- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
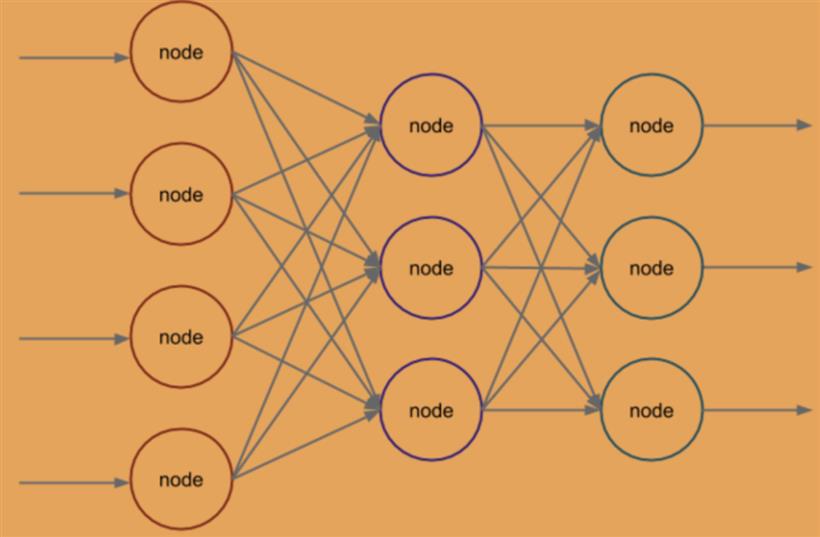
// neuralNet contains all of the information
// that defines a trained neural network.
type neuralNet struct {
config neuralNetConfig
wHidden *mat.Dense
bHidden *mat.Dense
wOut *mat.Dense
bOut *mat.Dense
}
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
// neuralNetConfig defines our neural network
// architecture and learning parameters.
type neuralNetConfig struct {
inputNeurons int
outputNeurons int
hiddenNeurons int
numEpochs int
learningRate float64
}
这里neuralNet是神经网络结构体,同时定义输入、隐藏和输出层神经元的配置。func newNetwork(config neuralNetConfig) *neuralNet {
return &neuralNet{config: config}
}
这里返回神经网络的指针。// sigmoid implements the sigmoid function
// for use in activation functions.
func sigmoid(x float64) float64 {
return 1.0 / (1.0 + math.Exp(-x))
}
// sigmoidPrime implements the derivative
// of the sigmoid function for backpropagation.
func sigmoidPrime(x float64) float64 {
return sigmoid(x) * (1.0 - sigmoid(x))
}
实现反向传播// train trains a neural network using backpropagation.
func (nn *neuralNet) train(x, y *mat.Dense) error {
// Initialize biases/weights.
randSource := rand.NewSource(time.Now().UnixNano())
randGen := rand.New(randSource)
wHidden := mat.NewDense(nn.config.inputNeurons, nn.config.hiddenNeurons, nil)
bHidden := mat.NewDense(1, nn.config.hiddenNeurons, nil)
wOut := mat.NewDense(nn.config.hiddenNeurons, nn.config.outputNeurons, nil)
bOut := mat.NewDense(1, nn.config.outputNeurons, nil)
wHiddenRaw := wHidden.RawMatrix().Data
bHiddenRaw := bHidden.RawMatrix().Data
wOutRaw := wOut.RawMatrix().Data
bOutRaw := bOut.RawMatrix().Data
for _, param := range [][]float64{
wHiddenRaw,
bHiddenRaw,
wOutRaw,
bOutRaw,
} {
for i := range param {
param[i] = randGen.Float64()
}
}
// Define the output of the neural network.
output := new(mat.Dense)
// Use backpropagation to adjust the weights and biases.
if err := nn.backpropagate(x, y, wHidden, bHidden, wOut, bOut, output); err != nil {
return err
}
// Define our trained neural network.
nn.wHidden = wHidden
nn.bHidden = bHidden
nn.wOut = wOut
nn.bOut = bOut
return nil
}
接着实现具体的反向传播逻辑:// backpropagate completes the backpropagation method.
func (nn *neuralNet) backpropagate(x, y, wHidden, bHidden, wOut, bOut, output *mat.Dense) error {
// Loop over the number of epochs utilizing
// backpropagation to train our model.
for i := 0; i < nn.config.numEpochs; i++ {
// Complete the feed forward process.
hiddenLayerInput := new(mat.Dense)
hiddenLayerInput.Mul(x, wHidden)
addBHidden := func(_, col int, v float64) float64 { return v + bHidden.At(0, col) }
hiddenLayerInput.Apply(addBHidden, hiddenLayerInput)
hiddenLayerActivations := new(mat.Dense)
applySigmoid := func(_, _ int, v float64) float64 { return sigmoid(v) }
hiddenLayerActivations.Apply(applySigmoid, hiddenLayerInput)
outputLayerInput := new(mat.Dense)
outputLayerInput.Mul(hiddenLayerActivations, wOut)
addBOut := func(_, col int, v float64) float64 { return v + bOut.At(0, col) }
outputLayerInput.Apply(addBOut, outputLayerInput)
output.Apply(applySigmoid, outputLayerInput)
// Complete the backpropagation.
networkError := new(mat.Dense)
networkError.Sub(y, output)
slopeOutputLayer := new(mat.Dense)
applySigmoidPrime := func(_, _ int, v float64) float64 { return sigmoidPrime(v) }
slopeOutputLayer.Apply(applySigmoidPrime, output)
slopeHiddenLayer := new(mat.Dense)
slopeHiddenLayer.Apply(applySigmoidPrime, hiddenLayerActivations)
dOutput := new(mat.Dense)
dOutput.MulElem(networkError, slopeOutputLayer)
errorAtHiddenLayer := new(mat.Dense)
errorAtHiddenLayer.Mul(dOutput, wOut.T())
dHiddenLayer := new(mat.Dense)
dHiddenLayer.MulElem(errorAtHiddenLayer, slopeHiddenLayer)
// Adjust the parameters.
wOutAdj := new(mat.Dense)
wOutAdj.Mul(hiddenLayerActivations.T(), dOutput)
wOutAdj.Scale(nn.config.learningRate, wOutAdj)
wOut.Add(wOut, wOutAdj)
bOutAdj, err := sumAlongAxis(0, dOutput)
if err != nil {
return err
}
bOutAdj.Scale(nn.config.learningRate, bOutAdj)
bOut.Add(bOut, bOutAdj)
wHiddenAdj := new(mat.Dense)
wHiddenAdj.Mul(x.T(), dHiddenLayer)
wHiddenAdj.Scale(nn.config.learningRate, wHiddenAdj)
wHidden.Add(wHidden, wHiddenAdj)
bHiddenAdj, err := sumAlongAxis(0, dHiddenLayer)
if err != nil {
return err
}
bHiddenAdj.Scale(nn.config.learningRate, bHiddenAdj)
bHidden.Add(bHidden, bHiddenAdj)
}
return nil
}
接着声明一个工具函数,它帮助我们沿一个矩阵维度求和,同时保持另一个维度不变:// sumAlongAxis sums a matrix along a particular dimension,
// preserving the other dimension.
func sumAlongAxis(axis int, m *mat.Dense) (*mat.Dense, error) {
numRows, numCols := m.Dims()
var output *mat.Dense
switch axis {
case 0:
data := make([]float64, numCols)
for i := 0; i < numCols; i++ {
col := mat.Col(nil, i, m)
data[i] = floats.Sum(col)
}
output = mat.NewDense(1, numCols, data)
case 1:
data := make([]float64, numRows)
for i := 0; i < numRows; i++ {
row := mat.Row(nil, i, m)
data[i] = floats.Sum(row)
}
output = mat.NewDense(numRows, 1, data)
default:
return nil, errors.New("invalid axis, must be 0 or 1")
}
return output, nil
}
实现前向传播进行预测// predict makes a prediction based on a trained
// neural network.
func (nn *neuralNet) predict(x *mat.Dense) (*mat.Dense, error) {
// Check to make sure that our neuralNet value
// represents a trained model.
if nn.wHidden == nil || nn.wOut == nil {
return nil, errors.New("the supplied weights are empty")
}
if nn.bHidden == nil || nn.bOut == nil {
return nil, errors.New("the supplied biases are empty")
}
// Define the output of the neural network.
output := new(mat.Dense)
// Complete the feed forward process.
hiddenLayerInput := new(mat.Dense)
hiddenLayerInput.Mul(x, nn.wHidden)
addBHidden := func(_, col int, v float64) float64 { return v + nn.bHidden.At(0, col) }
hiddenLayerInput.Apply(addBHidden, hiddenLayerInput)
hiddenLayerActivations := new(mat.Dense)
applySigmoid := func(_, _ int, v float64) float64 { return sigmoid(v) }
hiddenLayerActivations.Apply(applySigmoid, hiddenLayerInput)
outputLayerInput := new(mat.Dense)
outputLayerInput.Mul(hiddenLayerActivations, nn.wOut)
addBOut := func(_, col int, v float64) float64 { return v + nn.bOut.At(0, col) }
outputLayerInput.Apply(addBOut, outputLayerInput)
output.Apply(applySigmoid, outputLayerInput)
return output, nil
}
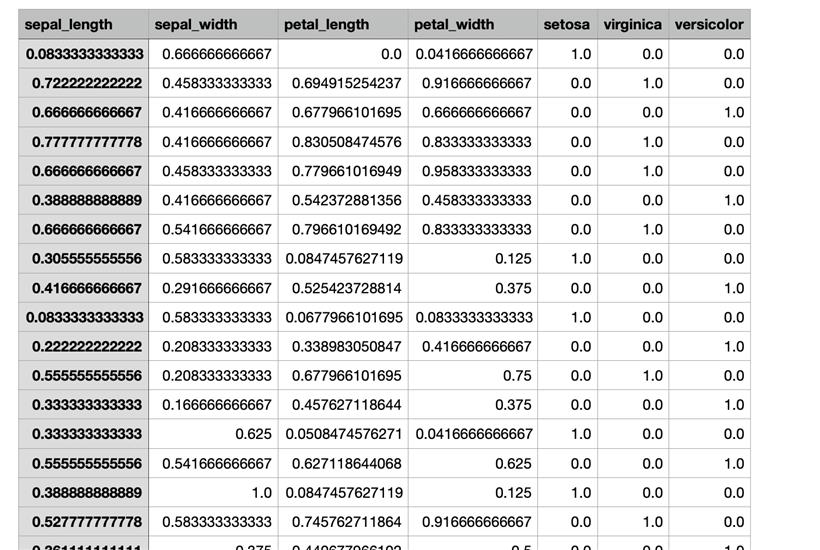
go get gonum.org/v1/gonum/floats安装后之后,编写脚本:
package main
import (
"encoding/csv"
"errors"
"fmt"
"log"
"math"
"math/rand"
"os"
"strconv"
"time"
"gonum.org/v1/gonum/floats"
"gonum.org/v1/gonum/mat"
)
// neuralNet contains all of the information
// that defines a trained neural network.
type neuralNet struct {
config neuralNetConfig
wHidden * mat.Dense
bHidden * mat.Dense
wOut * mat.Dense
bOut * mat.Dense
}
// neuralNetConfig defines our neural network
// architecture and learning parameters.
type neuralNetConfig struct {
inputNeurons int
outputNeurons int
hiddenNeurons int
numEpochs int
learningRate float64
}
func main() {
// Form the training matrices.
inputs, labels: = makeInputsAndLabels("data/train.csv")
// Define our network architecture and learning parameters.
config: = neuralNetConfig {
inputNeurons: 4,
outputNeurons: 3,
hiddenNeurons: 3,
numEpochs: 5000,
learningRate: 0.3,
}
// Train the neural network.
network: = newNetwork(config)
if err: = network.train(inputs, labels);
err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Form the testing matrices.
testInputs, testLabels: = makeInputsAndLabels("data/test.csv")
// Make the predictions using the trained model.
predictions, err: = network.predict(testInputs)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Calculate the accuracy of our model.
var truePosNeg int
numPreds, _: = predictions.Dims()
for i: = 0;
i < numPreds;
i++{
// Get the label.
labelRow: = mat.Row(nil, i, testLabels)
var prediction int
for idx,
label: = range labelRow {
if label == 1.0 {
prediction = idx
break
}
}
// Accumulate the true positive/negative count.
if predictions.At(i, prediction) == floats.Max(mat.Row(nil, i, predictions)) {
truePosNeg++
}
}
// Calculate the accuracy (subset accuracy).
accuracy: = float64(truePosNeg) / float64(numPreds)
// Output the Accuracy value to standard out.
fmt.Printf("\nAccuracy = %0.2f\n\n", accuracy)
}
// NewNetwork initializes a new neural network.
func newNetwork(config neuralNetConfig) * neuralNet {
return &neuralNet {
config: config
}
}
// train trains a neural network using backpropagation.
func(nn * neuralNet) train(x, y * mat.Dense) error {
// Initialize biases/weights.
randSource: = rand.NewSource(time.Now().UnixNano())
randGen: = rand.New(randSource)
wHidden: = mat.NewDense(nn.config.inputNeurons, nn.config.hiddenNeurons, nil)
bHidden: = mat.NewDense(1, nn.config.hiddenNeurons, nil)
wOut: = mat.NewDense(nn.config.hiddenNeurons, nn.config.outputNeurons, nil)
bOut: = mat.NewDense(1, nn.config.outputNeurons, nil)
wHiddenRaw: = wHidden.RawMatrix().Data
bHiddenRaw: = bHidden.RawMatrix().Data
wOutRaw: = wOut.RawMatrix().Data
bOutRaw: = bOut.RawMatrix().Data
for _,
param: = range[][] float64 {
wHiddenRaw,
bHiddenRaw,
wOutRaw,
bOutRaw,
} {
for i: = range param {
param[i] = randGen.Float64()
}
}
// Define the output of the neural network.
output: = new(mat.Dense)
// Use backpropagation to adjust the weights and biases.
if err: = nn.backpropagate(x, y, wHidden, bHidden, wOut, bOut, output);err != nil {
return err
}
// Define our trained neural network.
nn.wHidden = wHidden
nn.bHidden = bHidden
nn.wOut = wOut
nn.bOut = bOut
return nil
}
// backpropagate completes the backpropagation method.
func(nn * neuralNet) backpropagate(x, y, wHidden, bHidden, wOut, bOut, output * mat.Dense) error {
// Loop over the number of epochs utilizing
// backpropagation to train our model.
for i: = 0;
i < nn.config.numEpochs;
i++{
// Complete the feed forward process.
hiddenLayerInput: = new(mat.Dense)
hiddenLayerInput.Mul(x, wHidden)
addBHidden: = func(_, col int, v float64) float64 {
return v + bHidden.At(0, col)
}
hiddenLayerInput.Apply(addBHidden, hiddenLayerInput)
hiddenLayerActivations: = new(mat.Dense)
applySigmoid: = func(_, _ int, v float64) float64 {
return sigmoid(v)
}
hiddenLayerActivations.Apply(applySigmoid, hiddenLayerInput)
outputLayerInput: = new(mat.Dense)
outputLayerInput.Mul(hiddenLayerActivations, wOut)
addBOut: = func(_, col int, v float64) float64 {
return v + bOut.At(0, col)
}
outputLayerInput.Apply(addBOut, outputLayerInput)
output.Apply(applySigmoid, outputLayerInput)
// Complete the backpropagation.
networkError: = new(mat.Dense)
networkError.Sub(y, output)
slopeOutputLayer: = new(mat.Dense)
applySigmoidPrime: = func(_, _ int, v float64) float64 {
return sigmoidPrime(v)
}
slopeOutputLayer.Apply(applySigmoidPrime, output)
slopeHiddenLayer: = new(mat.Dense)
slopeHiddenLayer.Apply(applySigmoidPrime, hiddenLayerActivations)
dOutput: = new(mat.Dense)
dOutput.MulElem(networkError, slopeOutputLayer)
errorAtHiddenLayer: = new(mat.Dense)
errorAtHiddenLayer.Mul(dOutput, wOut.T())
dHiddenLayer: = new(mat.Dense)
dHiddenLayer.MulElem(errorAtHiddenLayer, slopeHiddenLayer)
// Adjust the parameters.
wOutAdj: = new(mat.Dense)
wOutAdj.Mul(hiddenLayerActivations.T(), dOutput)
wOutAdj.Scale(nn.config.learningRate, wOutAdj)
wOut.Add(wOut, wOutAdj)
bOutAdj,
err: = sumAlongAxis(0, dOutput)
if err != nil {
return err
}
bOutAdj.Scale(nn.config.learningRate, bOutAdj)
bOut.Add(bOut, bOutAdj)
wHiddenAdj: = new(mat.Dense)
wHiddenAdj.Mul(x.T(), dHiddenLayer)
wHiddenAdj.Scale(nn.config.learningRate, wHiddenAdj)
wHidden.Add(wHidden, wHiddenAdj)
bHiddenAdj,
err: = sumAlongAxis(0, dHiddenLayer)
if err != nil {
return err
}
bHiddenAdj.Scale(nn.config.learningRate, bHiddenAdj)
bHidden.Add(bHidden, bHiddenAdj)
}
return nil
}
// predict makes a prediction based on a trained
// neural network.
func(nn * neuralNet) predict(x * mat.Dense)( * mat.Dense, error) {
// Check to make sure that our neuralNet value
// represents a trained model.
if nn.wHidden == nil || nn.wOut == nil {
return nil, errors.New("the supplied weights are empty")
}
if nn.bHidden == nil || nn.bOut == nil {
return nil, errors.New("the supplied biases are empty")
}
// Define the output of the neural network.
output: = new(mat.Dense)
// Complete the feed forward process.
hiddenLayerInput: = new(mat.Dense)
hiddenLayerInput.Mul(x, nn.wHidden)
addBHidden: = func(_, col int, v float64) float64 {
return v + nn.bHidden.At(0, col)
}
hiddenLayerInput.Apply(addBHidden, hiddenLayerInput)
hiddenLayerActivations: = new(mat.Dense)
applySigmoid: = func(_, _ int, v float64) float64 {
return sigmoid(v)
}
hiddenLayerActivations.Apply(applySigmoid, hiddenLayerInput)
outputLayerInput: = new(mat.Dense)
outputLayerInput.Mul(hiddenLayerActivations, nn.wOut)
addBOut: = func(_, col int, v float64) float64 {
return v + nn.bOut.At(0, col)
}
outputLayerInput.Apply(addBOut, outputLayerInput)
output.Apply(applySigmoid, outputLayerInput)
return output, nil
}
// sigmoid implements the sigmoid function
// for use in activation functions.
func sigmoid(x float64) float64 {
return 1.0 / (1.0 + math.Exp(-x))
}
// sigmoidPrime implements the derivative
// of the sigmoid function for backpropagation.
func sigmoidPrime(x float64) float64 {
return sigmoid(x) * (1.0 - sigmoid(x))
}
// sumAlongAxis sums a matrix along a
// particular dimension, preserving the
// other dimension.
func sumAlongAxis(axis int, m * mat.Dense)( * mat.Dense, error) {
numRows, numCols: = m.Dims()
var output * mat.Dense
switch axis {
case 0:
data: = make([] float64, numCols)
for i: = 0;
i < numCols;
i++{
col: = mat.Col(nil, i, m)
data[i] = floats.Sum(col)
}
output = mat.NewDense(1, numCols, data)
case 1:
data: = make([] float64, numRows)
for i: = 0;
i < numRows;
i++{
row: = mat.Row(nil, i, m)
data[i] = floats.Sum(row)
}
output = mat.NewDense(numRows, 1, data)
default:
return nil, errors.New("invalid axis, must be 0 or 1")
}
return output, nil
}
func makeInputsAndLabels(fileName string)( * mat.Dense, * mat.Dense) {
// Open the dataset file.
f, err: = os.Open(fileName)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer f.Close()
// Create a new CSV reader reading from the opened file.
reader: = csv.NewReader(f)
reader.FieldsPerRecord = 7
// Read in all of the CSV records
rawCSVData, err: = reader.ReadAll()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// inputsData and labelsData will hold all the
// float values that will eventually be
// used to form matrices.
inputsData: = make([] float64, 4 * len(rawCSVData))
labelsData: = make([] float64, 3 * len(rawCSVData))
// Will track the current index of matrix values.
var inputsIndex int
var labelsIndex int
// Sequentially move the rows into a slice of floats.
for idx, record: = range rawCSVData {
// Skip the header row.
if idx == 0 {
continue
}
// Loop over the float columns.
for i, val: = range record {
// Convert the value to a float.
parsedVal, err: = strconv.ParseFloat(val, 64)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Add to the labelsData if relevant.
if i == 4 || i == 5 || i == 6 {
labelsData[labelsIndex] = parsedVal
labelsIndex++
continue
}
// Add the float value to the slice of floats.
inputsData[inputsIndex] = parsedVal
inputsIndex++
}
}
inputs: = mat.NewDense(len(rawCSVData), 4, inputsData)
labels: = mat.NewDense(len(rawCSVData), 3, labelsData)
return inputs, labels
}
代码最后将测试集数据导入, 并且开始进行预测:
// Form the testing matrices.
testInputs, testLabels: = makeInputsAndLabels("data/test.csv")
fmt.Println(testLabels)
// Make the predictions using the trained model.
predictions, err: = network.predict(testInputs)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// Calculate the accuracy of our model.
var truePosNeg int
numPreds, _: = predictions.Dims()
for i: = 0;
i < numPreds;
i++{
// Get the label.
labelRow: = mat.Row(nil, i, testLabels)
var prediction int
for idx,
label: = range labelRow {
if label == 1.0 {
prediction = idx
break
}
}
// Accumulate the true positive/negative count.
if predictions.At(i, prediction) == floats.Max(mat.Row(nil, i, predictions)) {
truePosNeg++
}
}
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
// Calculate the accuracy (subset accuracy).
accuracy: = float64(truePosNeg) / float64(numPreds)
// Output the Accuracy value to standard out.
fmt.Printf("\nAccuracy = %0.2f\n\n", accuracy)
程序输出:
&{{31 3 [0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0] 3} 31 3}
Accuracy = 0.97
可以看到,一共31个测试样本,只错了3次,成功率达到了97%。当然,就算是自己实现的小型神经网络,预测结果正确率也不可能达到100%,因为机器学习也是基于概率学范畴的学科。