- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
{
"name": {
"firstName": "yi",
"lastName": "li"
},
"age": 23,
"roles": ['developer', 'admin'],
"projects": [{
"name": "demo",
"repo": ""
}]
}
页面上提供一个搜索框,用户通过输入搜索的内容可以找到包含这个内容的数据。注意,只要任意数据对象的任意属性值 (比如在上面的数据结构中,只要 name, age, roles 任何一个属性的值)包含这个关键词即可。如果属性值是数组或者对象,那么数组的元素或者对象的值继续对输入内容进行匹配检测,并递归的检测下去,只要有命中,便算该数据匹配。如何设计这个功能,让搜索功能尽可能的快?2.如果要求够快的话遍历我就输了
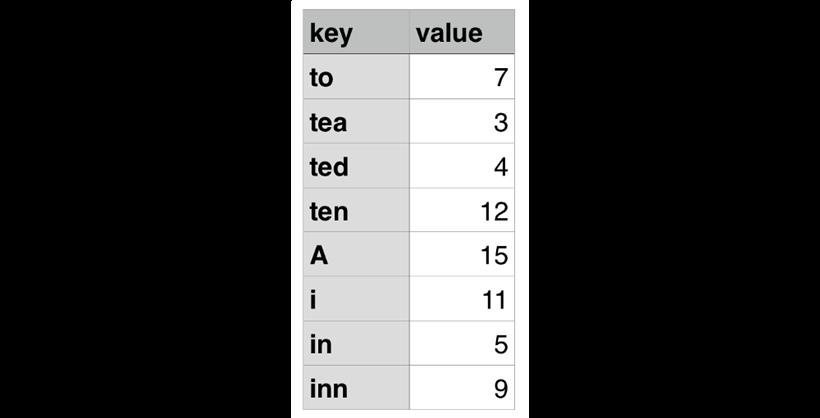
const o = {
message: 'ack'
fruit: 'apple',
unit: 'an',
name: 'anna',
}
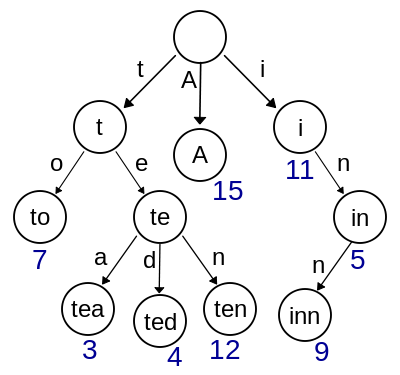
建立的树状结构如下:root--a
|--c
|--k
|--p
|--p
|--l
|--e
|--n
|--n
|--a
当用户搜索 apple 时,从a开始访问,至最后访问到字母 e 时,若在树中有对应的节点,表示命中;当用户搜索 aha 时,在访问 h 时就已经无法在树中找到对应的节点了,表示该对象不符合搜索条件。但实际工作中我们会有非常多个对象值,多个对象值之间可能有重复的值,所以匹配时,我们要把所有可能的匹配结果都返回。比如[
{
id: 1,
message: 'ack'
fruit: 'apple',
unit: 'an',
name: 'anna',
},
{
id: 2,
message: 'ack'
fruit: 'banana',
unit: 'an',
name: 'lee',
},
]
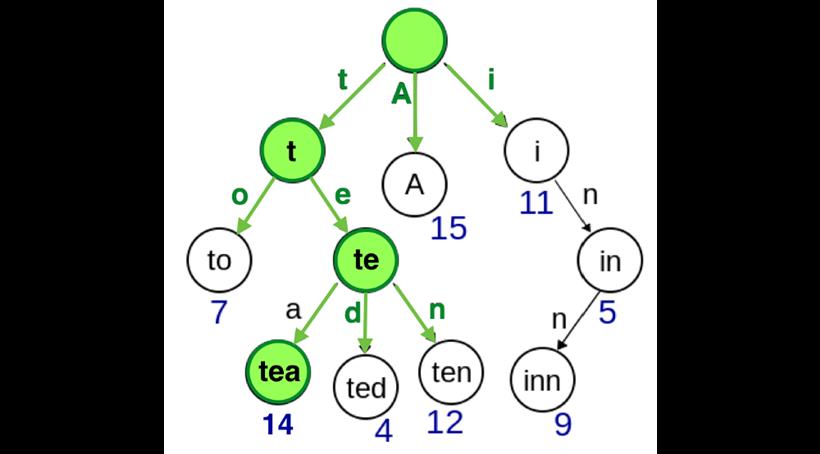
上面两个对象有相同的值 ack 和 an,所以在树上的叶子节点中我们还要添加对象的 id 辨识信息root--a
|--c
|--k (ids: [1,2])
|--p
|--p
|--l
|--e (ids: [1])
|--n (ids: [1, 2])
|--n
|--a (ids: [1])
这样当用户搜索 an 时,我们能返回所有的匹配项。{
"results": [
{
"gender": "male",
"email": "enzo.dumont@example.com",
"phone": "02-65-13-26-00",
"cell": "06-09-02-19-99",
"nat": "FR"
},
{
"gender": "male",
"email": "gerald.omahony@example.com",
"phone": "011-376-3811",
"cell": "081-697-1414",
"nat": "IE"
}
//...
]
}
叶子节点数据结构class Leaf {
constructor(id = "", value = "") {
this.ids = id ? [id] : [];
this.value = value;
this.children = {};
}
share(id) {
this.ids.push(id);
}
}
share方法用于向该叶子节点添加多个相同的匹配的iddistinct: 移除一个数组中的重复元素
[
{
id: 1,
message: 'ack'
fruit: 'apple',
unit: 'an',
name: 'anna',
},
{
id: 2,
message: 'ack'
fruit: 'banana',
unit: 'an',
name: 'lee',
},
]
扁平化之后为{
'1': {
id: 1,
message: 'ack'
fruit: 'apple',
unit: 'an',
name: 'anna',
},
'2': {
id: 2,
message: 'ack'
fruit: 'banana',
unit: 'an',
name: 'lee',
}
}
之所以要这么做是为了当检索结果返回一个 id 数组时:[1, 2, 3],我们只需要遍历一边返回结果就能通过 id 在扁平化的 Map 里立即找到对应的数据。否则还要不停的遍历原始数据数组找到对应的数据。因为 randomuser.me 返回的信息中不包含 id 信息,所以我们暂时用 email 信息作为唯一标示。normalize 的实现如下:function normalize(identify, data) {
const id2Value = {};
data.forEach(item => {
const idValue = item[identify];
id2Value[idValue] = item;
});
return id2Value;
}
构建一棵树fetch("https://randomuser.me/api/?results=5000&inc=gender,email,phone,cell,nat")
.then(response => {
return response.json();
})
.then(data => {
const { results } = data;
const root = new Leaf();
const identifyKey = "email";
results.forEach(item => {
const identifyValue = item[identifyKey];
Object.values(item).forEach(itemValue => {
// 注意这里会把 Number 和 Boolean 类型也字符串化
const stringifiedValue = String(itemValue);
let tempRoot = root;
const arraiedStringifiedValue = Array.from(stringifiedValue);
arraiedStringifiedValue.forEach((character, characterIndex) => {
const reachEnd =
characterIndex === arraiedStringifiedValue.length - 1;
if (!tempRoot.children[character]) {
tempRoot.children[character] = new Leaf(
reachEnd ? identifyValue : "",
character
);
tempRoot = tempRoot.children[character];
} else {
if (reachEnd) {
tempRoot.children[character].share(identifyValue);
}
tempRoot = tempRoot.children[character];
}
});
});
});
模糊搜索function searchBlurry(root, keyword, userMap) {
const keywordArr = Array.from(String(keyword));
let tempRoot = root;
let result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < keywordArr.length; i++) {
const character = keywordArr[i];
if (!tempRoot.children[character]) {
break;
} else {
tempRoot = tempRoot.children[character];
}
if (keywordArr.length - 1 === i) {
result = [
...tempRoot.ids,
...collectChildrenInsideIds(tempRoot.children)
];
}
}
return distinct(result).map(id => {
return userMap[id];
});
}
注意这里有一个collectChildrenInsideIds方法,这个方法用于收集该叶子节点下所有的子节点的 id。这么做是因为当前操作模糊匹配,当你搜索a时,apple, anna, ack 都算匹配。function regularSearch(searchKeyword) {
const regularSearchResults = [];
results.forEach(item => {
for (const key in item) {
const value = item[key];
if (String(value).startsWith(searchKeyword)) {
regularSearchResults.push(item);
break;
}
}
});
return regularSearchResults
}
注意在测试对象值是否匹配搜索词时,我们使用了startsWith,而不是indexOf,这是因为字典树的缺陷在于只能匹配以搜索词开头的词!比如当你搜索a时,只能匹配apple、anna而不能匹配banana。为了便于对比,我们不得不使用startsWith2.当数据量较大时,比如 5000 条的情况下,当你的搜索词非常短小,比如a,那么字典树的查找效率会比遍历搜索低,也就是反而花费的时间长;当搜索词变得具体时,比如ali,字典树的查找效率会比遍历搜索高。
function decorateWithChildrenIds(root) {
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
const { children } = root;
root.childrenIds = collectChildrenInsideIds(root.children);
for (const character in children) {
const characterLeaf = children[character];
characterLeaf.childrenIds = collectChildrenInsideIds(
characterLeaf.children
);
decorateWithChildrenIds(characterLeaf);
}
}
那么在构建完树之后,用这个方法把所有叶子节点「装饰」一遍就好了。