- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>
堆代码 duidaima.com
</title>
<meta name="keywords" content="网页关键词,SEO" />
<meta name="description" content="网页描述,SEO" />
<!-- html中内联css写法 -->
<style>
.foo { color: red; }
</style>
<!-- html引入外部单独的css文件写法 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://x.alicdn.com/xx/xxx/screen.css" />
</head>
<body>
<!-- 网页内容 -->
<div class="foo">
Page Content
</div>
<!-- html中内联js脚本写法 -->
<script>
function log(param) {
console.log(param)
}
log('解析并执行这段js代码')
</script>
<!-- html引入外部单独的js文件写法 -->
<script src="https://x.alicdn.com/xx/xxx/screen.js">
</script>
</body>
</html>
用户访问任意网站之前,要先在地址栏输入一个有效地址,接着浏览器会向服务器发起请求,去拿到该地址对应的网页入口文件即"xxx.html",打开浏览器 Network 控制台便可以看到,这一定是浏览器第一个接收到的响应内容。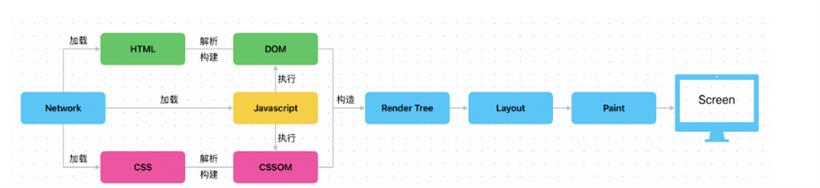
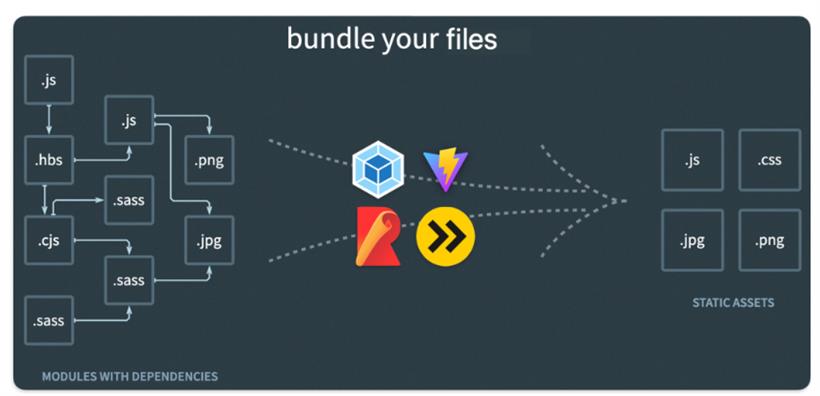
import '@/common/style.scss' // 引入scss
import arrowBack from '@/common/arrow-back.svg' // 引入svg
import { loadScript } from '@/common/utils.js' // 引入js中的函数
区别于开发阶段,构建工具还针对生产环境提供了丰富的构建能力,能将业务源码进行压缩、tree-shaking 优化,uglify 混淆、兼容、extract 抽离等处理,成为适用于生产环境的最优代码。!
function() {
"use strict";
function t(t) {
if (null == t) return - 1;
var e = Number(t);
return isNaN(e) ? -1 : Math.trunc(e)
}
function e(t) {
var e = t.name;
return /(\.css|\.js|\.woff2)/.test(e) && !/(\.json)/.test(e)
}
function n(t) {
var e = "__";
return "".concat(t.protocol).concat(e).concat(t.name).concat(e).concat(t.decodedBodySize).concat(e).concat(t.encodedBodySize).concat(e).concat(t.transferSize).concat(e).concat(t.startTime).concat(e).concat(t.duration).concat(e).concat(t.requestStart).concat(e).concat(t.responseEnd).concat(e).concat(t.responseStart).concat(e).concat(t.secureConnectionStart)
}
var r = function() {
return /WindVane/i.test(navigator.userAgent)
};
function o() {
return r()
}
function c() {
return !! window.goldlog
}
var i = function() {
return a()
},
a = function() {
var t = function(t) {
var e = document.querySelector('meta[name="'.concat(t, '"]'));
if (!e) return;
return e.getAttribute("content")
} ("data-spm"),
e = document.body && document.body.getAttribute("data-spm");
return t && e && "".concat(t, ".")......
构建出来的生产环境CSS:@charset "UTF-8";
.free-shipping-block {
-webkit-box-orient:horizontal;
-webkit-box-direction:normal;
-webkit-box-align:center;
-ms-flex-align:center;
-webkit-align-items:center;
align-items:center;
background-color:#ffe8da;
background-position:100% 100%;
background-repeat:no-repeat;
background-size:200px 100px;
border-radius:8px;
display:-webkit-box;
display:-webkit-flex;
display:-ms-flexbox;
display:flex;
-webkit-flex-direction:row;
-ms-flex-direction:row;
flex-direction:row;
margin-top:24px;
padding:12px
}
.free-shipping-block .content {
-webkit-box-flex:1;
-ms-flex-positive:1;
color:#4b1d1f;
-webkit-flex-grow:1;
flex-grow:1;
font-size:14px;
margin-left:8px;
margin-top:0!important
}
.free-shipping-block .content .desc img {
padding-top:2px;
vertical-align:text-top;
width:120px
}
.free-shipping-block .co.....
构建出来的生产环境HTML:<!doctype html> <html> <head> <script defer="defer" src="/build/xxx.js"> </script> <link href="/build/xxx.css" rel="stylesheet"> </head> <body> <div id="root"> </div> </body> </html>三.代码部署

index.css:
.foo {
background-color: red;
}
对于 index.css,如果用户每次打开页面都要重新发起对该文件的请求,不仅浪费带宽而且用户还要多等待一段下载时间,完全可以利用 HTTP 缓存中的强缓存将静态资源缓存在浏览器本地,使用户更快看到页面(快体现在浏览器直接从 memory/dist cache 中读取文件,省去了下载时间)。Cache-Control: max-age=2592000,s-maxage=86400对于静态资源,服务器往往设置一个非常大的缓存过期时间以充分利用缓存,这样浏览器就彻底不用发起请求了。但是浏览器都不发请求了,如果我们页面有更新/bug 修复该怎么办呢?很容易想到的办法是在资源 url 上拼接版本号,如:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<script defer="defer" src="https://x.alicdn.com/build/foo.js?t=0.0.1"></script>
<link href="https://x.alicdn.com/build/index.css?t=0.0.1" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="foo"></div>
</body>
</html>
下次更新时更换版本号就能强制让浏览器重新发起新的请求:<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<script defer="defer" src="https://x.alicdn.com/build/foo.js?t=0.0.2"></script>
<link href="https://x.alicdn.com/build/index.css?t=0.0.2" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="foo"></div>
</body>
</html>
但这样做存在一个问题,HTML 同时引用了多个文件,如果在一次迭代中只变更了其中的某个文件,其他文件没做修改,统一加版本号的方法岂不是连带让其他文件的本地缓存都失效了!<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- foo.js 无修改继续使用缓存 -->
<script defer="defer" src="https://x.alicdn.com/build/foo.js"></script>
<!-- index.css 改了样式,得请求更新后的文件并缓存 -->
<link href="https://x.alicdn.com/build/index_1i0gdg6ic.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="foo"></div>
</body>
</html>
或者通过迭代版本号加入资源路径 Path 的方式:<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- 资源路径更新,请求新的资源 -->
<script defer="defer" src="https://x.alicdn.com/0.0.2/build/foo.js"></script>
<!-- 资源路径更新,请求新的资源 -->
<link href="https://x.alicdn.com/0.0.2/build/index.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="foo"></div>
</body>
</html>
▐ 动静分离<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- 资源还没发布完 -->
<script defer="defer" src="https://x.alicdn.com/0.0.1/build/foo.js"></script>
<link href="https://x.alicdn.com/0.0.1/build/index.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<!-- 页面修改了 -->
<div class="bar"></div>
</body>
</html>
静态资源发布完成前,期间用户访问到新的页面结构,但是静态资源还是老的,用户可能会看到一个样式错乱的页面,也可能因旧的 JS 脚本找不到元素节点而执行错误的白屏页面,不可行。<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- 资源已发布 -->
<script defer="defer" src="https://x.alicdn.com/0.0.2/build/foo.js"></script>
<link href="https://x.alicdn.com/0.0.2/build/index.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<!-- 页面还没发布 -->
<div class="foo"></div>
</body>
</html>
页面发布完成前,页面结构没变,而资源是新的了,如果用户此前访问过,本地存在老资源的缓存,那么他看到的页面是正常的,否则访问到旧页面却加载新资源,还会出现上述一样的问题,要么样式错乱、要么 JS 执行错误导致白屏,不可行。所以先部署谁都不行!这也是为啥古早上线项目时要辛苦程序员大佬们半夜偷偷上,挑流量低谷时上的缘故了,毕竟影响面能小些。但是哇,这对于大厂来说可没有绝对的低峰期只有相对低峰期。但哪怕是相对低峰期,对于做事追求极致的我们,也是不可接受的!4.以非覆盖式发布更新资源,平滑过渡升级。