- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
JavaScript 在处理文件、二进制数据和数据转换时,提供了一系列的 API 和对象,比如File、Blob、FileReader、ArrayBuffer、Base64、Object URL 和 DataURL。每个概念在不同场景中都有重要作用。下面的内容我们将会详细学习每个概念及其在实际应用中的用法。接下来的内容中我们将来了解File和Blob这两个对象。
const blob = new Blob(blobParts, options);blobParts: 一个数组,包含将被放入 Blob 对象中的数据,可以是字符串、数组缓冲区(ArrayBuffer)、TypedArray、Blob 对象等。
const blob = new Blob(["Hello, world!"], { type: "text/plain" });
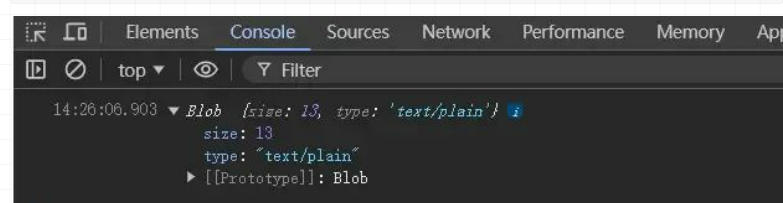
console.log(blob.type); // 输出 Blob 的 MIME 类型
const blob = new Blob(["Hello, world!"], { type: "text/plain" });
const partialBlob = blob.slice(0, 5);
2.text()blob.text().then((text) => {
console.log(text); // 输出 "Hello, world!"
});
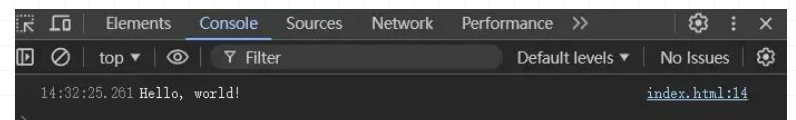
const blob = new Blob(["Hello, world!"], { type: "text/plain" });
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
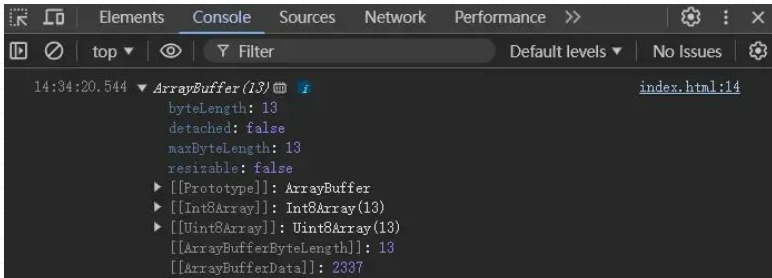
blob.arrayBuffer().then((buffer) => {
console.log(buffer);
});
const stream = blob.stream();
const blob = new Blob(["This is a test file."], { type: "text/plain" });
const url = URL.createObjectURL(blob); // 创建一个 Blob URL
const a = document.createElement("a");
a.href = url;
a.download = "test.txt";
a.click();
URL.revokeObjectURL(url); // 释放 URL 对象
当我们刷新浏览器的时候发现是可以自动给我们下载图片了: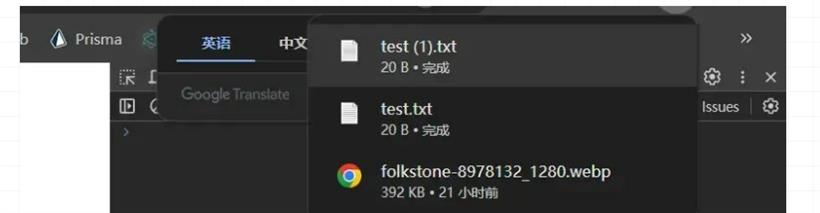
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append("file", blob, "example.txt");
fetch("/upload", {
method: "POST",
body: formData,
}).then((response) => {
console.log("File uploaded successfully");
});
3.读取图片或其他文件<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<input type="file" id="fileInput" accept="image/*" />
<div id="imageContainer"></div>
<script>
const fileInput = document.getElementById("fileInput");
const imageContainer = document.getElementById("imageContainer");
fileInput.addEventListener("change", function (event) {
const file = event.target.files[0];
if (file && file.type.startsWith("image/")) {
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = function (e) {
const img = document.createElement("img");
img.src = e.target.result;
img.style.maxWidth = "500px";
img.style.margin = "10px";
imageContainer.innerHTML = "";
imageContainer.appendChild(img);
};
reader.readAsDataURL(file);
} else {
alert("请选择一个有效的图片文件。");
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
const reader = new FileReader();
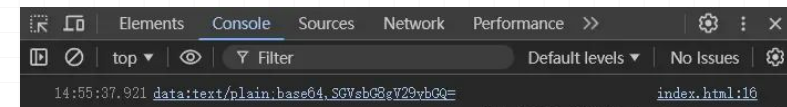
reader.onloadend = function () {
const base64data = reader.result;
console.log(base64data); // 输出 base64 编码的数据
};
reader.readAsDataURL(blob); // 将 Blob 读取为 base64
<input type="file" id="fileInput" />
<script>
document.getElementById("fileInput").addEventListener("change", (event) => {
const file = event.target.files[0];
console.log("文件名:", file.name);
console.log("文件类型:", file.type);
console.log("文件大小:", file.size);
});
</script>
最终输出结果如下图所示: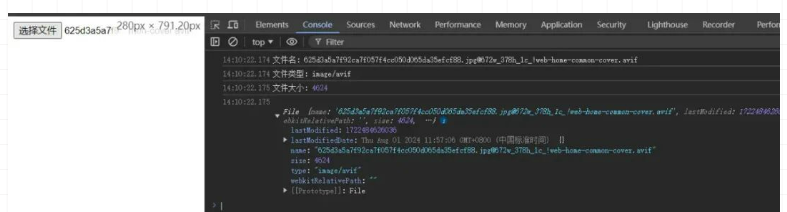
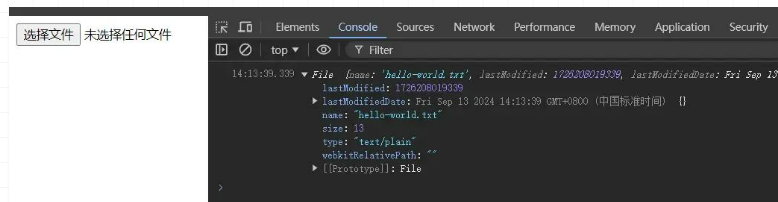
const file = new File(["Hello, world!"], "hello-world.txt", {
type: "text/plain",
});
console.log(file);
const blob = file.slice(0, 1024); // 获取文件的前 1024 个字节2.text(): 读取文件内容,并将其作为文本返回(这是 Blob 的方法,但可以用于 File 对象)。
file.text().then((text) => {
console.log(text); // 输出文件的文本内容
});
3.arrayBuffer(): 将文件内容读取为 ArrayBuffer(用于处理二进制数据)。file.arrayBuffer().then((buffer) => {
console.log(buffer); // 输出文件的 ArrayBuffer
});
4.stream(): 返回一个 ReadableStream 对象,可以通过流式读取文件内容。const stream = file.stream();总结
const file = new File(["Hello, world!"], "hello.txt", { type: "text/plain" });
console.log(file instanceof Blob); // true
二者在文件上传和二进制数据处理的场景中被广泛使用。Blob 更加通用,而 File 更专注于与文件系统的交互。