- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
class Person {
const Person(this.name);
final String name;
}
final Person bob = Person("Bob");
print(bob == Person("Bob")); // false
那么如果需要它们相等,如下代码所示,我们需要 override == 操作符去自定义所需的判断逻辑,这样看起来貌似也不麻烦,但是如果一个类参数很多,那么类似的重复性代码就会很多,这时候就需要 equatable 这个包来减轻工作量。class Person {
const Person(this.name);
final String name;
@override
bool operator ==(Object other) =>
identical(this, other) ||
other is Person &&
runtimeType == other.runtimeType &&
name == other.name;
@override
int get hashCode => name.hashCode;
}
如下代码所示,通过 equatable 你只需要 extends Equatable ,然后 override props 参数即可实现对应的 ==自定义,这样从代码层级上看是不是更清晰简约了?import 'package:equatable/equatable.dart';
class Person extends Equatable {
const Person(this.name);
final String name;
@override
List<Object> get props => [name];
}
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
class Person2 extends Equatable {
const Person2(this.name, [this.age]);
final String name;
final int? age;
@override
List<Object?> get props => [name, age];
}
当然,对于 equatable 还是有一些限制,例如所有成员变量都必须是 final, 因为 Dart 官方在说明自定义 == 逻辑就表示过, 用可变值覆盖 hashCode 可能会破坏基于哈希的集合: @override
bool operator ==(Object other) {
return identical(this, other) ||
other is Equatable &&
runtimeType == other.runtimeType &&
equals(props, other.props);
}
@override
int get hashCode => runtimeType.hashCode ^ mapPropsToHashCode(props);
首先自定义的 equals 判断其实就是对于两个 class 的 props 列表进行拆分判断,这里主要需要注意的是,由于类变量可以是任何对象,那么也就可以能是集合,例如 Map、Set 等,所以需要用到 Dart 的 DeepCollectionEquality 对象来处理,可以减轻很多判断的工作量。const DeepCollectionEquality _equality = DeepCollectionEquality();
/// Determines whether [list1] and [list2] are equal.
bool equals(List<Object?>? list1, List<Object?>? list2) {
if (identical(list1, list2)) return true;
if (list1 == null || list2 == null) return false;
final length = list1.length;
if (length != list2.length) return false;
for (var i = 0; i < length; i++) {
final unit1 = list1[i];
final unit2 = list2[i];
if (_isEquatable(unit1) && _isEquatable(unit2)) {
if (unit1 != unit2) return false;
} else if (unit1 is Iterable || unit1 is Map) {
if (!_equality.equals(unit1, unit2)) return false;
} else if (unit1?.runtimeType != unit2?.runtimeType) {
return false;
} else if (unit1 != unit2) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool _isEquatable(Object? object) {
return object is Equatable || object is EquatableMixin;
}
而对于生成哈希,equatable 用了 Jenkins 哈希算法,核心就是将任意长度的数值转换为固定长度的哈希值,算法的实现也相对简单,它只需要利用位移操作和迭代来生成哈希值,通过不断递归将所有参数进行 Jenkins 哈希计算,例如:int mapPropsToHashCode(Iterable<Object?>? props) {
return _finish(props == null ? 0 : props.fold(0, _combine));
}
int _combine(int hash, Object? object) {
if (object is Map) {
object.keys
.sorted((Object? a, Object? b) => a.hashCode - b.hashCode)
.forEach((Object? key) {
hash = hash ^ _combine(hash, [key, (object! as Map)[key]]);
});
return hash;
}
if (object is Set) {
object = object.sorted((Object? a, Object? b) => a.hashCode - b.hashCode);
}
if (object is Iterable) {
for (final value in object) {
hash = hash ^ _combine(hash, value);
}
return hash ^ object.length;
}
hash = 0x1fffffff & (hash + object.hashCode);
hash = 0x1fffffff & (hash + ((0x0007ffff & hash) << 10));
return hash ^ (hash >> 6);
}
int _finish(int hash) {
hash = 0x1fffffff & (hash + ((0x03ffffff & hash) << 3));
hash = hash ^ (hash >> 11);
return 0x1fffffff & (hash + ((0x00003fff & hash) << 15));
}
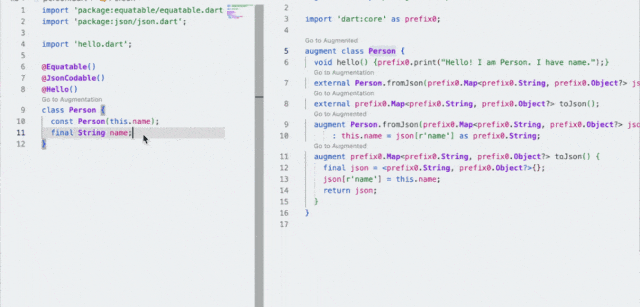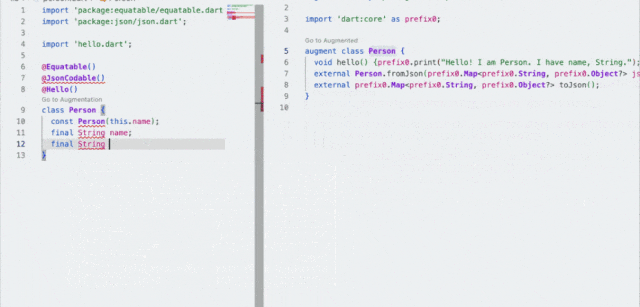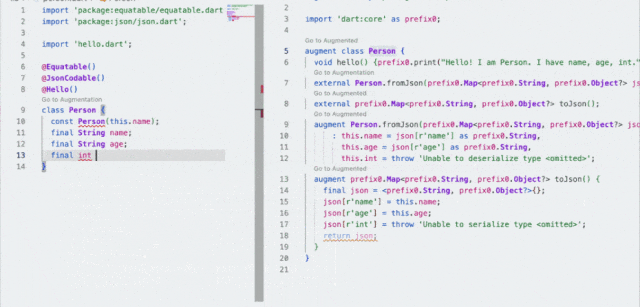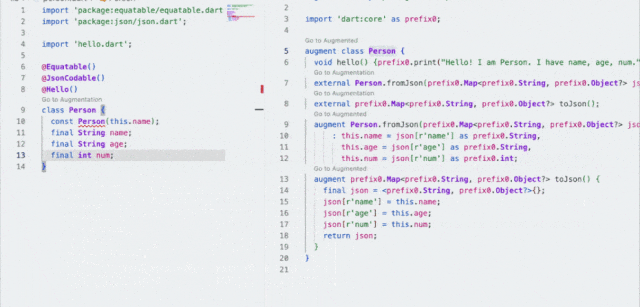
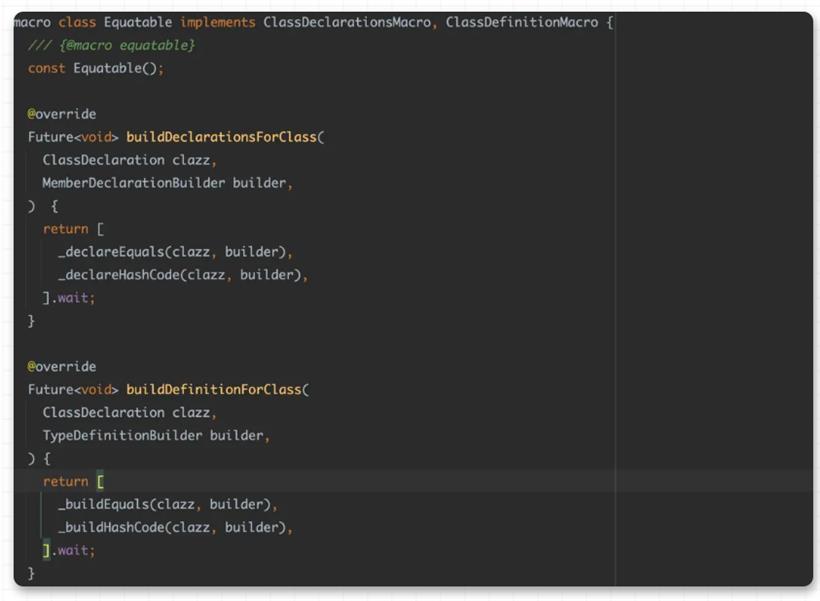
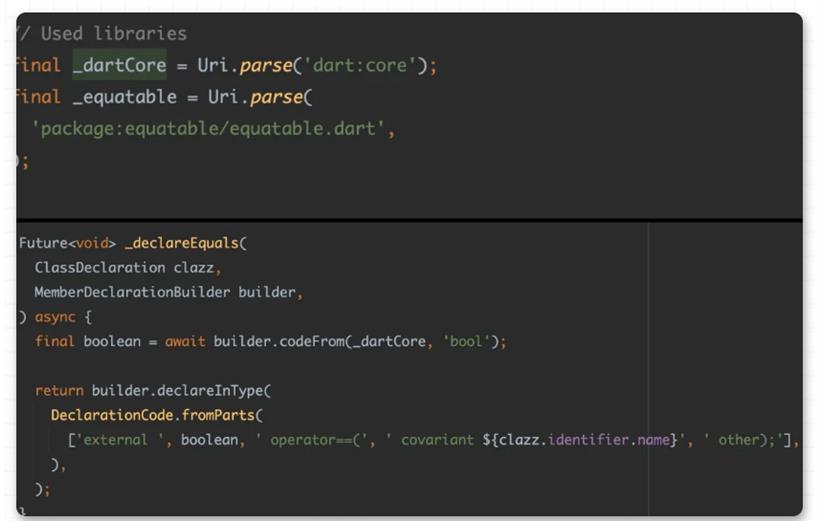
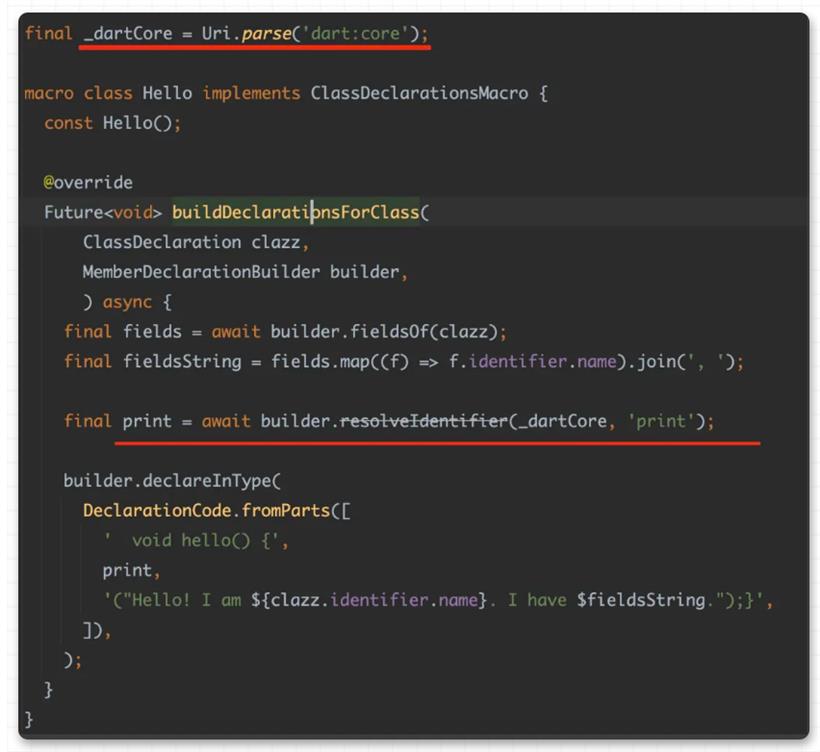
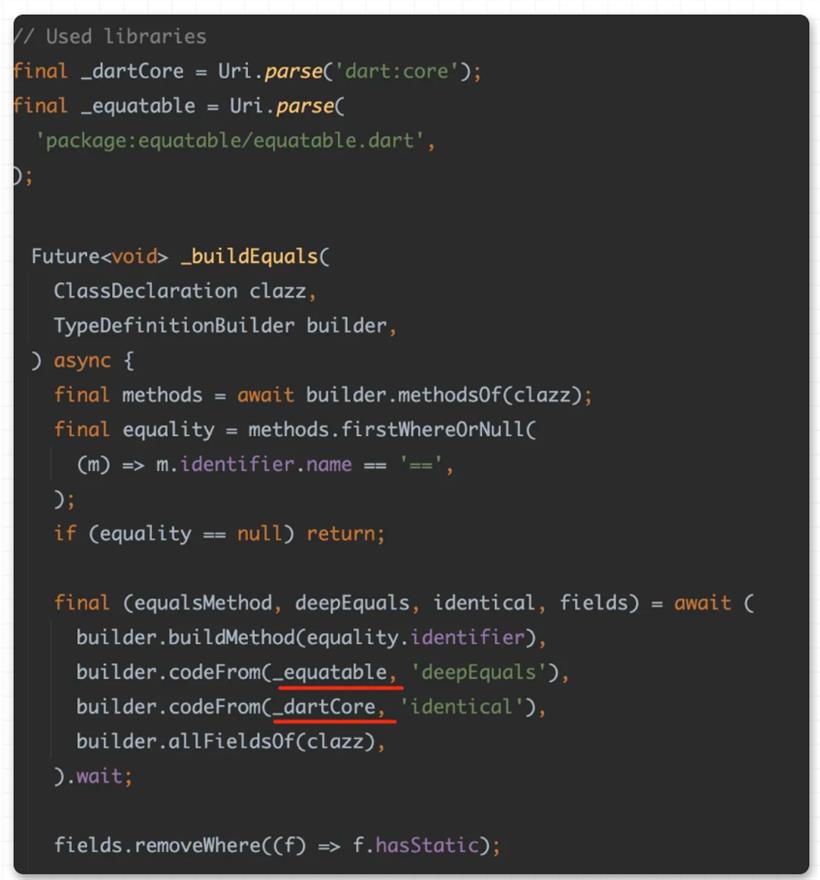
到这里我们大概就解析了 equatable 的作用和实现,但是其实在使用上还不够优雅简介,因为需要手写 props 和显式继承的操作,还是让人觉得侵入性太强,那么这时候就该说宏编程的作用了。@Equatable()
class Person {
const Person(this.name);
final String name;
}
可以看到,他就是一个正常的 class ,你只需要添加 @Equatable() 注释,它就拥有了前面所说的 equatable class 的特性,这样看是不是优雅和简单了不少?并且和之前旧的 build_runner 等不同,它不会在你项目里直接生产 .g.dart 的文件。在引入带有宏编程的 equatable 包之后,只需要运行 flutter run --enable-experiment=macros ,就可以直接得到之前一样的结果: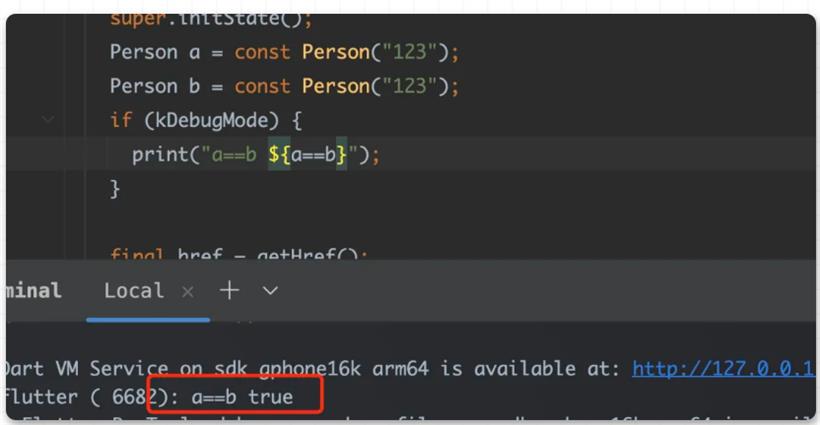
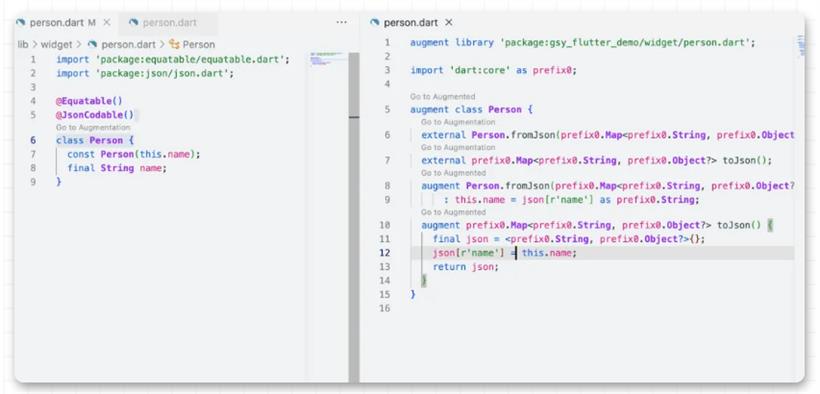
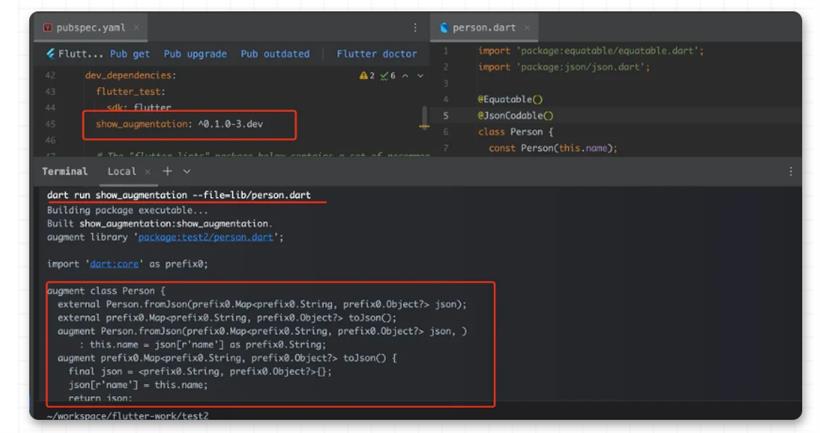


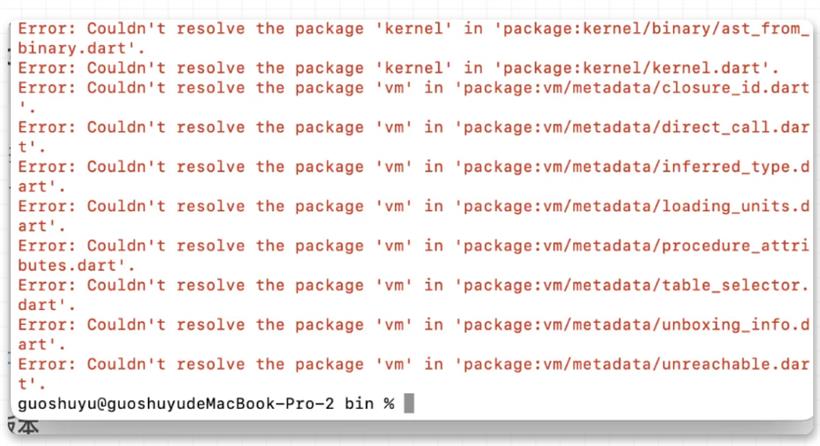
.现在你就可以通过 dart pkg/vm/bin/dump_kernel.dart xxxxxx/app.dill xxxxxx/app.dill.txt 去 dump kernel ,这里的 pkg/vm/bin/dump_kernel.dart 路径就是前面 sdk 下的路径。