- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
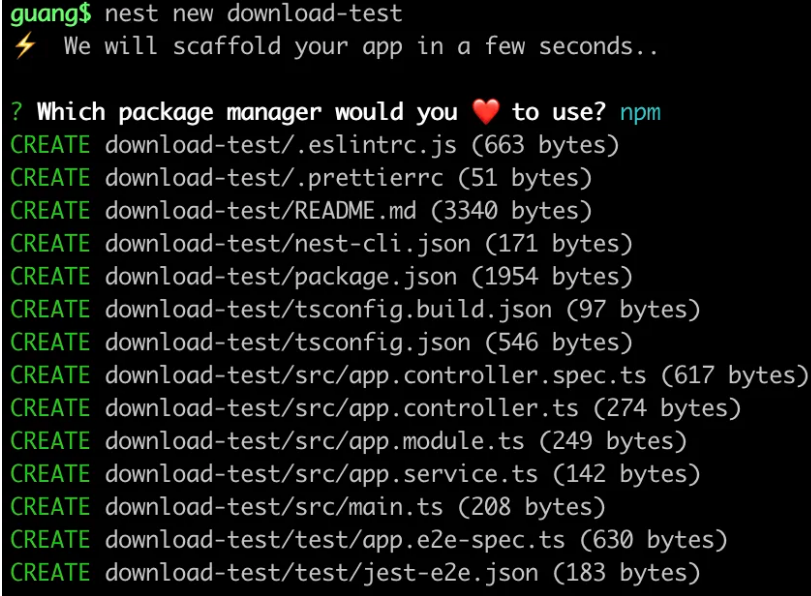
nest new download-test
import { Controller, Get, Res } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
import { Response } from 'express';
import * as fs from 'fs';
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
@Controller()
export class AppController {
constructor(private readonly appService: AppService) {}
@Get()
getHello(): string {
return this.appService.getHello();
}
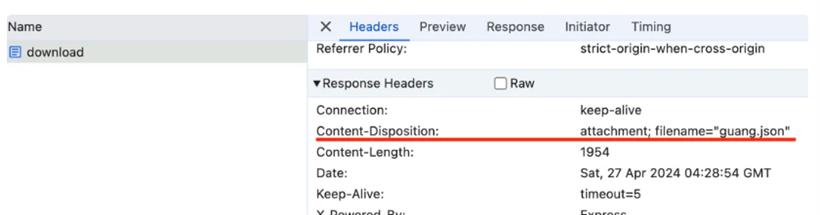
@Get('download')
download(@Res() res: Response) {
const content = fs.readFileSync('package.json');
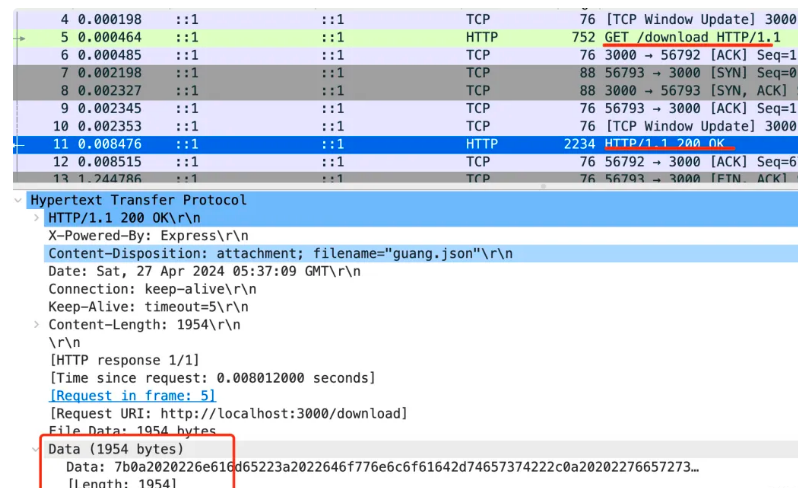
res.set('Content-Disposition', `attachment; filename="guang.json"`);
res.end(content);
}
}
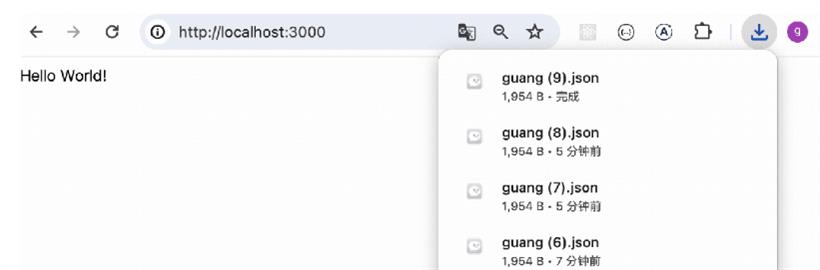
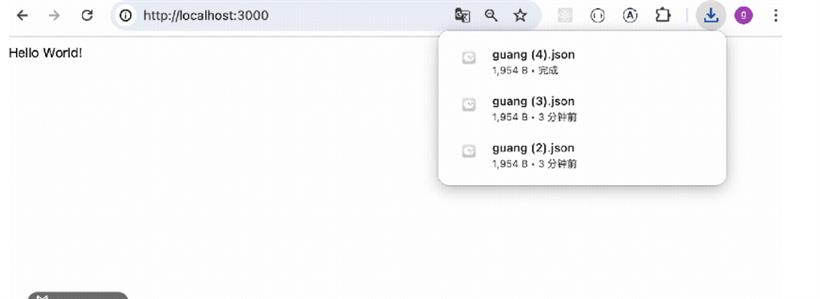
把服务跑起来:npm run start:dev浏览器访问下:

@Get('download')
@Header('Content-Disposition', `attachment; filename="guang.json"`)
download(@Res() res: Response) {
const content = fs.readFileSync('package.json');
res.end(content);
}

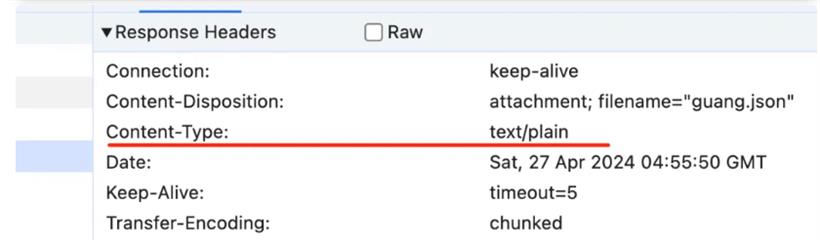
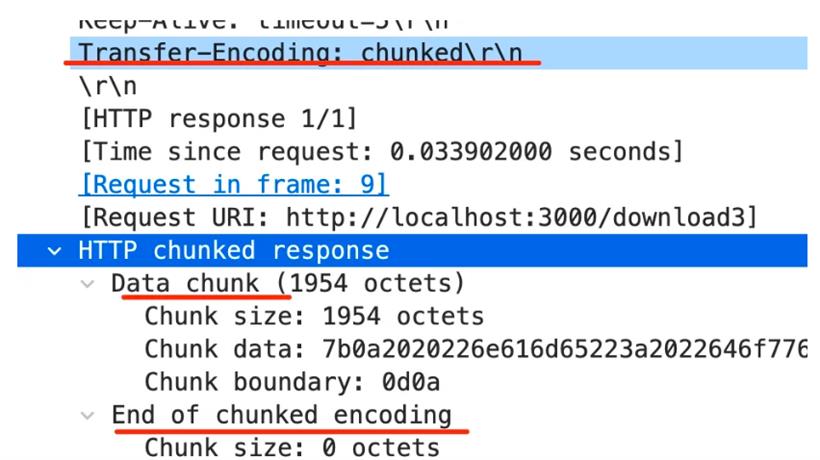
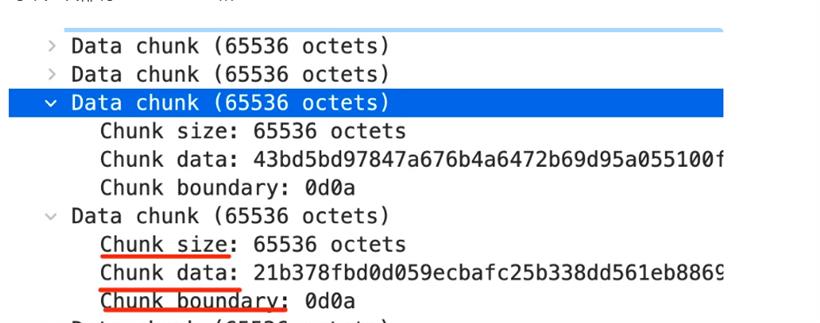
5 Hello 1 , 5 World 1 ! 0这里分了 “Hello” “,” “World”“!” 这 4 个块,长度分别为 5、1、5、1。最后以一个长度为 0 的块代表传输结束。这样,不管内容多少都可以分块返回,就不用指定 Content-Length 了。这就是大文件的流式传输的原理,就是 transfer-encoding:chunked。
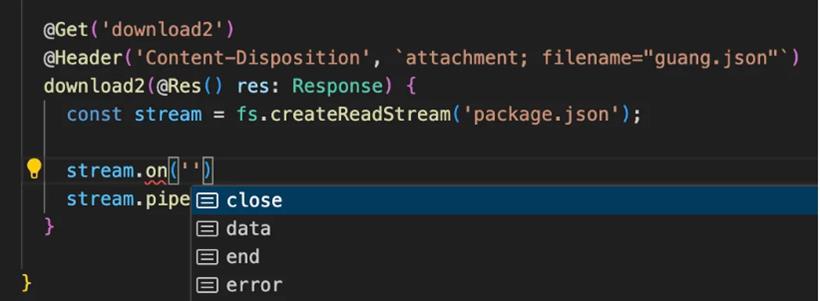
@Get('download2')
@Header('Content-Disposition', `attachment; filename="guang.json"`)
download2(@Res() res: Response) {
const stream = fs.createReadStream('package.json');
stream.pipe(res);
}
node 的 stream 本来就是分块读取内容的,这里配合流式返回数据很合适。


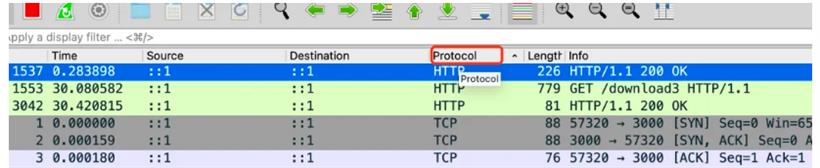
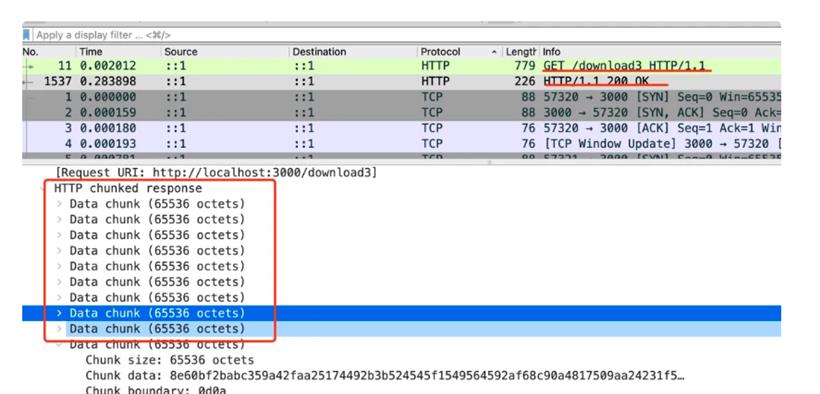
@Get('download3')
download3() {
const stream = fs.createReadStream('package.json');
return new StreamableFile(stream, {
disposition: `attachment; filename="guang.json"`
});
}
试一下:

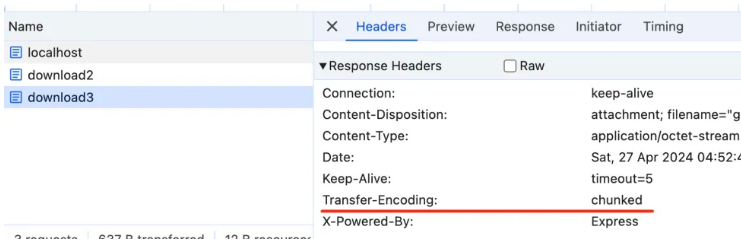
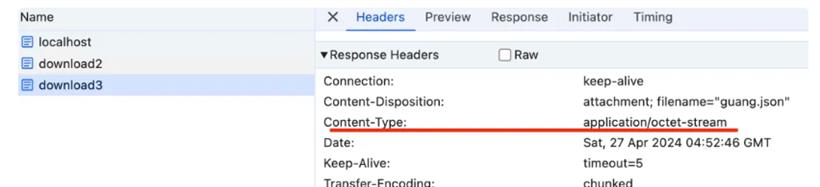
@Get('download3')
download3() {
const stream = fs.createReadStream('package.json');
return new StreamableFile(stream, {
type: 'text/plain',
disposition: `attachment; filename="guang.json"`
});
}