- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号

type Data struct {
x int64 // 线程A更新的变量
y int64 // 线程B更新的变量
}
如果变量 x 和 y 位于同一个 cache line 中,那么线程 A 更新 x 后,线程 B 也会因为缓存失效而重新加载 y,尽管 B 实际上并未使用 x 的值。这种情况下,虽然两个变量并没有直接共享,但每次写操作都会导致另一方的缓存失效,从而形成了伪共享。type Data struct {
x int64 // 线程A更新的变量
_ [7]int64 // 填充7个int64以对齐至64字节的cache line大小
y int64 // 线程B更新的变量
}
2. **将变量分散到不同的结构体中**:对于经常被多个线程更新的变量,可以考虑将它们分散到不同的结构体,避免同一结构体被多个线程同时频繁更新。```go
package main
import (
"testing"
)
// NonAlignedStruct 未对齐的结构体,补充后占24个字节
type NonAlignedStruct struct {
a byte // 1字节,补齐7字节
b int64 // 8字节
c byte // 1字节,补齐7字节
}
// AlignedStruct 已对齐的结构体,补充后占16个字节
type AlignedStruct struct {
b int64 // 8字节
a byte // 1字节
c byte // 1字节
_ [6]byte // 填充6个字节,总共16个字节
}
const arraySize = 1024 * 1024
var (
nonAlignedArray [arraySize]NonAlignedStruct
alignedArray [arraySize]AlignedStruct
result int64
)
// 初始化数组
func init() {
for i := 0; i < arraySize; i++ {
nonAlignedArray[i] = NonAlignedStruct{
a: byte(i),
b: int64(i),
c: byte(i),
}
alignedArray[i] = AlignedStruct{
a: byte(i),
b: int64(i),
c: byte(i),
}
}
}
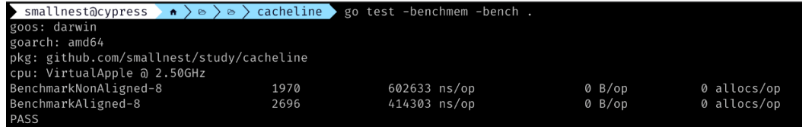
// BenchmarkNonAligned 测试未对齐结构体的性能
func BenchmarkNonAligned(b *testing.B) {
var sum int64
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
for j := 0; j < arraySize; j++ {
sum += nonAlignedArray[j].b // 读取未对齐结构体的字段
}
}
result = sum // 防止编译器优化
}
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
// BenchmarkAligned 测试已对齐结构体的性能
func BenchmarkAligned(b *testing.B) {
var sum int64
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
for j := 0; j < arraySize; j++ {
sum += alignedArray[j].b // 读取已对齐结构体的字段
}
}
result = sum // 防止编译器优化
}

// CacheLinePad 用来填充结构体,避免伪共享
type CacheLinePad struct{ _ [CacheLinePadSize]byte }
// CacheLineSize 是 CPU 的缓存行大小,不同的 CPU 架构可能不同.
// 目前 Go 运行时没有检测真实的缓存行大小,所以代码实现使用每个 GOARCH 的常量 CacheLinePadSize 作为近似值。
var CacheLineSize uintptr = CacheLinePadSize
然后针对不同的 CPU 架构定义不同的缓存行大小。 比如 arm64 的 CPU, 文件go/src/internal/cpu/cpu_arm64.go中定义了缓存行大小为 128 字节:// CacheLinePadSize is used to prevent false sharing of cache lines. // We choose 128 because Apple Silicon, a.k.a. M1, has 128-byte cache line size. // It doesn't cost much and is much more future-proof. const CacheLinePadSize = 128比如 64bit 的龙芯, 缓存行大小是 64 字节,文件go/src/internal/cpu/cpu_loong64.go中定义了缓存行大小为 64 字节:
// CacheLinePadSize is used to prevent false sharing of cache lines. // We choose 64 because Loongson 3A5000 the L1 Dcache is 4-way 256-line 64-byte-per-line. const CacheLinePadSize = 64又比如 x86 和 amd64 的 CPU, 缓存行大小是 64 字节,文件go/src/internal/cpu/cpu_x86.go中定义了缓存行大小为 64 字节:
//go:build 386 || amd64 package cpu const CacheLinePadSize = 64所以 Go 运行时是根据它支持的不同的 CPU 架构,定义不同的缓存行大小,以此来避免伪共享问题。但是这个数据结构是定义在 Go 运行时internal库中,不对外暴露,那么我们怎么用的?
type CacheLinePad struct{ _ [cacheLineSize]byte }
它的实现和 Go 运行时中的一样,只是把CacheLinePad暴露出来了,所以我们可以在自己的项目中直接使用。type semaRoot struct {
lock mutex
treap *sudog // root of balanced tree of unique waiters.
nwait atomic.Uint32 // Number of waiters. Read w/o the lock.
}
var semtable semTable
// Prime to not correlate with any user patterns.
const semTabSize = 251
type semTable [semTabSize]struct {
root semaRoot
pad [cpu.CacheLinePadSize - unsafe.Sizeof(semaRoot{})]byte
}
等并发读取semTable时,由于semTable中的root是一个semaRoot结构体,semaRoot中有mutex,treap等字段,这些字段可能会被不同的 CPU 核心同时访问,导致伪共享问题。 为了解决伪共享问题,它增加了一个Pad字段,补齐字段的大小到CacheLineSize,这样就可以避免伪共享问题。当然这里可以确定semaRoot的大小不会超过一个CacheLineSize。type mheap struct {
_ sys.NotInHeap
lock mutex
pages pageAlloc // page allocation data structure
sweepgen uint32 // sweep generation, see comment in mspan; written during STW
allspans []*mspan // all spans out there
pagesInUse atomic.Uintptr // pages of spans in stats mSpanInUse
pagesSwept atomic.Uint64 // pages swept this cycle
pagesSweptBasis atomic.Uint64 // pagesSwept to use as the origin of the sweep ratio
sweepHeapLiveBasis uint64 // value of gcController.heapLive to use as the origin of sweep ratio; written with lock, read without
sweepPagesPerByte float64 // proportional sweep ratio; written with lock, read without
reclaimIndex atomic.Uint64
reclaimCredit atomic.Uintptr
_ cpu.CacheLinePad // prevents false-sharing between arenas and preceding variables
arenas [1 << arenaL1Bits]*[1 << arenaL2Bits]*heapArena
...
}
go/src/runtime/stack.go中stackpool结构体中也使用了CacheLinePad,展示了另外一种用法:
var stackpool [_NumStackOrders]struct {
item stackpoolItem
_ [(cpu.CacheLinePadSize - unsafe.Sizeof(stackpoolItem{})%cpu.CacheLinePadSize) % cpu.CacheLinePadSize]byte
}
因为 item 的大小不确定,可能小于一个CacheLineSize,也可能大于一个CacheLineSize,所以这里对CacheLinePad求余,只需补充一个小于CacheLineSize的字节即可。