一:背景
1. 讲故事
在windows平台上,相信很多人都知道.NET异步机制是借助了Windows自带的 IO完成端口 实现的异步交互,那在 Linux 下.NET 又是怎么玩的呢?主要还是传统的 select,poll,epoll 的IO多路复用,在 coreclr源代码中我们都能找到它们的影子。
select & poll
在平台适配层的 pal.cpp 文件中,有这样的一句话。
#if HAVE_POLL
#include <poll.h>
#else
#include "pal/fakepoll.h"
#endif // HAVE_POLL
简而言之就是在不支持 poll 的linux版本中使用 select(fakepoll) 模拟,参考代码如下:
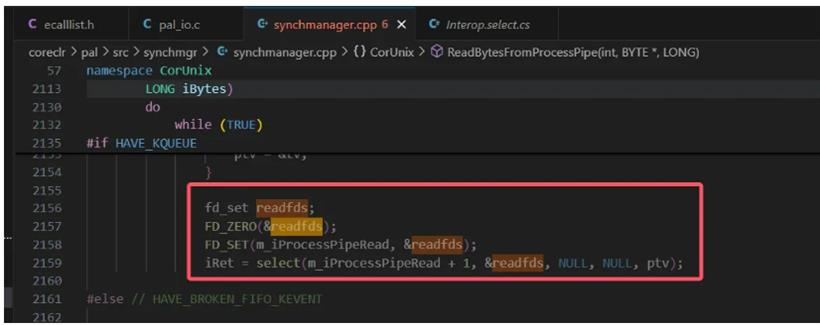
2. epoll
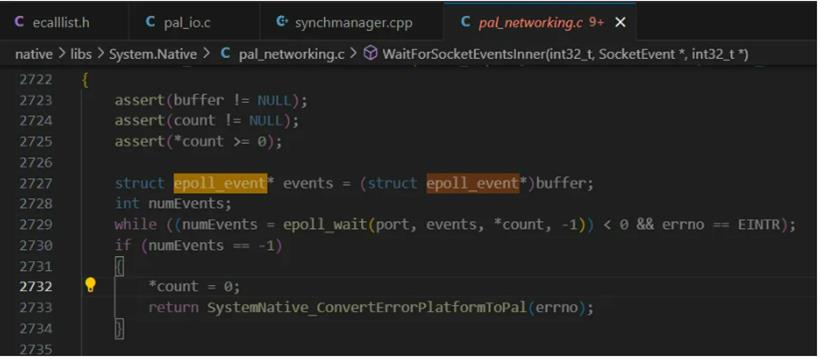
同样的在 linux 中你也会发现很多,截图如下:
 二:select IO多路复用
1. select 解读
二:select IO多路复用
1. select 解读
在没有 select 之前,我们需要手工管理多句柄的收发,在使用select IO多路复用技术之后,这些多句柄管理就由用户转交给linux系统了,这个也可以从核心的 select 函数看出。
# 堆代码 duidaima.com
int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds, fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);
readfds,writefds,exceptfds
这三个字段依次监视着哪些句柄已成可读状态,哪些句柄已成可写状态,哪些句柄已成异常状态,那技术上是如何实现的呢?在libc 中定义了一个 bit 数组,刚好文件句柄fd值作为 bit数组的索引,linux 在内核中只需要扫描 __fds_bits 中哪些位为1 即可找到需要监控的句柄。
/* fd_set for select and pselect. */
typedef struct
{
/* XPG4.2 requires this member name. Otherwise avoid the name
from the global namespace. */
#ifdef __USE_XOPEN
__fd_mask fds_bits[__FD_SETSIZE / __NFDBITS];
# define __FDS_BITS(set) ((set)->fds_bits)
#else
__fd_mask __fds_bits[__FD_SETSIZE / __NFDBITS];
# define __FDS_BITS(set) ((set)->__fds_bits)
#endif
} fd_set;
nfds,timeout
为了减少扫描范围,提高程序性能,需要用户指定一个最大的扫描值到 nfds 上。后面的timeout即超时时间。
2. select 的一个小例子
说了再多还不如一个例子有说服力,我们使用 select 机制对 Console 控制台句柄 (STDIN_FILENO) 进行监控,一旦有数据进来立马输出,参考代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
fd_set readfds;
struct timeval timeout;
char buf[256];
printf("Enter text (press Ctrl+D to end):\n");
while (1)
{
FD_ZERO(&readfds);
FD_SET(STDIN_FILENO, &readfds);
timeout.tv_sec = 5; // 5秒超时
timeout.tv_usec = 0;
int ready = select(STDIN_FILENO + 1, &readfds, NULL, NULL, &timeout);
if (ready == -1)
{
perror("select");
break;
}
elseif (ready == 0)
{
printf("\nTimeout (5秒无输入).\n");
break;
}
elseif (FD_ISSET(STDIN_FILENO, &readfds))
{
// 使用 fgets 逐行读取
if (fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin) != NULL)
{
printf("You entered: %s", buf); // 输出整行(包含换行符)
}
else
{
printf("\nEnd of input (Ctrl+D pressed).\n");
break;
}
}
}
return0;
}
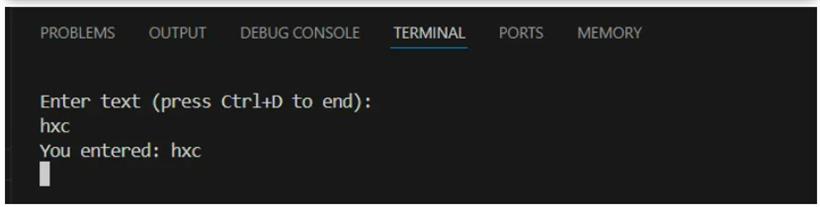
稍微解释下代码逻辑。
/* Standard file descriptors. */
#define STDIN_FILENO 0 /* Standard input. */
#define STDOUT_FILENO 1 /* Standard output. */
#define STDERR_FILENO 2 /* Standard error output. */
.将 STDIN_FILENO=0 塞入到可读句柄监控 (readfds) 中。
.数据进来之后 select 被唤醒,执行后续逻辑。
.通过 FD_ISSET 判断 bit=0 的位置(STDIN_FILENO)是否可用,可用的话读取数据。
如果大家对 select 底层代码感兴趣,可以看下 linux 的 do_select 简化实现,大量的遍历逻辑(bit)。
static noinline_for_stack int do_select(int n, fd_set_bits *fds, struct timespec64 *end_time)
{
for (;;) {
unsignedlong *rinp, *routp, *rexp, *inp, *outp, *exp;
bool can_busy_loop = false;
inp = fds->in; outp = fds->out; exp = fds->ex;
rinp = fds->res_in; routp = fds->res_out; rexp = fds->res_ex;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++rinp, ++routp, ++rexp) {
in = *inp++; out = *outp++; ex = *exp++;
all_bits = in | out | ex;
for (j = 0; j < BITS_PER_LONG; ++j, ++i, bit <<= 1) {
mask = select_poll_one(i, wait, in, out, bit,busy_flag);
if ((mask & POLLIN_SET) && (in & bit)) {
res_in |= bit;
retval++;
wait->_qproc = NULL;
}
if ((mask & POLLOUT_SET) && (out & bit)) {
res_out |= bit;
retval++;
wait->_qproc = NULL;
}
if ((mask & POLLEX_SET) && (ex & bit)) {
res_ex |= bit;
retval++;
wait->_qproc = NULL;
}
}
}
if (!poll_schedule_timeout(&table, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, to, slack))
timed_out = 1;
}
return retval;
}
三:epoll IO多路复用
1. epoll 解读
现在主流的软件(Redis,Nigix) 都是采用 epoll,它解决了select低效的遍历,毕竟数组最多支持1024个bit位,一旦句柄过多会影响异步读取的效率。epoll的底层借助了。
红黑树:对句柄进行管理,复杂度为 O(logN)。
就绪队列:一旦句柄变得可读或可写,内核会直接将句柄送到就绪队列。
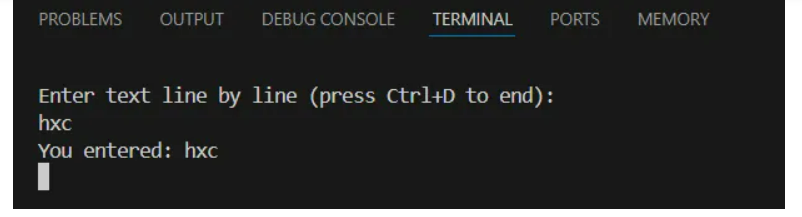
libc中使用 epoll_wait 函数监视着就绪队列,一旦有数据立即提取,复杂度 O(1),其实这个机制和 Windows 的IO完成端口 已经很靠近了,最后配一下参考代码。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define MAX_EVENTS 10 // 最大监听事件数
#define TIMEOUT_MS 5000 // epoll_wait 超时时间(毫秒)
int main()
{
int epoll_fd, nfds; // epoll 文件描述符和返回的事件数
struct epoll_event ev, events[MAX_EVENTS];// epoll 事件结构体
char buf[256];
// 创建 epoll 实例
epoll_fd = epoll_create1(0);
if (epoll_fd == -1)
{
perror("epoll_create1");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 配置并添加标准输入到 epoll 监听
ev.events = EPOLLIN; // 监听文件描述符的可读事件(输入)
ev.data.fd = STDIN_FILENO; // 监听标准输入(文件描述符 0)
if (epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, STDIN_FILENO, &ev) == -1)
{
perror("epoll_ctl: STDIN_FILENO");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Enter text line by line (press Ctrl+D to end):\n");
// 主循环:监听事件
while (1)
{
// 等待事件发生或超时
nfds = epoll_wait(epoll_fd, events, MAX_EVENTS, TIMEOUT_MS);
if (nfds == -1)
{
perror("epoll_wait");
break;
}
elseif (nfds == 0)
{
printf("\nTimeout (5秒无输入).\n");
break;
}
// 处理所有触发的事件
for (int n = 0; n < nfds; ++n)
{
if (events[n].data.fd == STDIN_FILENO)
{
// 使用 fgets 逐行读取输入
if (fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin) != NULL)
{
printf("You entered: %s", buf);
}
else
{
// 输入结束(用户按下 Ctrl+D)
printf("\nEnd of input (Ctrl+D pressed).\n");
break;
}
}
}
}
close(epoll_fd);
return0;
}
 四:总结
四:总结
说了这么多,文尾总结下目前主流的 epoll 和 iocp 各自的特点。
|
特性
|
epoll (Linux)
|
IOCP (Windows)
|
|
模型
|
事件驱动 (Reactor)
|
完成端口 (Proactor)
|
|
核心思想
|
通知可读写事件
|
通知I/O操作完成
|
|
适用场景
|
高并发网络编程
|
高并发I/O操作
|
|
编程复杂度
|
较低
|
较高
|
|
网络I/O性能
|
极佳(百万级连接)
|
优秀
|
|
磁盘I/O支持
|
有限
|
完善
|
|
CPU利用率
|
高
|
中
|
|
内存开销
|
低
|
中
|
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号




