = maxOrder - (log2(normCapacity) - pageShifts);
// 查找对应高度中是否存在可用节点
int id = allocateNode(d);
if (id < 0) {
return id;
}
// 减去以分配的内存大小
freeBytes -= runLength(id);
return id;
}
第一次在分配 8k 大小的内存时,计算得到二叉树所在节点高度为 11,8k= 2^13. 然后从第 11 层查找可用的 Page,下标为 2048 的节点可以被用于分配内存,即 page[0] 被分配使用,此时赋值 memoryMap[2048] =12,表示该节点已经不可用,然后递归更新父节点的值,父节点的值取两个子节点的最小值,即 memoryMap[1024]=11,memory[512]=10。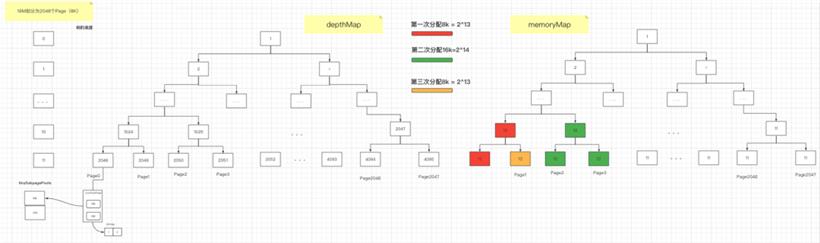
private long allocateSubpage(int normCapacity) {
// Obtain the head of the PoolSubPage pool
// that is owned by the PoolArena and synchronize on it.
// This is need as we may add it back and so alter the linked-list structure.
// 根据内存大小找到PoolArena中Subpage数组对应的头节点
PoolSubpage<T> head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(normCapacity);
// 从最底层开始查找
// subpages are only be allocated from pages i.e., leaves
int d = maxOrder;
synchronized (head) {
//找到一个可用的节点
int id = allocateNode(d);
if (id < 0) {
return id;
}
//把转化为Subpage的Page给记录下来
final PoolSubpage<T>[] subpages = this.subpages;
final int pageSize = this.pageSize;
freeBytes -= pageSize;
//pageId 到subpageId的转化,pageId=2048 subpageId = 0
int subpageIdx = subpageIdx(id);
PoolSubpage<T> subpage = subpages[subpageIdx];
if (subpage == null) {
//创建PoolSubPage,并切分为相同大小的子内存块,然后加入PoolArena对应的双向链表中
subpage = new PoolSubpage<T>(head, this, id, runOffset(id), pageSize, normCapacity);
subpages[subpageIdx] = subpage;
} else {
subpage.init(head, normCapacity);
}
//执行内存分配并返回内存地址
return subpage.allocate();
}
}
如果我们分配 20B 大小的内存,20B 属于 Tiny 场景,按照内存规格的分类,20B 需要向上取整到 32B。在满二叉树中寻找可用的节点用于内存分配,假如 2049 节点时可用的,那么返回的 ID=2049,然后将 pageId 转换成了 subpageIdx, 2049 对应 1 ,如果 PoolChunk 中 subpages 数组的 subpageIdx 下标对应的 PoolSubpage 不存在,那么就新创建一个 PoolSubpage,并将 PoolSubpage 切分为相同大小的子内存块,这边对应的子内存块是32B,然后找到 PoolArena 中 tinySubpagePools 数组对应的头节点,32B 对应的tinySubpagePools[1] 的 head 节点连接成双向链表,最后执行内存分配返回内存地址。// 默认执行 8192 次 allocate(),就会调用 trim() 进行内存整理
boolean allocated = cache.allocate(buf, reqCapacity);
if (++ allocations >= freeSweepAllocationThreshold) {
allocations = 0;
trim();
}
void trim() {
trim(tinySubPageDirectCaches);
trim(smallSubPageDirectCaches);
trim(normalDirectCaches);
trim(tinySubPageHeapCaches);
trim(smallSubPageHeapCaches);
trim(normalHeapCaches);
}
private static void trim(MemoryRegionCache<?>[] caches) {
if (caches == null) {
return;
}
for (MemoryRegionCache<?> c: caches) {
trim(c);
}
}
public final void trim() {
/**
* 通过 size - allocations 衡量内存分配执行的频繁程度,
* 其中 size 为该 MemoryRegionCache 对应的内存规格大小,size 为固定值,
* 例如 Tiny 类型默认为 512。
* allocations 表示 MemoryRegionCache 距离上一次内存整理已经发生了多少次 allocate 调用,
* 当调用次数小于 size 时,
* 表示 MemoryRegionCache 中缓存的内存块并不常用,从队列中取出内存块依次释放。
*/
int free = size - allocations;
allocations = 0;
// We not even allocated all the number that are
if (free > 0) {
free(free, false);
}
}
// 最终会执行native方法 这是一个native方法
public native void freeMemory(long var1);
// 详见源码。PoolThreadCache # allocate