- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
Awaiter
话不多说,我们逐个研究下底层是咋玩的?
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
UseAwaitAsync();
Console.ReadLine();
}
static async Task<string> UseAwaitAsync()
{
var html = await Task.Run(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
var response = "<html><h1>博客园</h1></html>";
return response;
});
Console.WriteLine($"GetStringAsync 的结果:{html}");
return html;
}
}
那这段代码在底层是如何运作的呢?刚才也说到了asyncawait只是迷惑你的一种幻象,我们必须手握辟邪宝剑斩开幻象显真身,这里借助 ilspy 截图如下: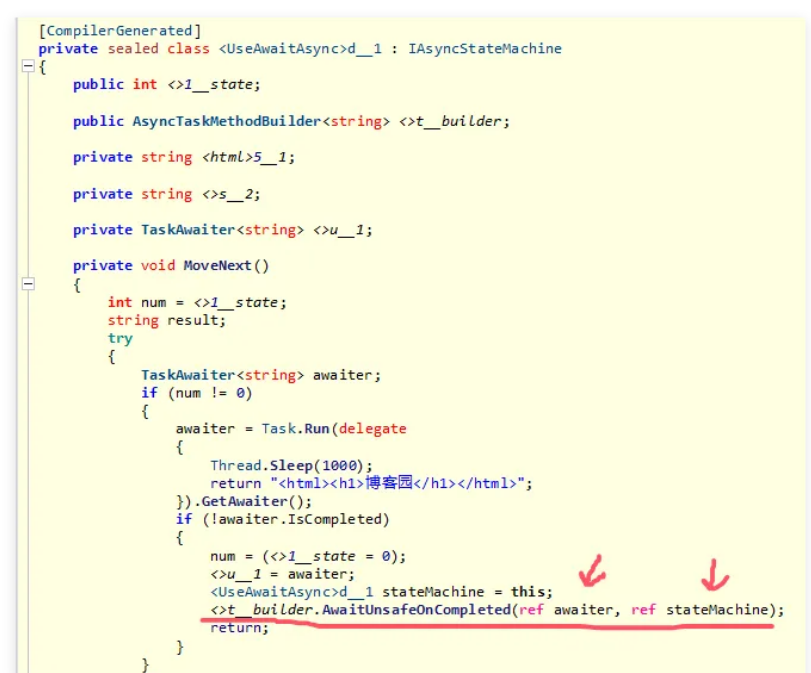
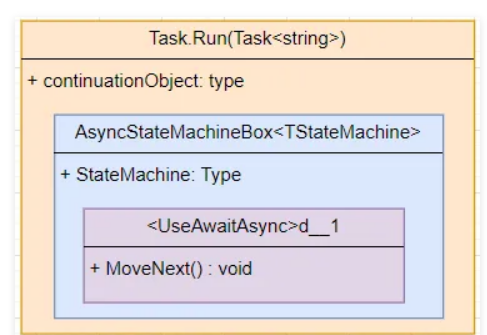
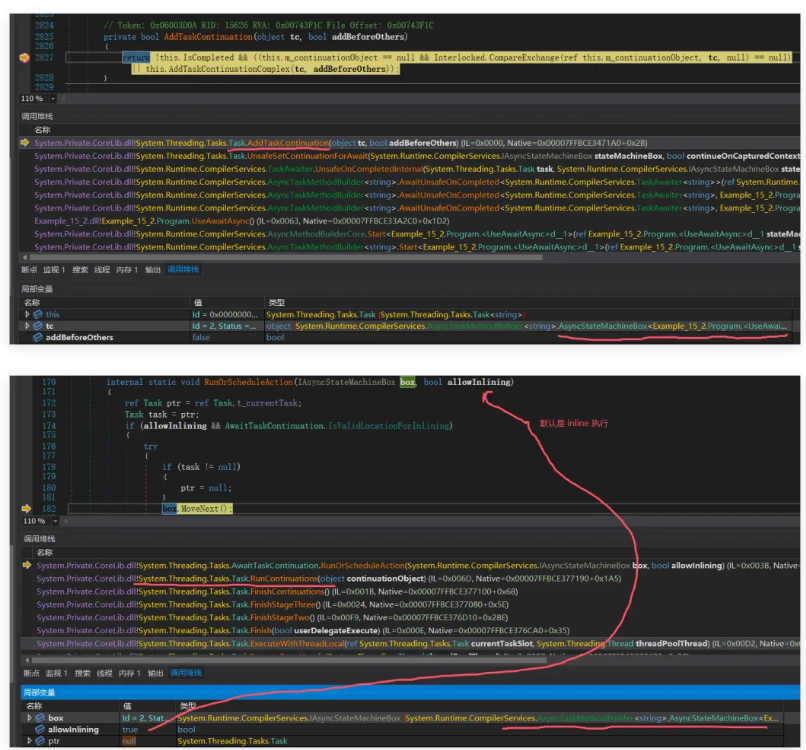
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
var html = await Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>{}, TaskCreationOptions.RunContinuationsAsynchronously);
2. ContinueWith internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
UseContinueWith();
Console.ReadLine();
}
static Task<string> UseContinueWith()
{
var query = Task.Run(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
var response = "<html><h1>博客园</h1></html>";
return response;
}).ContinueWith(t =>
{
var html = t.Result;
Console.WriteLine($"GetStringAsync 的结果:{html}");
return html;
});
return query;
}
}
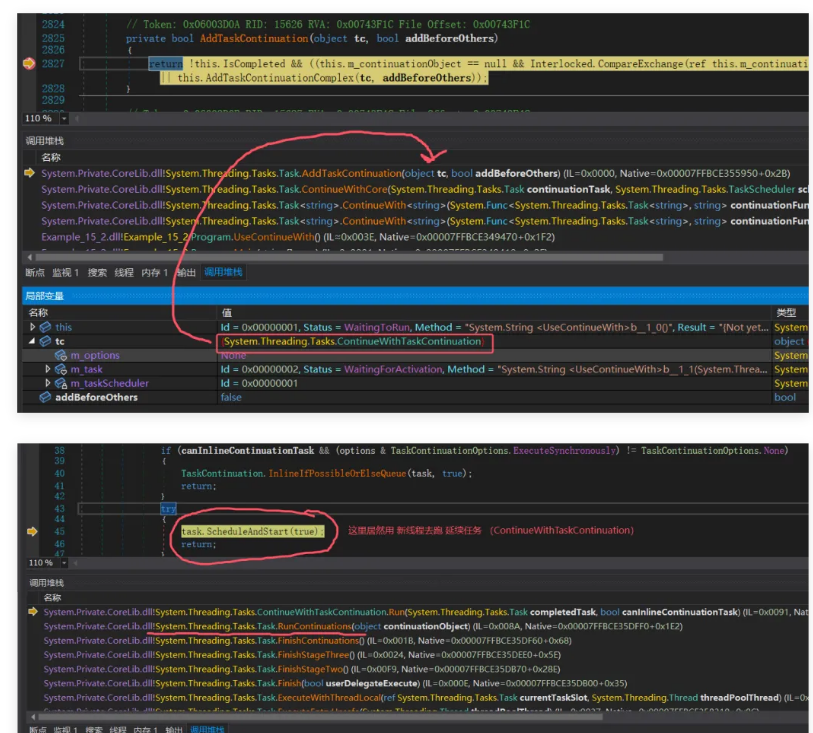
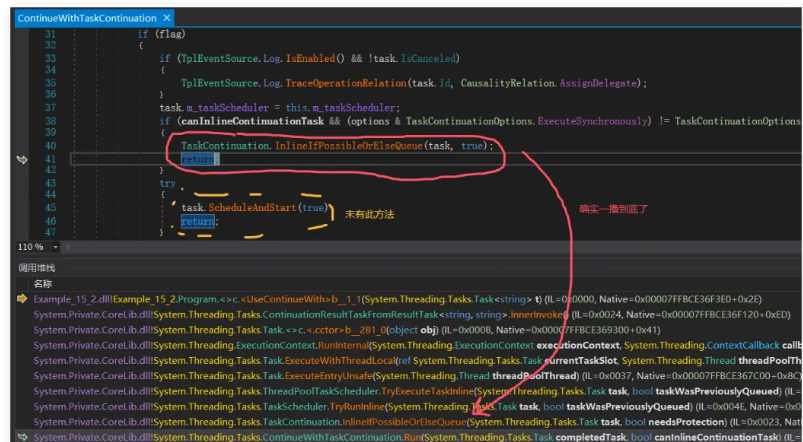
从卦代码看确实没有asyncawait简洁,那 ContinueWith 内部做了什么呢?感兴趣的朋友可以跟踪一下,本质上和 StateMachine 的玩法是一样的,都是借助 m_continuationObject 来实现延续,画个简图如下: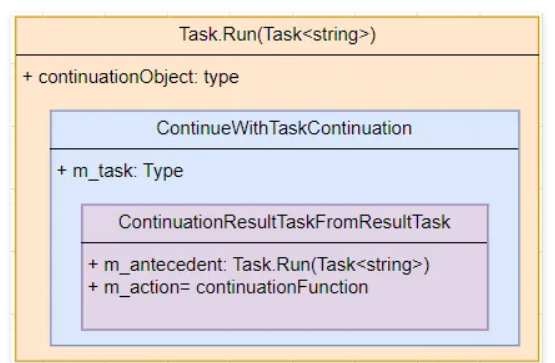
static Task<string> UseAwaiter()
{
var awaiter = Task.Run(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
var response = "<html><h1>博客园</h1></html>";
return response;
}).GetAwaiter();
awaiter.OnCompleted(() =>
{
var html = awaiter.GetResult();
Console.WriteLine($"UseAwaiter 的结果:{html}");
});
return Task.FromResult(string.Empty);
}
前面两种我配了图,这里没有理由不配了,哈哈,模型图如下: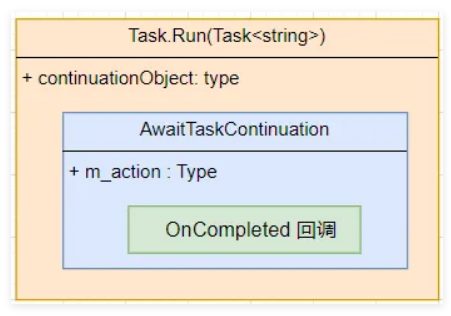

从卦中观察,它和StateMachine一样,默认都是 一撸到底 的方式。
private void RunContinuations(object continuationObject) // separated out of FinishContinuations to enable it to be inlined
{
bool canInlineContinuations =
(m_stateFlags & (int)TaskCreationOptions.RunContinuationsAsynchronously) == 0 &&
RuntimeHelpers.TryEnsureSufficientExecutionStack();
switch (continuationObject)
{
// Handle the single IAsyncStateMachineBox case. This could be handled as part of the ITaskCompletionAction
// but we want to ensure that inlining is properly handled in the face of schedulers, so its behavior
// needs to be customized ala raw Actions. This is also the most important case, as it represents the
// most common form of continuation, so we check it first.
case IAsyncStateMachineBox stateMachineBox:
AwaitTaskContinuation.RunOrScheduleAction(stateMachineBox, canInlineContinuations);
LogFinishCompletionNotification();
return;
// Handle the single Action case.
case Action action:
AwaitTaskContinuation.RunOrScheduleAction(action, canInlineContinuations);
LogFinishCompletionNotification();
return;
// Handle the single TaskContinuation case.
case TaskContinuation tc:
tc.Run(this, canInlineContinuations);
LogFinishCompletionNotification();
return;
// Handle the single ITaskCompletionAction case.
case ITaskCompletionAction completionAction:
RunOrQueueCompletionAction(completionAction, canInlineContinuations);
LogFinishCompletionNotification();
return;
}
}
卦中的 case 挺有意思的,除了本篇聊过的 TaskContinuation 和 IAsyncStateMachineBox 之外,还有另外两种 continuationObject,这里说一下 ITaskCompletionAction 是怎么回事,其实它是 Task.Result 的底层延续类型,所以大家应该能理解为什么 Task.Result 能唤醒,主要是得益于Task.m_continuationObject =completionAction 所致。 private bool SpinThenBlockingWait(int millisecondsTimeout, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var mres = new SetOnInvokeMres();
AddCompletionAction(mres, addBeforeOthers: true);
var returnValue = mres.Wait(Timeout.Infinite, cancellationToken);
}
private sealed class SetOnInvokeMres : ManualResetEventSlim, ITaskCompletionAction
{
internal SetOnInvokeMres() : base(false, 0) { }
public void Invoke(Task completingTask) { Set(); }
public bool InvokeMayRunArbitraryCode => false;
}
从卦中可以看到,其实就是把 ITaskCompletionAction 接口的实现类 SetOnInvokeMres 塞入了 Task.m_continuationObject 中,一旦Task执行完毕之后就会调用 Invoke() 下的 Set() 来实现事件唤醒。