- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
/**
* @堆代码 duidaima.com
* @date 2024/2/1 22:58
*/
public class DateFormatTest {
private static final SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat =
new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static Date parse(String dateString) {
Date date = null;
try {
date = simpleDateFormat.parse(dateString);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return date;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
executorService.execute(()->{
System.out.println(parse("2024-02-01 23:34:30"));
});
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
上述咱们通过线程池的方式针对SimpleDateFormat进行了测试(如果大家需要深入了解一下线程池的相关原理,可以戳“线程池 (opens new window)”)。其输出结果如下。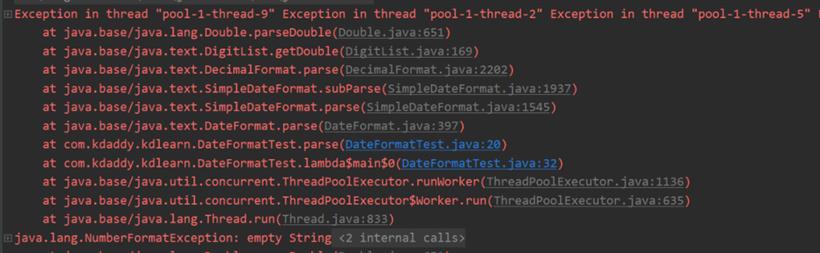
/**
* @堆代码 duidaima.com
* @date 2024/2/1 22:58
*/
public class DateFormatTest {
private static final ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> dateFormatThreadLocal =
ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
public static Date parse(String dateString) {
Date date = null;
try {
date = dateFormatThreadLocal.get().parse(dateString);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return date;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
executorService.execute(()->{
System.out.println(parse("2024-02-01 23:34:30"));
});
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
运行了一下,完全正常了。Thu Feb 01 23:34:30 CST 2024 Thu Feb 01 23:34:30 CST 2024 Thu Feb 01 23:34:30 CST 2024 Thu Feb 01 23:34:30 CST 2024 Thu Feb 01 23:34:30 CST 2024 Thu Feb 01 23:34:30 CST 2024 Thu Feb 01 23:34:30 CST 2024 Thu Feb 01 23:34:30 CST 2024 Thu Feb 01 23:34:30 CST 2024TheadLocal使用场景
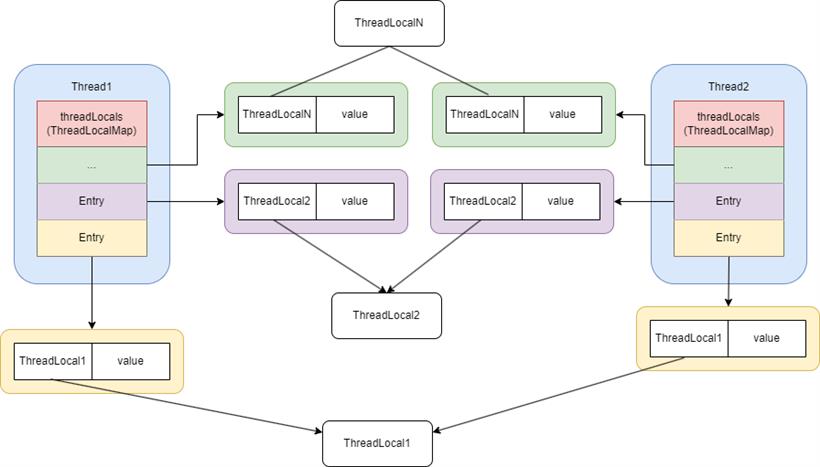
public class Thread implements Runnable {
...
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
...
}
在源码中threadLocals的初始值为Null。抽丝剥茧,咱们继续看一下ThreadLocalMap在调用构造函数进行初始化的源代码:static class ThreadLocalMap {
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; //初始化容量
private Entry[] table; //ThreadLocalMap数据真正存储在table中
private int size = 0; //ThreadLocalMap条数
private int threshold; // 默认为0,达到这个大小,则扩容
//类Entry的实现
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
//构造函数
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY]; //初始化table数组,INITIAL_CAPACITY默认值为16
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); //key和16取得哈希值
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);//创建节点,设置key-value
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY); //设置扩容阈值
}
}
在源码中涉及比较核心的还有set,get以及remove方法。我们依次来看一下: public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); //获取当前线程t
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); //根据当前线程获取到ThreadLocalMap
if (map != null) //如果获取的ThreadLocalMap对象不为空
map.set(this, value); //K,V设置到ThreadLocalMap中
else
createMap(t, value); //创建一个新的ThreadLocalMap
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals; //返回Thread对象的ThreadLocalMap属性
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { //调用ThreadLocalMap的构造函数
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); //this表示当前类ThreadLocal
}
get方法如下: public T get() {
//1、获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//2、获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
//3、如果map数据不为空,
if (map != null) {
//3.1、获取threalLocalMap中存储的值
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
//如果是数据为null,则初始化,初始化的结果,TheralLocalMap中存放key值为threadLocal,值为null
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
remove方法: public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
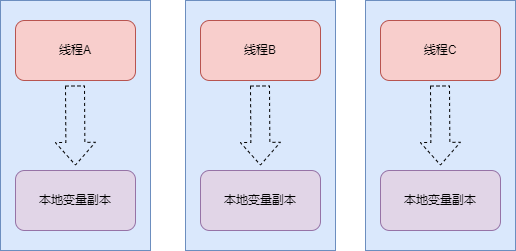
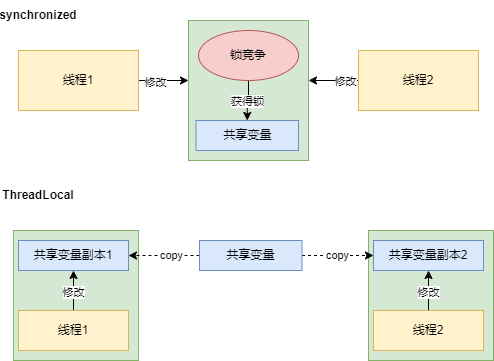
那么为什么需要remove方法呢?其实这里会涉及到内存泄漏的问题了。后面咱们细看。并发场景下,每个线程都会存储当前变量副本到自己的ThreadLocalMap中,后续这个线程对于共享变量的操作,都是从TheadLocalMap里进行变更,不会影响全局共享变量的值。
static class ThreadLocalMap {
...
//类Entry的实现
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
...
}
上文中其实我们已经知道Entry中以key和value的形式存储,key是ThreadLocal本身,上面代码中我们看到entry进行key设置的时候用的是super(k)。那就意味着调用的父类的方法去设置了key,我们再看一下父类是什么,父类其实是WeakReference。关于WeakReference底层的实现,大家有兴趣可以展开去看看源代码,老猫在这里直接说结果。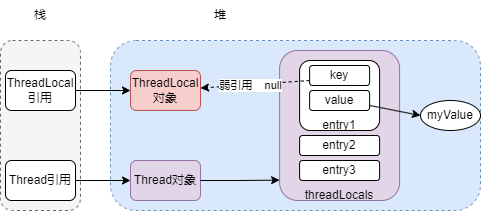
2.ThreadLocal变量尽量定义成static final类型,避免频繁创建ThreadLocal实例。这样可以保证程序中一直存在ThreadLocal强引用,也能保证任何时候都能通过ThreadLocal的弱引用访问Entry的value值,从而进行清除。