- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "stdint.h"
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
int main (int argc, char** argv) {
int u = atoi(argv[1]); // Get an input number from the command line
int r = rand() % 10000; // Get a random integer 0 <= r < 10k
int32_t a[10000] = {0}; // Array of 10k elements initialized to 0
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { // 10k outer loop iterations
for (int j = 0; j < 100000; j++) { // 100k inner loop iterations, per outer loop iteration
a[i] = a[i] + j%u; // Simple sum
}
a[i] += r; // Add a random value to each element in array
}
printf("%d\n", a[r]); // Print out a single element from the array
}
Rust 代码:use rand::Rng;
fn main() {
let n: usize = std::env::args() // Get an input number from the command line
.nth(1)
.unwrap()
.parse()
.unwrap();
let r: usize = rand::thread_rng() // Get a random number 0 <= r < 10k
.gen_range(0..10000);
let mut a = [0; 10000]; // Array of 10k elements initialized to 0
for i in 0..10000 { // 10k outer loop iterations
for j in 0..100000 { // 100k inner loop iterations
a[i] = a[i] + j % n; // Simple sum
}
a[i] += r; // Add a random value to each element in array
}
println!("{}", a[r]); // Print out a single element from the array
}
Zig 代码:const std = @import("std");
const rand = std.crypto.random;
const stdout = std.io.getStdOut().writer();
pub fn main() !void {
// Get an input number from the command line
var args = std.process.args();
_ = args.next() orelse unreachable; // skip first, which is program name
const arg = args.next() orelse unreachable;
const u = try std.fmt.parseInt(usize, arg, 10);
// Get a random number 0 <= r < 10k
const r = rand.intRangeAtMost(usize, 0, 10000);
// Array of 10k elements initialized to 0
var a: [10000]usize = undefined;
@memset(&a, 0);
// 10k outer loop iterations
for (0..10000) |i| {
// 100k inner loop iterations, per outer loop iteration
for (0..100000) |j| {
a[i] += j % u; // Simple sum
}
a[i] += r; // Add a random value to each element in array
}
try stdout.print("{d}\n", .{a[r]}); // Print out a single element from the array
}
Go 代码:package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"strconv"
"os"
)
func main() {
input, e := strconv.Atoi(os.Args[1]) // Get an input number from the command line
if e != nil { panic(e) }
u := int(input)
r := int(rand.Intn(10000)) // Get a random number 0 <= r < 10k
var a[10000]int // Array of 10k elements initialized to 0
for i := 0; i < 10000; i++ { // 10k outer loop iterations
for j := 0; j < 100000; j++ { // 100k inner loop iterations, per outer loop iteration
a[i] = a[i] + j%u // Simple sum
}
a[i] += r // Add a random value to each element in array
}
fmt.Println(a[r]) // Print out a single element from the array
}
测试的结果如下(作者每种语言测试几遍,每个语言挑选了最快的一次),作者还非常好的使用动画演示每种语言的快慢,执行越快,执行时间越短,小球移动的越快: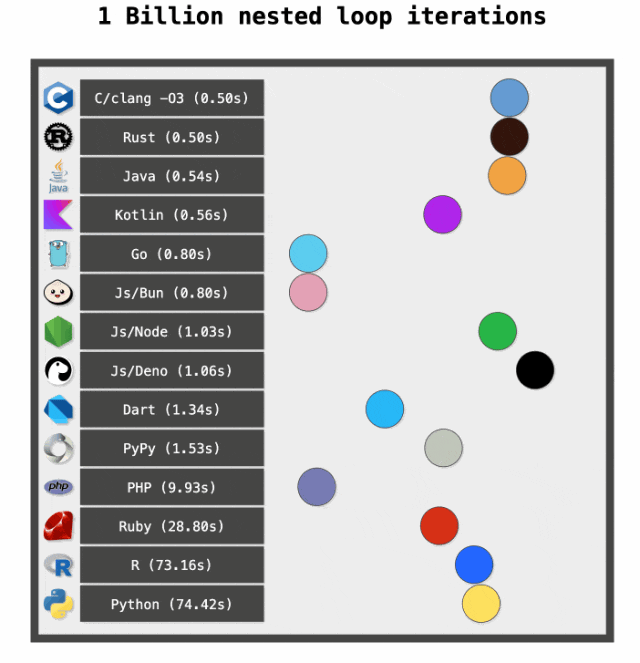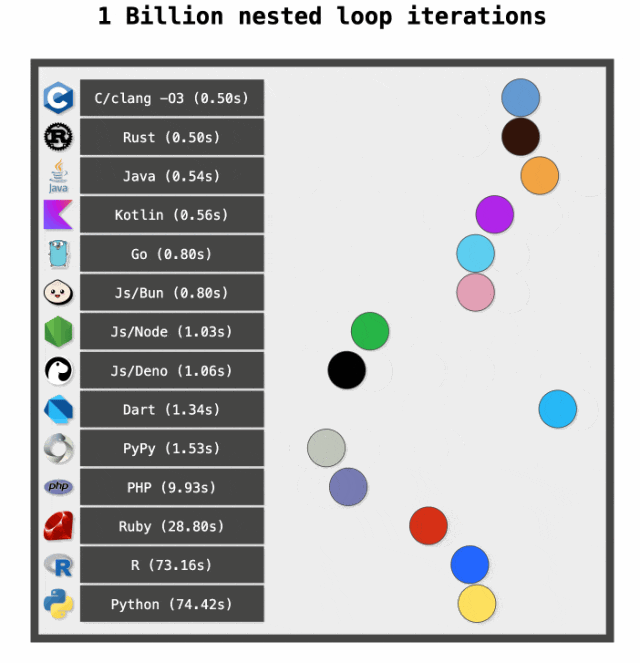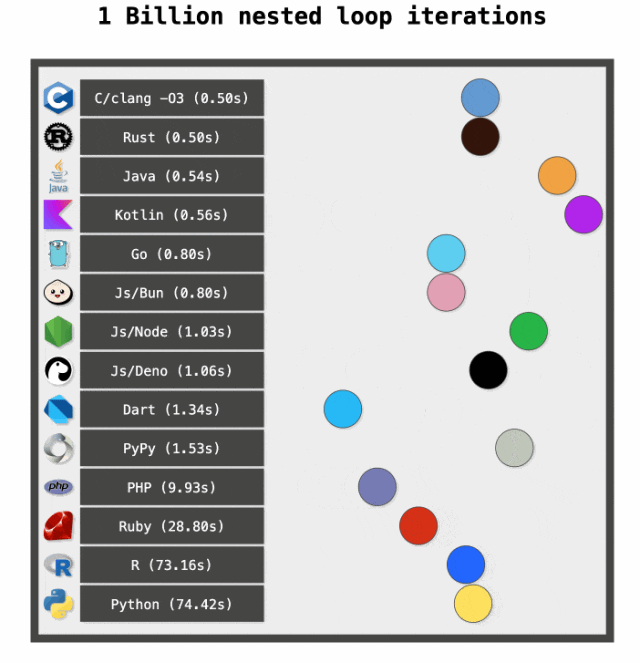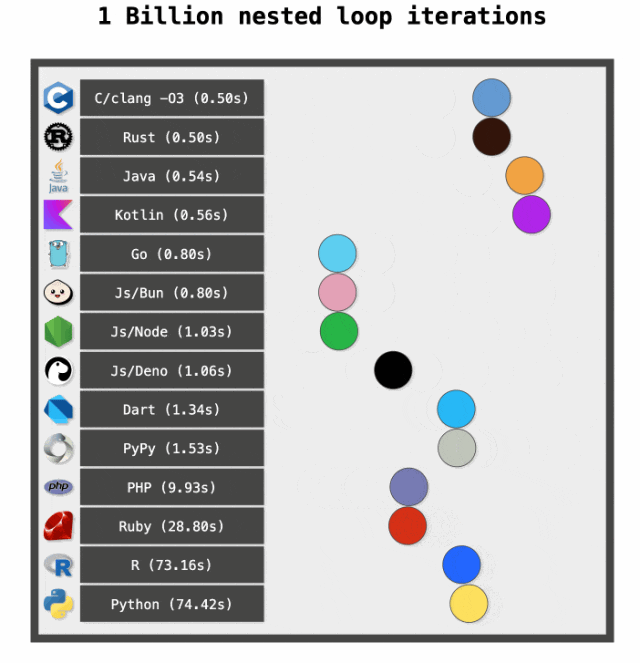
我自己的测试也是 c、zip、rust 属于第一梯队。作者还提供了的斐波那契函数的测试,所以总体来说主要堆这两个场景进行了测试。你支持哪种编程语言呢,还是置身事外?