- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
public class CountryDTO {
private String country;
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public String getCountry() {
return this.country;
}
public Boolean isChinaName() {
return this.country.equals("中国");
}
}
❝定义测试类 FastJonTest❞public class FastJonTest {
@Test
public void testSerialize() {
CountryDTO countryDTO = new CountryDTO();
String str = JSON.toJSONString(countryDTO);
System.out.println(str);
}
}
运行时报空指针错误:
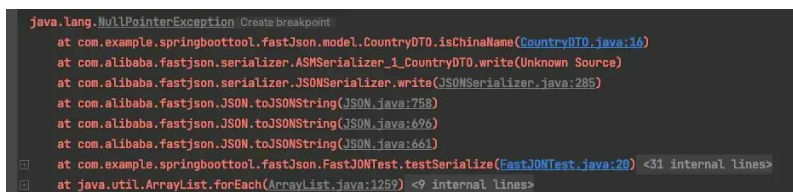
2.引申一下,序列化过程中会执行那些方法呢?
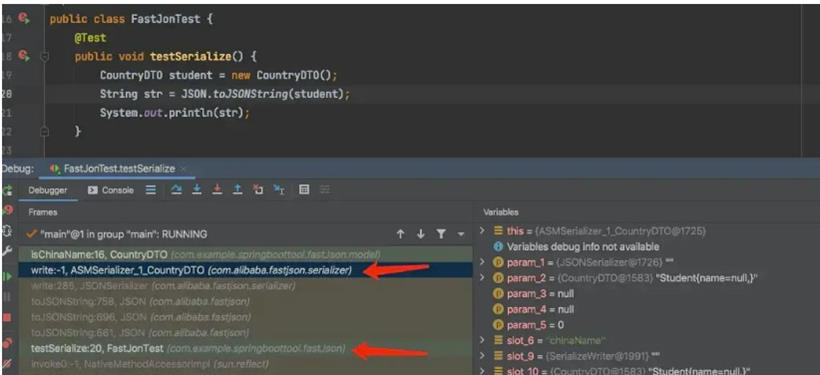
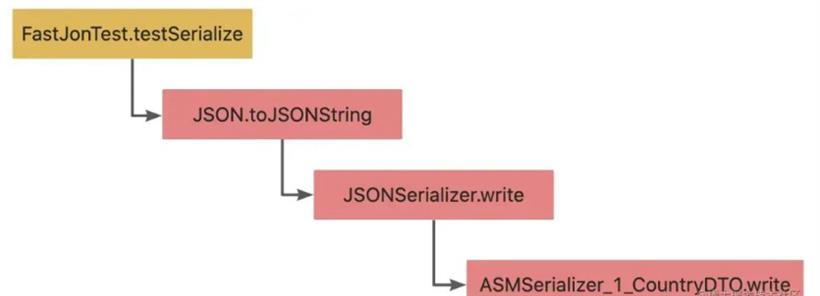
❝asm技术其中一项使用场景就是通过到动态生成类用来代替java反射,从而避免重复执行时的反射开销❞
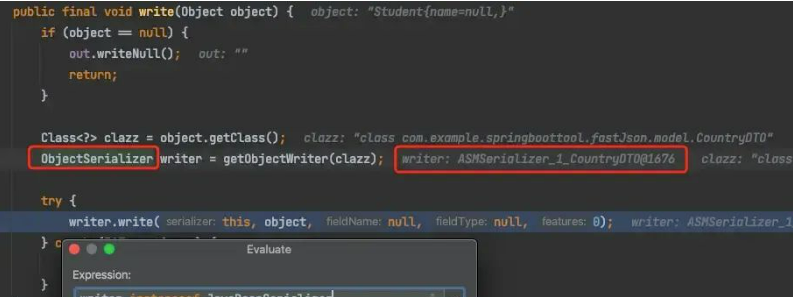
而JavaBeanSerializer主要是通过getObjectWriter()方法获取,通过对getObjectWriter()执行过程的调试,找到比较关键的
com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializeConfig#createJavaBeanSerializer方法,进而找到 com.alibaba.fastjson.util.TypeUtils#computeGetters
public static List<FieldInfo> computeGetters(Class<?> clazz, //
JSONType jsonType, //
Map<String,String> aliasMap, //
Map<String,Field> fieldCacheMap, //
boolean sorted, //
PropertyNamingStrategy propertyNamingStrategy //
){
//省略部分代码....
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for(Method method : methods){
//省略部分代码...
if(method.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE)){
continue;
}
if(method.getParameterTypes().length != 0){
continue;
}
//省略部分代码...
JSONField annotation = TypeUtils.getAnnotation(method, JSONField.class);
//省略部分代码...
if(annotation != null){
if(!annotation.serialize()){
continue;
}
if(annotation.name().length() != 0){
//省略部分代码...
}
}
if(methodName.startsWith("get")){
//省略部分代码...
}
if(methodName.startsWith("is")){
//省略部分代码...
}
}
}
从代码中大致分为三种情况:/**
* case1: @JSONField(serialize = false)
* case2: getXxx()返回值为void
* case3: isXxx()返回值不等于布尔类型
* case4: @JSONType(ignores = "xxx")
*/
@JSONType(ignores = "otherName")
public class CountryDTO {
private String country;
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public String getCountry() {
return this.country;
}
public static void queryCountryList() {
System.out.println("queryCountryList()执行!!");
}
public Boolean isChinaName() {
System.out.println("isChinaName()执行!!");
return true;
}
public String getEnglishName() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
public String getOtherName() {
System.out.println("getOtherName()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
/**
* case1: @JSONField(serialize = false)
*/
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public String getEnglishName2() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName2()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
/**
* case2: getXxx()返回值为void
*/
public void getEnglishName3() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName3()执行!!");
}
/**
* case3: isXxx()返回值不等于布尔类型
*/
public String isChinaName2() {
System.out.println("isChinaName2()执行!!");
return "isChinaName2";
}
}
运行结果为:isChinaName()执行!!
getEnglishName()执行!!
{"chinaName":true,"englishName":"lucy"}
public class CountryDTO {
private String country;
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public String getCountry() {
return this.country;
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public static void queryCountryList() {
System.out.println("queryCountryList()执行!!");
}
public Boolean isChinaName() {
System.out.println("isChinaName()执行!!");
return true;
}
public String getEnglishName() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public String getOtherName() {
System.out.println("getOtherName()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public String getEnglishName2() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName2()执行!!");
return "lucy";
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public void getEnglishName3() {
System.out.println("getEnglishName3()执行!!");
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public String isChinaName2() {
System.out.println("isChinaName2()执行!!");
return "isChinaName2";
}
}
三个频率高的序列化的情况

围绕技术上:解决单个问题,顺着单个问题掌握这条线上的原理。