- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
本来想研究一下 IL编织和反向补丁的相关harmony知识,看了下其实这些东西对 .NET高级调试 没什么帮助,所以本篇就来说一些比较实用的反射工具包吧。
//
// Summary:
// An annotation that specifies a method, property or constructor to patch
//
// Parameters:
// typeName:
// The full name of the declaring class/type
//
// methodName:
// The name of the method, property or constructor to patch
//
// methodType:
// The HarmonyLib.MethodType
public HarmonyPatch(string typeName, string methodName, MethodType methodType = MethodType.Normal)
{
info.declaringType = AccessTools.TypeByName(typeName);
info.methodName = methodName;
info.methodType = methodType;
}
现在的好消息是你也可以直接使用 AccessTools,使用方式和 HarmonyPatch的构造函数注入方式几乎一摸一样, 为了方便演示,我们还是用 Thread 来跟大家聊一聊,我用大模型生成了一批例子。参考如下: static void Main(string[] args)
{
var thread = new Thread(() => { });
thread.Start();
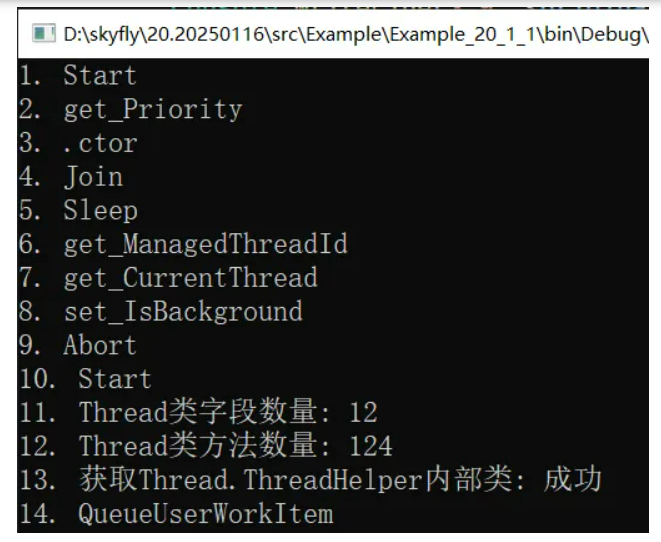
//1. 反射出 Thread.Start 方法。
var original1 = AccessTools.Method(typeof(Thread), "Start", new Type[] { });
Console.WriteLine($"1. {original1.Name}");
//2. 获取 Thread.Priority 属性
var original2 = AccessTools.PropertyGetter(typeof(Thread), "Priority");
Console.WriteLine($"2. {original2.Name}");
//3. 获取 Thread(ThreadStart start) 构造函数信息
var original3 = AccessTools.Constructor(typeof(Thread), new Type[] { typeof(ThreadStart) });
Console.WriteLine($"3. {original3.Name}");
//4. 获取 Thread.Join() 方法
var original4 = AccessTools.Method(typeof(Thread), "Join", new Type[] { });
Console.WriteLine($"4. {original4.Name}");
//5. 获取 Thread.Sleep(int) 方法
var original5 = AccessTools.Method(typeof(Thread), "Sleep", new Type[] { typeof(int) });
Console.WriteLine($"5. {original5.Name}");
//6. 获取 Thread.ManagedThreadId 属性
var original6 = AccessTools.PropertyGetter(typeof(Thread), "ManagedThreadId");
Console.WriteLine($"6. {original6.Name}");
//7. 获取 Thread.CurrentThread 静态属性
var original7 = AccessTools.PropertyGetter(typeof(Thread), "CurrentThread");
Console.WriteLine($"7. {original7.Name}");
//8. 获取 Thread.IsBackground 属性设置器
var original8 = AccessTools.PropertySetter(typeof(Thread), "IsBackground");
Console.WriteLine($"8. {original8.Name}");
//9. 获取 Thread.Abort() 方法 (已过时,但仍可获取)
var original9 = AccessTools.Method(typeof(Thread), "Abort", new Type[] { });
Console.WriteLine($"9. {original9?.Name ?? "null"}");
//10. 获取 Thread.Start(object) 方法 (参数化线程启动)
var original10 = AccessTools.Method(typeof(Thread), "Start", new Type[] { typeof(object) });
Console.WriteLine($"10. {original10?.Name ?? "null"}");
//11. 获取 Thread 类的所有字段
var allFields = AccessTools.GetDeclaredFields(typeof(Thread));
Console.WriteLine($"11. Thread类字段数量: {allFields.Count}");
//12. 获取 Thread 类的所有方法
var allMethods = AccessTools.GetDeclaredMethods(typeof(Thread));
Console.WriteLine($"12. Thread类方法数量: {allMethods.Count}");
//13. 获取 Thread 类的内部类 "StartHelper"
var threadHelperType = AccessTools.Inner(typeof(Thread), "StartHelper");
Console.WriteLine($"13. 获取Thread.ThreadHelper内部类: {(threadHelperType != null ? "成功" : "失败")}");
//14. 获取 ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem 方法
var original15 = AccessTools.Method(typeof(ThreadPool), "QueueUserWorkItem",
new Type[] { typeof(WaitCallback) });
Console.WriteLine($"14. {original15.Name}");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var thread = new Thread(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("5. 线程执行完成");
});
// 使用 Traverse 访问线程内部状态
var traverse = Traverse.Create(thread);
// 1. 获取线程的委托 (_start 字段)
var startDelegate = traverse.Field("_startHelper").Field("_start").GetValue<ThreadStart>();
Console.WriteLine($"1. 线程委托方法: {startDelegate?.Method.Name ?? "null"}");
// 2. 获取线程的执行状态 (_threadState 字段)
var threadState = traverse.Field("_threadState").GetValue<int>();
Console.WriteLine($"2. 线程状态: {threadState} (0=未启动, 1=运行中, 2=停止)");
// 3. 设置线程的 IsBackground 属性
traverse.Property("IsBackground").SetValue(true);
Console.WriteLine($"3. 设置后台线程: {thread.IsBackground}");
// 4. 调用 Start 方法
traverse.Method("Start").GetValue();
Console.WriteLine("4. 调用 Start() 方法启动线程");
Console.ReadLine();
}

internal classProgram
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Harmony.DEBUG = true;
var harmony = new Harmony("com.example.threadhook");
harmony.PatchAll();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
[HarmonyPatch(typeof(Thread), "Start", new Type[] { typeof(object) })]
publicclassThreadStartHook
{
public static void Prefix(Thread __instance)
{
}
}

### Harmony id=com.example.threadhook, version=2.3.6.0, location=D:\skyfly\20.20250116\src\Example\Example_20_1_1\bin\Debug\net8.0\0Harmony.dll, env/clr=8.0.13, platform=Win32NT ### Started from static System.Void Example_20_1_1.Program::Main(System.String[] args), location D:\skyfly\20.20250116\src\Example\Example_20_1_1\bin\Debug\net8.0\Example_20_1_1.dll ### At 2025-05-21 05.43.09 ### Patch: System.Void System.Threading.Thread::Start(System.Object parameter) ### Replacement: static System.Void System.Threading.Thread::System.Threading.Thread.Start_Patch1(System.Threading.Thread this, System.Object parameter) IL_0000: ldarg.0 IL_0001: call static System.Void Example_20_1_1.ThreadStartHook::Prefix(System.Threading.Thread __instance) IL_0006: // start original IL_0006: ldarg.0 IL_0007: ldarg.1 IL_0008: ldc.i4.1 IL_0009: ldc.i4.0 IL_000A: call System.Void System.Threading.Thread::Start(System.Object parameter, System.Boolean captureContext, System.Boolean internalThread) IL_000F: // end original IL_000F: ret DONE其实这些日志底层都是通过 FileLog 来写的,万幸的是它也开了口子给开发者,见下面参考代码。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Harmony.DEBUG = true;
var harmony = new Harmony("com.example.threadhook");
harmony.PatchAll();
FileLog.Debug("hello world!");
Console.ReadLine();
}

