- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
在玩游戏的时候,我们必须得遵守游戏的规则,那么游戏才能够进行下去。同理我们在使用任何语言开发的时候,无一例外,都要遵守该语言的语法。在使用任何框架的时候,我们都必须遵守框架的规则。在React Hooks中,也有诸多的规则,那我们就一起来看看这些规则、技巧以及正确的使用姿势。
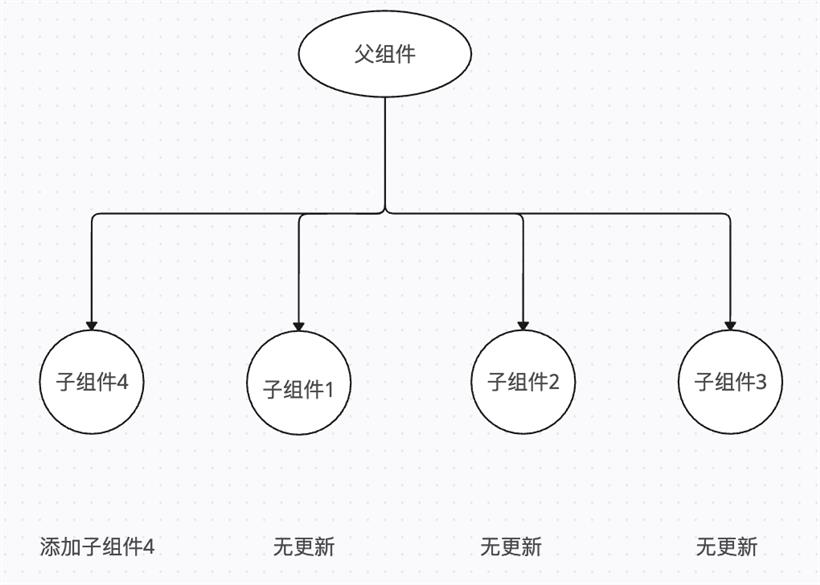
这是个基本入门的问题了,也是React Hooks的首要规则,这是因为React Hooks 是以单向循环链表的形式存储,即是有序的。循环是为了从最后一个节点移到一个节点的时候,只需通过next一步就可以拿到第一个节点,而不需要一层层回溯。React Hooks的执行,分为 mount 和 update 阶段,在mount阶段的时候,通过mountWorkInProgressHook() 创建各个hooks (如useState, useMemo, useEffect, useCallback等),并且将当前hook添加到表尾。
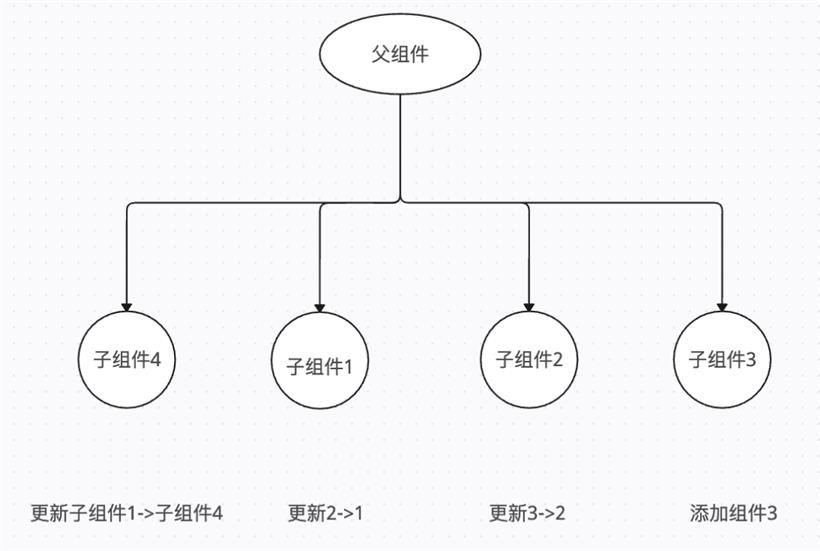
在update阶段,在获取或者更新hooks值的时候,会先获取当前hook的状态,hook.memoizedState,并且是按照顺序或读写更新hook,若在条件或者循环语句使用hooks,那么在更新阶段,若增加或者减少了某个hook,hooks的数量发生变化,而React是按照顺序,通过next读取下一个hook,则导致后面的hooks和挂载阶段对应不上,发生读写错值的情况,从而引发bug。
我们可以看看useState在mount阶段的源码:function mountState<S>(
initialState: (() => S) | S,
): [S, Dispatch<BasicStateAction<S>>] {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === 'function') {
// $FlowFixMe: Flow doesn't like mixed types
initialState = initialState();
}
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
const queue: UpdateQueue<S, BasicStateAction<S>> = {
pending: null,
lanes: NoLanes,
dispatch: null,
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer,
lastRenderedState: (initialState: any),
};
hook.queue = queue;
const dispatch: Dispatch<
BasicStateAction<S>,
> = (queue.dispatch = (dispatchSetState.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber,
queue,
): any));
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}
useCallback在mount阶段的源码:function mountCallback<T>(callback: T, deps: Array<mixed> | void | null): T {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
hook.memoizedState = [callback, nextDeps];
return callback;
}
然后mountWorkInProgressHook的源码如下:function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
// This is the first hook in the list
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
// Append to the end of the list
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
其他hooks的源码也是类似,以mountWorkInProgressHook创建当前hooks, 并且把hook的数据存到hook.memoizedState上,而在update阶段,则是依次读取hooks链表的memoizedState属性来获取状态 (数据)。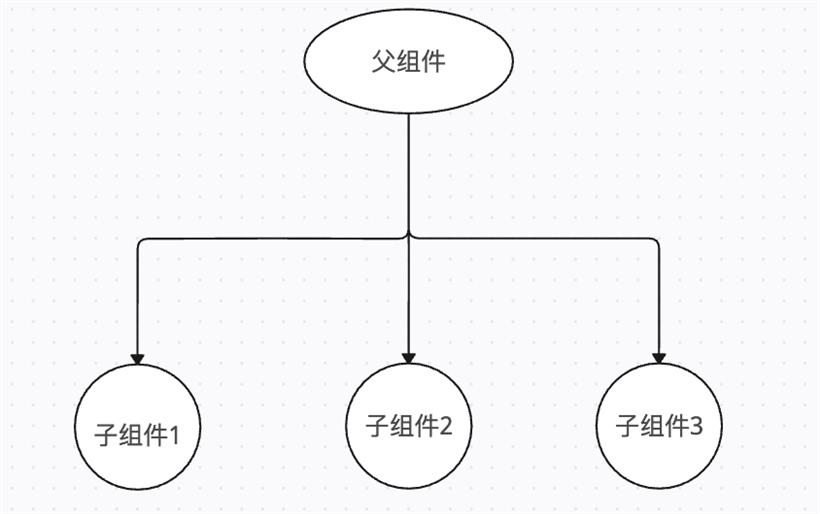
在react中,当我们setState之后,若值发生变化,则会重新render当前组件以及其子组件 (默认情况下),在必要的时候,我可使用memo (class组件则对应shouldComponentUpdate、PureComponent)进行优化,来减少无效渲染。memo是一个高阶组件,接受一个组件作为参数,并返回一个原组件为基础的新组件,而在memo内部,则会使用Object.is来遍历对比新旧props是否发生变化,以决定是否需要重新render。
function updateMemo<T>(
nextCreate: () => T,
deps: Array<mixed> | void | null,
): T {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
const nextDeps = deps === undefined ? null : deps;
const prevState = hook.memoizedState;
if (prevState !== null) {
// Assume these are defined. If they're not, areHookInputsEqual will warn.
if (nextDeps !== null) {
const prevDeps: Array<mixed> | null = prevState[1];
if (areHookInputsEqual(nextDeps, prevDeps)) {
return prevState[0];
}
}
}
const nextValue = nextCreate();
hook.memoizedState = [nextValue, nextDeps];
return nextValue;
}
useImperativeHandle (forwardRef)
我们会遇到这样的场景:某个组件想要暴露一些方法,来供外部组件来调用。例如我们在开发form表单的时候,就需要把设置表单值、重置值、提交等方法暴露给外部使用。会有如下代码:import { forwardRef } from 'react';
const Form = forwardRef(function MyForm(props, ref) {
useImperativeHandle(ref, () => {
return {
// ... 你的方法 ...
};
}, []);
return (
<div {...props} ref={ref}>
<input type="text" />
</div>
);
});
在组件外部,只需传入ref属性,即可调用form组件提供的方法。function dispatchSetState<S, A>(
fiber: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<S, A>,
action: A,
)
// 计算更新优先级
const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber);
const update: Update<S, A> = {
lane,
action,
hasEagerState: false,
eagerState: null,
next: (null: any),
};
// 判断当前fiber是否正在处于更新中,若是则把当前更新进行排队
if (isRenderPhaseUpdate(fiber)) {
enqueueRenderPhaseUpdate(queue, update);
} else {
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
if (
fiber.lanes === NoLanes &&
(alternate === null || alternate.lanes === NoLanes)
) {
const lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer;
if (lastRenderedReducer !== null) {
let prevDispatcher;
try {
const currentState: S = (queue.lastRenderedState: any);
const eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action);
update.hasEagerState = true;
update.eagerState = eagerState;
// 若新旧状态无变化,则直接返回,啥也不干
if (is(eagerState, currentState)) {
enqueueConcurrentHookUpdateAndEagerlyBailout(fiber, queue, update);
return;
}
} catch (error) {
// Suppress the error. It will throw again in the render phase.
} finally {
if (__DEV__) {
ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = prevDispatcher;
}
}
}
}
const root = enqueueConcurrentHookUpdate(fiber, queue, update, lane);
if (root !== null) {
const eventTime = requestEventTime();
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(root, fiber, lane, eventTime);
entangleTransitionUpdate(root, queue, lane);
}
}
markUpdateInDevTools(fiber, lane, action);
}
scheduleUpdateOnFiber则是react内部的核心调度方法,源码如下:
export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(
root: FiberRoot,
fiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
eventTime: number,
) {
checkForNestedUpdates();
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
// Mark that the root has a pending update.
markRootUpdated(root, lane, eventTime);
if (
(executionContext & RenderContext) !== NoLanes &&
root === workInProgressRoot
) {
warnAboutRenderPhaseUpdatesInDEV(fiber);
// Track lanes that were updated during the render phase
workInProgressRootRenderPhaseUpdatedLanes = mergeLanes(
workInProgressRootRenderPhaseUpdatedLanes,
lane,
);
} else {
// This is a normal update, scheduled from outside the render phase. For
// example, during an input event.
if (enableUpdaterTracking) {
if (isDevToolsPresent) {
addFiberToLanesMap(root, fiber, lane);
}
}
warnIfUpdatesNotWrappedWithActDEV(fiber);
if (enableProfilerTimer && enableProfilerNestedUpdateScheduledHook) {
if (
(executionContext & CommitContext) !== NoContext &&
root === rootCommittingMutationOrLayoutEffects
) {
if (fiber.mode & ProfileMode) {
let current = fiber;
while (current !== null) {
if (current.tag === Profiler) {
const {id, onNestedUpdateScheduled} = current.memoizedProps;
if (typeof onNestedUpdateScheduled === 'function') {
onNestedUpdateScheduled(id);
}
}
current = current.return;
}
}
}
}
if (enableTransitionTracing) {
const transition = ReactCurrentBatchConfig.transition;
if (transition !== null) {
if (transition.startTime === -1) {
transition.startTime = now();
}
addTransitionToLanesMap(root, transition, lane);
}
}
if (root === workInProgressRoot) {
if (
deferRenderPhaseUpdateToNextBatch ||
(executionContext & RenderContext) === NoContext
) {
workInProgressRootInterleavedUpdatedLanes = mergeLanes(
workInProgressRootInterleavedUpdatedLanes,
lane,
);
}
if (workInProgressRootExitStatus === RootSuspendedWithDelay) {
markRootSuspended(root, workInProgressRootRenderLanes);
}
}
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);
if (
lane === SyncLane &&
executionContext === NoContext &&
(fiber.mode & ConcurrentMode) === NoMode &&
// Treat `act` as if it's inside `batchedUpdates`, even in legacy mode.
!(__DEV__ && ReactCurrentActQueue.isBatchingLegacy)
) {
resetRenderTimer();
flushSyncCallbacksOnlyInLegacyMode();
}
}
}
我们继续追踪ensureRootIsScheduled方法,此源码就省略了,然后会调用scheduleMicrotask方法,源码如下:export const scheduleMicrotask: any =
typeof queueMicrotask === 'function'
? queueMicrotask
: typeof localPromise !== 'undefined'
? callback =>
localPromise
.resolve(null)
.then(callback)
.catch(handleErrorInNextTick)
: scheduleTimeout;
会优先使用queueMicrotask来添加一个微任务,此方法是一个标准的web api,可以不借助Promise来往微任务队列里面添加一个任务。若当前环境不支持queueMicrotask,则依次优先使用Promise,setTimeout。这与vue的nextTick源码实现是基本一致的。通过以上的分析,我们可以大致了解了react异步批量更新的调度过程。function mountRef<T>(initialValue: T): {|current: T|} {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const ref = {current: initialValue};
hook.memoizedState = ref;
return ref;
}
function updateRef<T>(initialValue: T): {|current: T|} {
const hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
return hook.memoizedState;
}
可以看到,代码实现非常简单,创建一个ref对象,然后挂载到hook.memoizedState, 我们在修改的时候,就是直接修改ref.current。useRef其实就是提供一个稳定的变量,在组件的整个生命周期都是持续存在且是同一个引用。function mountRef<T>(initialValue: T): {|current: T|} {
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
const ref = {current: initialValue};
hook.memoizedState = ref;
return ref;
}
mount在整个组件生命周期,只会触发一次,因此只会创建一次。然后这也是为什么要创建一个对象,而对象上近仅创建一个current属性来存储数据,正是为了让开发者在整个生命周期,拿到的始终是同一个引用,可以把它想象成当前组件域下的一个全局变量了,而修改数据仅仅在这个引用上的current属性修改。简单思考
为什么vue composition api 的 setup函数不存在闭包引用导致的setTimeout回调函数中拿到的是旧值呢?
因为setup 函数只会执行一次,返回一个render函数,在更新阶段,始终执行的是render函数,因此setTimeout回调函数的闭包引用中引用的是setup函数的状态,不会发生改变。而react中,整个组件函数就是一个render函数,所以引用的状态在每次render的时候都是不同的变量。这是它们的本质区别。