- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
“能不能加点冰块到辣酱里?”
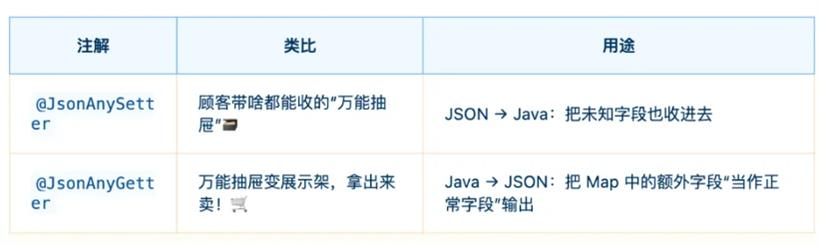
@JsonAnySetter
publicvoidadd(String key, Object value){
otherProps.put(key, value);
}
比如这个 JSON:{
"name": "豆瓣酱",
"spicy": true,
"limited_edition": "yes",
"extra_notes": "只在冬天卖"
}
你类里只定义了 name 和 spicy 字段,但 limited_edition 和 extra_notes 也能顺利进货,被收纳进了 otherProps 这个万能抽屉里。@JsonAnySetter 用于标注一个方法,该方法可以接收 JSON 中没有预定义的属性。当 Jackson 反序列化 JSON 时,如果遇到未在 Java 类中显式定义的字段,它会调用这个方法并将字段名和字段值作为参数传递给它。public class Person {
private String name;
privateint age;
// 存储额外的动态属性
private Map < String, Object > additionalProperties = new HashMap < > (); // 添加动态属性
@
JsonAnySetter publicvoidaddAdditionalProperty(String key, Object value) {
this.additionalProperties.put(key, value);
}
// 省略 getter 和 setter 方法
public Map < String, Object > getAdditionalProperties() {
return additionalProperties;
}
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) throws Exception {
String json = "{"
name ":"
John ","
age ":30,"
address ":"
123 Street ","
nickname ":"
Johnny "}";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Person person = mapper.readValue(json, Person.class);
System.out.println("Name: " + person.name);
// 输出:Name: John
System.out.println("Age: " + person.age); // 输出:Age: 30
System.out.println("Additional Properties: " + person.getAdditionalProperties()); // 输出:Additional Properties: {address=123 Street, nickname=Johnny} }}
在这个例子中:Name: John
Age: 30
Additional Properties: {address=123 Street, nickname=Johnny}
@JsonAnyGetter:随便拿!需要啥我都能给@JsonAnyGetter
public Map<String, Object> getOtherProps(){
return otherProps;
}
这样序列化输出的 JSON 会自动把 otherProps 里的内容平铺出去,和其他字段“融为一体”。@JsonAnyGetter 用于标注一个方法,该方法返回一个 Map 或类似结构,它将包含对象的 动态属性(即对象中没有显式定义的字段)。当 Jackson 序列化对象时,它会将这个 Map 中的键值对当作额外的 JSON 属性来序列化。public class Person {
private String name;
privateint age; // 存储额外的动态属性
private Map < String, Object > additionalProperties = new HashMap < > ();
publicPerson(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 通过该方法返回所有额外的动态属性
@JsonAnyGetter public Map < String, Object > getAdditionalProperties() {
return additionalProperties;
}
publicvoidaddAdditionalProperty(String key, Object value) {
this.additionalProperties.put(key, value);
}
// 省略 getter 和 setter 方法
}
public class Main {
publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args) throws Exception {
Person person = new Person("John", 30);
person.addAdditionalProperty("address", "123 Street");
person.addAdditionalProperty("nickname", "Johnny");
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(person);
System.out.println(json);
// 输出:{"name":"John","age":30,"address":"123 Street","nickname":"Johnny"}
}
}
在这个例子中:Person 类包含一个 Map<String, Object> 来存储动态属性。使用 @JsonAnyGetter 标注 getAdditionalProperties() 方法,表示 additionalProperties 中的键值对应该被序列化为 JSON 字段。通过调用 addAdditionalProperty() 方法向 additionalProperties 中添加动态字段。{
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"address": "123 Street",
"nickname": "Johnny"
}
总结一下