- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
<template>
<ChildDemo />
</template>
<script setup>
import ChildDemo from "./child.vue";
import { ref, provide } from "vue";
// 提供响应式的值
const count = ref(0);
provide("count", count);
</script>
在父组件中使用provide为后代组件注入一个count响应式变量。<template> <GrandChild /> </template> <script setup> import GrandChild from "./grand-child.vue"; </script>从上面的代码可以看到在子组件中什么事情都没做,只渲染了孙子组件。我们再来看看孙子组件grand-child.vue,代码如下:
<script setup>
import { inject } from "vue";
// 堆代码 duidaima.com
// 注入响应式的值
const count = inject("count");
console.log("inject count is:", count);
</script>
从上面的代码可以看到在孙子组件中使用inject函数拿到了父组件中注入的count响应式变量。我们先来debug看看provide函数的代码,给父组件中的provide函数打个断点,如下图:
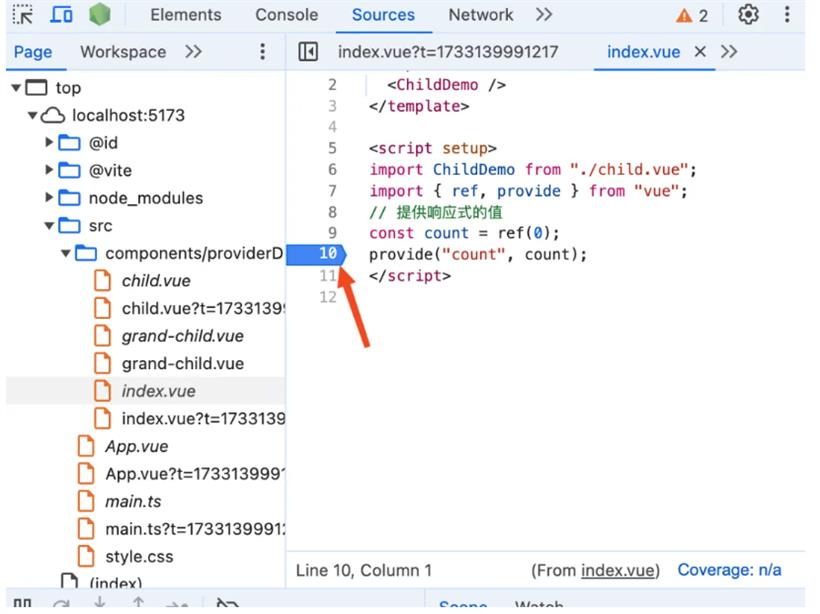
刷新页面,此时代码将会停留在断点处。让断点走进provide函数,代码如下:
function provide(key, value) {
if (!currentInstance) {
if (!!(process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production")) {
warn$1(`provide() can only be used inside setup().`);
}
} else {
let provides = currentInstance.provides;
const parentProvides = currentInstance.parent && currentInstance.parent.provides;
if (parentProvides === provides) {
provides = currentInstance.provides = Object.create(parentProvides);
}
provides[key] = value;
}
}
首先判断currentInstance是否有值,如果没有就说明当前没有vue实例,也就是说当前调用provide函数的地方是不在setup函数中执行的,然后给出警告provide只能在setup中使用。然后走进else逻辑中,首先从当前vue实例中取出存的provides属性对象。并且通过currentInstance.parent.provides拿到父组件vue实例中的provides属性对象。const instance: ComponentInternalInstance = {
uid: uid++,
vnode,
type,
parent,
provides: parent ? parent.provides : Object.create(appContext.provides),
// ...省略
}
从上面的代码可以看到如果有父组件,那么创建子组件实例的时候就直接使用父组件的provides属性对象。所以这里在provide函数中需要判断if (parentProvides === provides),如果相等说明当前父组件和子组件是共用的同一个provides属性对象。此时如果子组件调用了provide函数,说明子组件需要创建自己的provides属性对象。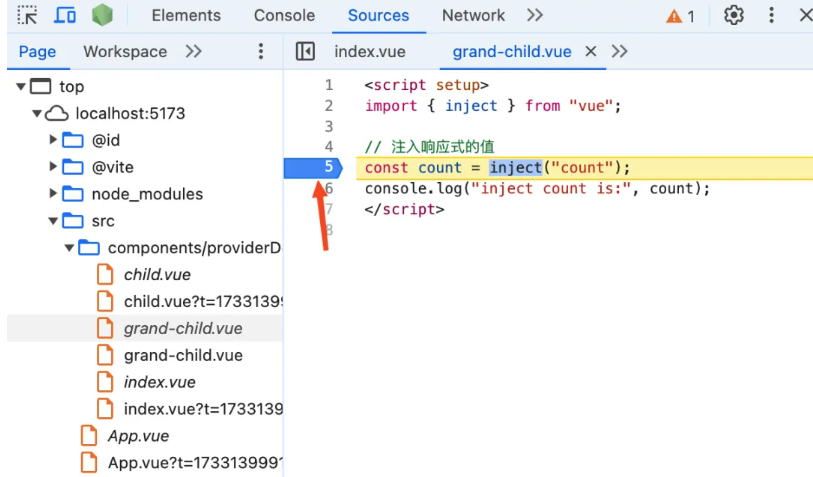
export function inject(
key: InjectionKey<any> | string,
defaultValue?: unknown,
treatDefaultAsFactory = false,
) {
// fallback to `currentRenderingInstance` so that this can be called in
// a functional component
const instance = currentInstance || currentRenderingInstance
//堆代码 duidaima.com
// also support looking up from app-level provides w/ `app.runWithContext()`
if (instance || currentApp) {
const provides = currentApp
? currentApp._context.provides
: instance
? instance.parent == null
? instance.vnode.appContext && instance.vnode.appContext.provides
: instance.parent.provides
: undefined
if (provides && key in provides) {
return provides[key]
} else if (arguments.length > 1) {
return treatDefaultAsFactory && isFunction(defaultValue)
? defaultValue.call(instance && instance.proxy)
: defaultValue
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(`injection "${String(key)}" not found.`)
}
} else if (__DEV__) {
warn(`inject() can only be used inside setup() or functional components.`)
}
}
首先拿到当前渲染的vue实例赋值给本地变量instance。接着使用if (instance || currentApp)判断当前是否有vue实例,如果没有看看有没有使用app.runWithContext手动注入了上下文,如果注入了那么currentApp就有值。