- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
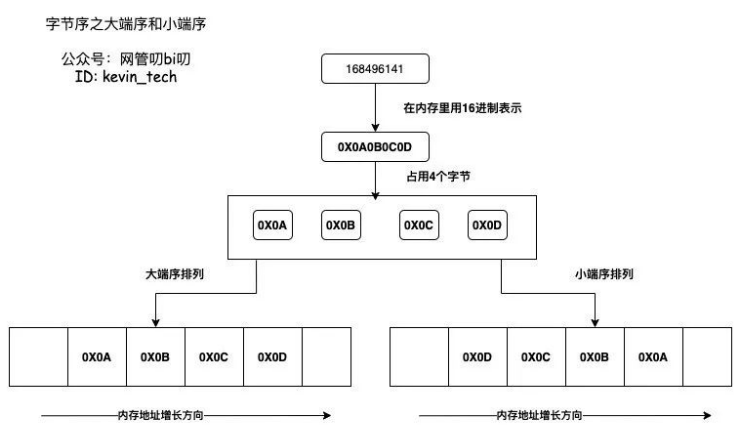
小端序(Little-Endian),将一个多位数的低位放在较小的地址处,高位放在较大的地址处,则称小端序。小端序与人类的阅读习惯相反,但更符合计算机读取内存的方式,因为CPU读取内存中的数据时,是从低地址向高地址方向进行读取的。
package main
import (
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
const INT_SIZE = int(unsafe.Sizeof(0)) //64位操作系统,8 bytes
//判断我们系统中的字节序类型
func systemEdian() {
var i = 0x01020304
fmt.Println("&i:",&i)
bs := (*[INT_SIZE]byte)(unsafe.Pointer(&i))
if bs[0] == 0x04 {
fmt.Println("system edian is little endian")
} else {
fmt.Println("system edian is big endian")
}
fmt.Printf("temp: 0x%x,%v\n",bs[0],&bs[0])
fmt.Printf("temp: 0x%x,%v\n",bs[1],&bs[1])
fmt.Printf("temp: 0x%x,%v\n",bs[2],&bs[2])
fmt.Printf("temp: 0x%x,%v\n",bs[3],&bs[3])
}
func testBigEndian() {
var testInt int32 = 0x01020304
fmt.Printf("%d use big endian: \n", testInt)
testBytes := make([]byte, 4)
binary.BigEndian.PutUint32(testBytes, uint32(testInt))
fmt.Println("int32 to bytes:", testBytes)
fmt.Printf("int32 to bytes: %x \n", testBytes)
convInt := binary.BigEndian.Uint32(testBytes)
fmt.Printf("bytes to int32: %d\n\n", convInt)
}
func testLittleEndian() {
var testInt int32 = 0x01020304
fmt.Printf("%x use little endian: \n", testInt)
testBytes := make([]byte, 4)
binary.LittleEndian.PutUint32(testBytes, uint32(testInt))
fmt.Printf("int32 to bytes: %x \n", testBytes)
convInt := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(testBytes)
fmt.Printf("bytes to int32: %d\n\n", convInt)
}
func main() {
systemEdian()
fmt.Println("")
testBigEndian()
testLittleEndian()
}
运行上面的程序会在终端里输出:&i: 0xc000084000 system edian is little endian temp: 0x4,0xc000084000 temp: 0x3,0xc000084001 temp: 0x2,0xc000084002 temp: 0x1,0xc000084003 16909060 use big endian: int32 to bytes: [1 2 3 4] int32 to bytes: 01020304 bytes to int32: 16909060 1020304 use little endian: int32 to bytes: 04030201 bytes to int32: 16909060