- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
Navigator.of(context).pushNamed(String routeName, {Object? arguments,});
通过这种方式可以传参,然后在新的页面可以通过ModalRoute.of(context).settings.arguments获取传参并使用。但是如果是web页面,通过浏览器刷新后发现arguments变成null的,所以说flutter内部并没有将这部分持久化,刷新就被清空了,这样就导致页面出错。同时,如果我们通过static变量来存储一些全局的信息,在刷新时同样会被清空,也会导致问题。import 'dart:html'; ... var local = windows.localStorage或
// 堆代码 duidaima.com import 'dart:html' as html; ... var local = html.windows.localStorage它是一个Storage类,定义了"[]"运算符,所以可以像map那样使用即可,如下:
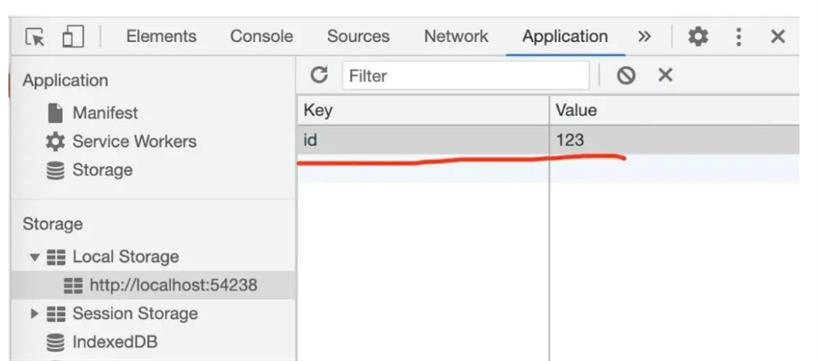
//存储"id"这个key的value设置为“123” window.localStorage["id"] = "123"; //取出“id”这个key的value使用 Text(window.localStorage["id"])是不是非常简单。存储后我们通过chrome的开发者工具,就可以看到这个存储了,如下:
window.cookieStore.set("id", "123");
报错:Cannot modify a secure cookie on insecure origin[
{
"domain": null,
"expires": 1712743928000,
"name": "p_h5_u",
"path": "/xxx/dev",
"sameSite": "lax",
"secure": false,
"value": "26EC4EAC-1537-4A7A-B813-0F2171704651"
}
]
所以我们如果要获取具体某一个cookie的值,则需要进行遍历,代码如下:cookie.getAll().then((value) => {
value.forEach((item){
if(item.name == "UCENTER_IUCTOKEN"){
showToast(item.value);
}
})
});
这里我们获取的是cookies中UCENTER_IUCTOKEN对应的值import 'dart:html';
import 'package:flutter/cupertino.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class PageC extends StatefulWidget{
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() {
return _PageC();
}
}
class _PageC extends State<PageC>{
int count = 3;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return WillPopScope(
child: Scaffold(
body: Column(
children: [
Text(""),
RaisedButton(
child: Text("like"),
onPressed: (){
},
),
],
),
),
onWillPop: _requestPop,
);
}
Future<bool> _requestPop() {
count--;
print("$count");
if(count == 0){
return new Future.value(true);
}
else {
return new Future.value(false);
}
}
}
当返回false的时候就拦截了系统的回退操作,当返回ture则正常回退。这里我们做一个计数,当点击第三次再执行退出。但是这里有一个问题,点击返回按钮后,虽然拦截了不会回退到上一页面,但是地址栏中的url变成了首页的url,但是页面还是当前页面,而且点击三次后确实返回了上一页,但是刷新就出问题了。因为url变成了首页,所以一刷新就便会首页了,而不是显示当前页面。class History extends Interceptor implements HistoryBase {
/**
* Checks if the State APIs are supported on the current platform.
*
* See also:
*
* * [pushState]
* * [replaceState]
* * [state]
*/
static bool get supportsState => JS('bool', '!!window.history.pushState');
// To suppress missing implicit constructor warnings.
factory History._() {
throw new UnsupportedError("Not supported");
}
int get length native;
String? get scrollRestoration native;
set scrollRestoration(String? value) native;
dynamic get state =>
convertNativeToDart_SerializedScriptValue(this._get_state);
@JSName('state')
@annotation_Creates_SerializedScriptValue
@annotation_Returns_SerializedScriptValue
dynamic get _get_state native;
void back() native;
void forward() native;
void go([int? delta]) native;
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.CHROME)
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.FIREFOX)
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.IE, '10')
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.SAFARI)
void pushState(/*SerializedScriptValue*/ data, String title, String? url) {
var data_1 = convertDartToNative_SerializedScriptValue(data);
_pushState_1(data_1, title, url);
return;
}
@JSName('pushState')
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.CHROME)
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.FIREFOX)
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.IE, '10')
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.SAFARI)
void _pushState_1(data, title, url) native;
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.CHROME)
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.FIREFOX)
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.IE, '10')
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.SAFARI)
void replaceState(/*SerializedScriptValue*/ data, String title, String? url) {
var data_1 = convertDartToNative_SerializedScriptValue(data);
_replaceState_1(data_1, title, url);
return;
}
@JSName('replaceState')
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.CHROME)
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.FIREFOX)
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.IE, '10')
@SupportedBrowser(SupportedBrowser.SAFARI)
void _replaceState_1(data, title, url) native;
}
这样我们就可以通过它来处理history了,在html中我们知道replaceState就是将当前的url改成一个新的url,我们就通过这个来纠正上面url的问题,修改_requestPop()代码如下:Future<bool> _requestPop() {
History history = window.history;
count--;
print("$count");
if(count == 0){
return new Future.value(true);
}
else {
setState(() {
history.replaceState(null, null, "#pageC");
});
return new Future.value(false);
}
}
可以看到在返回false之前,通过replaceState重新将当前url改回原url,这样点击后退键的时候url就还保持原样,不会变成首页url,刷新就没有问题了。@optionalTypeArgs
Future<T?> pushNamed<T extends Object?>(
String routeName, {
Object? arguments,
}) {
return push<T>(_routeNamed<T>(routeName, arguments: arguments)!);
}
继续@optionalTypeArgs
Future<T?> push<T extends Object?>(Route<T> route) {
_pushEntry(_RouteEntry(route, initialState: _RouteLifecycle.push));
return route.popped;
}
继续void _pushEntry(_RouteEntry entry) {
assert(!_debugLocked);
assert(() {
_debugLocked = true;
return true;
}());
assert(entry.route != null);
assert(entry.route._navigator == null);
assert(entry.currentState == _RouteLifecycle.push);
_history.add(entry);
_flushHistoryUpdates();
assert(() {
_debugLocked = false;
return true;
}());
_afterNavigation(entry.route);
}
可以看到Navigator内部用一个_history来维护历史路径,这个_history是一个list而已,如下:List<_RouteEntry> _history = <_RouteEntry>[];而pop代码如下:
@optionalTypeArgs
void pop<T extends Object?>([ T? result ]) {
assert(!_debugLocked);
assert(() {
_debugLocked = true;
return true;
}());
final _RouteEntry entry = _history.lastWhere(_RouteEntry.isPresentPredicate);
if (entry.hasPage) {
if (widget.onPopPage!(entry.route, result))
entry.currentState = _RouteLifecycle.pop;
} else {
entry.pop<T>(result);
}
if (entry.currentState == _RouteLifecycle.pop) {
// Flush the history if the route actually wants to be popped (the pop
// wasn't handled internally).
_flushHistoryUpdates(rearrangeOverlay: false);
assert(entry.route._popCompleter.isCompleted);
}
assert(() {
_debugLocked = false;
return true;
}());
_afterNavigation(entry.route);
}
可以看到也是通过_history来实现的。mixin WidgetsBinding on BindingBase, ServicesBinding, SchedulerBinding, GestureBinding, RendererBinding, SemanticsBinding {
@override
void initInstances() {
super.initInstances();
_instance = this;
assert(() {
_debugAddStackFilters();
return true;
}());
// Initialization of [_buildOwner] has to be done after
// [super.initInstances] is called, as it requires [ServicesBinding] to
// properly setup the [defaultBinaryMessenger] instance.
_buildOwner = BuildOwner();
buildOwner!.onBuildScheduled = _handleBuildScheduled;
window.onLocaleChanged = handleLocaleChanged;
window.onAccessibilityFeaturesChanged = handleAccessibilityFeaturesChanged;
SystemChannels.navigation.setMethodCallHandler(_handleNavigationInvocation);
FlutterErrorDetails.propertiesTransformers.add(transformDebugCreator);
}
...
这里我们看到有这样一行代码:SystemChannels.navigation.setMethodCallHandler(_handleNavigationInvocation);这是与native进行交互,或者当收到native的相关事件就会执行_handleNavigationInvocation
Future<dynamic> _handleNavigationInvocation(MethodCall methodCall) {
switch (methodCall.method) {
case 'popRoute':
return handlePopRoute();
case 'pushRoute':
return handlePushRoute(methodCall.arguments as String);
case 'pushRouteInformation':
return _handlePushRouteInformation(methodCall.arguments as Map<dynamic, dynamic>);
}
return Future<dynamic>.value();
}
浏览器的回退按钮就是一个popRoute事件,所以执行handlePopRoute@protected
Future<void> handlePopRoute() async {
for (final WidgetsBindingObserver observer in List<WidgetsBindingObserver>.from(_observers)) {
if (await observer.didPopRoute())
return;
}
SystemNavigator.pop();
}
继续执行didPopRoute,这个函数在widgets/app.dart中实现。@override
Future<bool> didPopRoute() async {
assert(mounted);
// The back button dispatcher should handle the pop route if we use a
// router.
if (_usesRouter)
return false;
final NavigatorState? navigator = _navigator?.currentState;
if (navigator == null)
return false;
return await navigator.maybePop();
}
这样就进入到Navigator中了@optionalTypeArgs
Future<bool> maybePop<T extends Object?>([ T? result ]) async {
final _RouteEntry? lastEntry = _history.cast<_RouteEntry?>().lastWhere(
(_RouteEntry? e) => e != null && _RouteEntry.isPresentPredicate(e),
orElse: () => null,
);
if (lastEntry == null)
return false;
assert(lastEntry.route._navigator == this);
final RoutePopDisposition disposition = await lastEntry.route.willPop(); // this is asynchronous
assert(disposition != null);
if (!mounted)
return true; // forget about this pop, we were disposed in the meantime
final _RouteEntry? newLastEntry = _history.cast<_RouteEntry?>().lastWhere(
(_RouteEntry? e) => e != null && _RouteEntry.isPresentPredicate(e),
orElse: () => null,
);
if (lastEntry != newLastEntry)
return true; // forget about this pop, something happened to our history in the meantime
switch (disposition) {
case RoutePopDisposition.bubble:
return false;
case RoutePopDisposition.pop:
pop(result);
return true;
case RoutePopDisposition.doNotPop:
return true;
}
}
上面我们知道刷新后_history中只有当前页面的router,这时候disposition就是RoutePopDisposition.bubble,我们看它的解释/// Delegate this to the next level of navigation. /// /// If [Route.willPop] returns [bubble] then the back button will be handled /// by the [SystemNavigator], which will usually close the application.会关闭当前应用,但是浏览器并未关闭,所以会重新加载默认页面。注意这与上面pop结果是不一样的,因为这时候还没有执行pop,而且也不会执行到pop了。如果是正常情况下_history有上一页记录,disposition是RoutePopDisposition.pop就会执行pop了。
对于这个问题很多人也在github的flutter项目中反馈 https://github.com/flutter/flutter/issues/59277
Future<dynamic> _handleNavigationInvocation(MethodCall methodCall) {
switch (methodCall.method) {
case 'popRoute':
return handlePopRoute();
case 'pushRoute':
return handlePushRoute(methodCall.arguments as String);
case 'pushRouteInformation':
return _handlePushRouteInformation(methodCall.arguments as Map<dynamic, dynamic>);
}
return Future<dynamic>.value();
}
但是在2.0中methodCall.method是pushRouteInformation,所以执行了_handlePushRouteInformation,这样就导致了与Navigator1.0的不同。而_handlePushRouteInformation就是执行了push流程,这里就不详细说了,所以最后执行了setNewRoutePath,这样也导致了文章中提到的问题