- 联系我们
- duidaima.com 版权声明
- 闽ICP备2020021581号
-
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
 闽公网安备 35020302035485号
闽公网安备 35020302035485号
2023年对于程序员来说是个艰难的一年,裁员潮从大西洋海岸的硅谷一直刮到了太平洋海岸的BAT巨头。大量被裁人员的疯狂涌入也让2023年的金三银四招聘季不再像往年那么熠熠生辉。作为前端开发者的我们,有躺平资本的可以选择躺平,没躺平资本的只能选择卷。今天我汇总了2023年最新的前端面试题,希望对于只能加入内卷行列的前端开发有所帮助。
hello(); // Prints "Hello world! " even though the function is called "before" declaration
function hello(){
console.log("Hello world! ");
}
对于变量,hoisting有点不同,它在定义变量范围之前,它们为 undefined 。console.log(dog); var dog = "Spot";结果是:
undefined这可能会令人惊讶,因为您可能预计它会导致错误。如果你声明一个函数或变量,无论你在哪里声明它,它总是被移动到范围的顶部。
/* 堆代码 duidaima.com */
function toPounds(kilos) {
if (isNaN(kilos)) {
return 'Not a Number! Cannot be a weight.';
}
return kilos * 2.2;
}
console.log(toPounds('this is a test'));
console.log(toPounds('100'));
输出:Not a Number! Cannot be a weight. 220.000000000000034. JavaScript 中的负无穷大是什么?
console.log(-10/0)输出:
-Infinity5. 什么是未声明变量?未定义的变量怎么样?
console.log(dog);输出:
error: Uncaught ReferenceError: dog is not defined未定义的变量在程序中声明但没有值。如果程序尝试读取未定义的变量,则会返回未定义的值并且应用程序不会崩溃。
let car; console.log(car);输出:
undefined6. JavaScript 中有哪几种弹出框?
window.alert("Hello, world!");
02).确认if (window.confirm("Are you sure you want to go?")) {
window.open("exit.html", "See you again!");
}
03).提示let person = window.prompt("Enter your name");
if (person != null) {
console.log('Hello', person);
}
7. == 和 === 有什么区别?var x = 100; var y = "100"; (x == y) // --> true because the value of x and y are the same (x === y) // --> false because the type of x is "number" and type of y is "string"8. 隐式类型强制有什么作用?举个例子。
var x = 1; var y = "2"; x + y // Returns "12"但是在处理减法时,强制以另一种方式起作用。它将字符串转换为数字。
var x = 10; var y = "10"; x - y // Returns 09. JavaScript 是静态类型语言还是动态类型语言?这是什么意思?
var num = 10; num = "Test";在静态类型语言(如 C++)中,不可能以这种方式将整数更改为字符串。
console.log(typeof(NaN))输出:
Number为避免混淆,请使用 isNaN() 来检查值的类型是 NaN 还是非数字。
function sum(a, b, c) {
return a + b + c;
}
const nums = [15, 25, 35];
console.log(sum(...nums));
输出:/* 堆代码 duidaima.com */
function createCounter() {
let counter = 0;
function increment() {
counter++;
console.log(counter);
}
return increment;
}
这里 createCounter() 是外部函数, increment() 是内部函数。现在您可以按如下方式使用它:const add = createCounter(); add(); add(); add();输出
function weekDay(dayNum) {
if (dayNum < 1 || dayNum > 7) {
throw 'InvalidDayNumber'
} else {
return ['Mon', 'Tue', 'Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri', 'Sat', 'Sun'][dayNum - 1];
}
}
try { // Try to run the following
let day = weekDay(8);
console.log(day);
}
catch (e) { // catch an error if the above try failed
let day = 'unknown';
console.log(e);
}
14. 什么是网络存储?// 堆代码 duidaima.com
// Save data to sessionStorage
sessionStorage.setItem('favoriteColor', 'gray');
// Get the color from the sessionStorage
let data = sessionStorage.getItem('favoriteColor');
console.log(data);
// Remove saved color preset from sessionStorage
sessionStorage.removeItem('favoriteColor');
// Remove ALL the saved data from sessionStorage
sessionStorage.clear();
以下是使用 localStorage 执行相同操作的方法:// Save data to localStorage
localStorage.setItem('favoriteColor', 'gray');
// Get the color from the localStorage
let data = localStorage.getItem('favoriteColor');
console.log(data);
// Remove saved color preset from localStorage
localStorage.removeItem('favoriteColor');
// Remove ALL the saved data from localStorage
localStorage.clear();
15. 为什么需要网络存储?import { hello } from './modules/helloWorld.js';
17. JavaScript 中的“作用域”是什么意思?if(true) {
let word = "Hello";
}
console.log(word); // ERROR OCCURS
在这里,除了在 if 语句中,不能从其他任何地方访问变量 word。function runThis(inputFunction) {
inputFunction();
}
runThis(function() { console.log("Hello world") });
输出Hello world另外一个例子:
function giveFunction() {
return function() {
console.log("Hello world")
}
}
var action = giveFunction();
action()
输出:var student = {
name: "Matt",
getName: function(){
console.log(this.name);
}
}
student.getName();
输出:var student = {
name: "Matt",
getName: function(){
console.log(this.name);
}
}
var anotherStudent = {
name: "Sophie"
};
student.getName.call(anotherStudent);
输出:SofieCall() 方法也可用于通过指定所有者对象来调用函数。
function sayHi(){
console.log("Hello " + this.name);
}
var person = {name: "Matt"};
sayHi.call(person);
输出:Hello Mattcall() 也可以接受参数。
function sayHi(adjective){
console.log("Hello " + this.name + ", You are " + adjective);
}
var obj = {name: "Matt"};
sayHi.call(obj, "awesome");
输出:Hello Matt, you are awesome21.什么是apply()方法?
const person = {
name: 'John'
}
function greet(greeting, message) {
return `${greeting} ${this.name}. ${message}`;
}
let result = greet.apply(person, ['Hello', 'How are you?']);
console.log(result);
输出:Hello John. How are you?在行中:
let result = greet.apply(person, ['Hello', 'How are you?']);在 greet() 函数中,“Hello”被分配给问候语,“How are you?”被分配给消息。
let person = {
name: 'John',
getName: function() {
console.log(this.name);
}
};
window.setTimeout(person.getName, 1000);
这不会打印名称“John”,而是打印 undefined。要理解为什么会发生这种情况,请以等效方式重写最后一行:let func = person.getName; setTimeout(func, 1000);setTimeout() 接收与人对象分开的函数,但没有人的名字。因此,当 setTimeout() 调用 person.getName 时,名称是未定义的。要解决此问题,您需要将 getName() 方法绑定到 person 对象:
let func = person.getName.bind(person); setTimeout(func, 1000);输出:
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
您可以通过以下方式调用此函数:function add(a) {
return function(b) {
return a + b;
}
}
现在您可以通过以下方式调用此柯里化函数:const promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// implement the promise here
})
例如,让我们创建一个在被调用两秒后解析的承诺。const promise = new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("Hello, world!");
}, 2000);
}, reject => {});
现在 promises 的关键是您可以在使用 .then() 方法解析 promise 后立即执行代码:promise.then(result => console.log(result));输出:
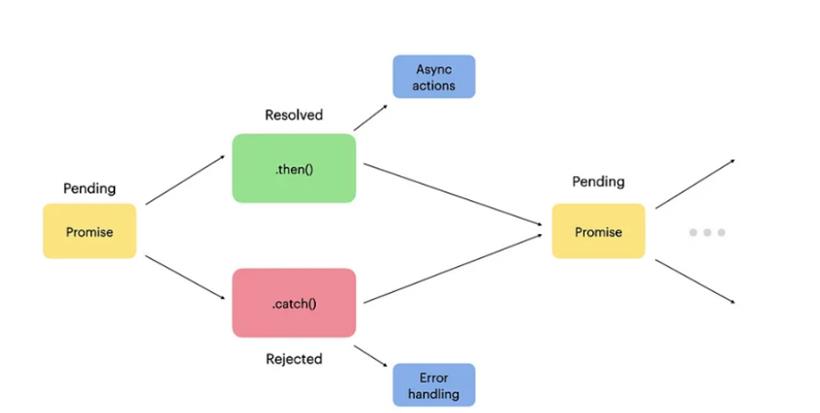
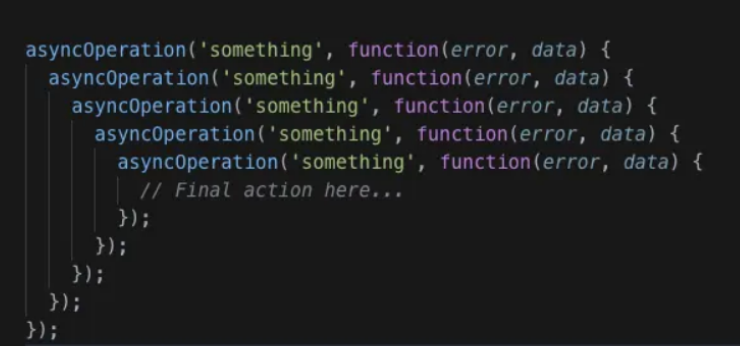
Promises 通过减少回调地狱和编写更清晰的代码,为回调提供了另一种方法。这是可能的,因为 promise 可以按以下方式链接:
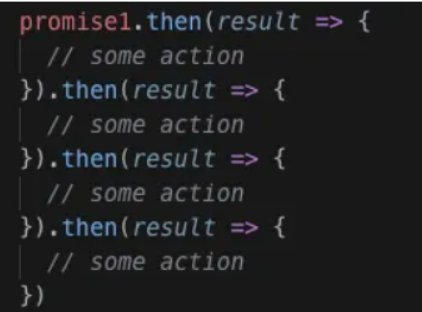
26. JavaScript 中的回调函数是什么?
回调函数是作为参数传递给另一个函数的函数。当某些动作完成时,此函数在传递给它的函数内部执行以“回调”。
让我们看一个例子:
function greetName(name) {
console.log('Hello ' + name);
}
function askName(callback) {
let name = prompt('Enter your name.');
callback(name);
}
askName(greetName);
此代码会提示您输入姓名,当您输入姓名时,它会对该姓名说“你好”。因此,回调函数(在本例中为 greetName)仅在您输入名称后执行。function greetName(name) {
console.log('Hello ' + name);
}
function askName(callback) {
let name = prompt('Enter your name.');
callback(name);
}
askName(greetName);
28. 什么是 JavaScript 中的严格模式?"use strict"; number = 1000;这会导致错误,因为严格模式会阻止您为未声明的变量赋值。
(function(){
// action here
})();
要了解 IIFE 的工作原理,请查看它周围的括号:当 JavaScript 看到关键字 function 时,它假设有一个函数声明来了。但是上面的声明是无效的,因为函数没有名字。为了解决这个问题,使用了声明周围的第一组括号,这告诉解释器这是一个函数表达式,而不是声明。(function (){
// action here;
})
然后,要调用该函数,需要在函数声明的末尾添加另一组括号,这类似于调用任何其他函数:(function (){
// action here
})();
30. 什么是cookie?document.cookie = "username=foobar123";31. 为什么要在 JavaScript 中使用严格模式?
'use strict'; const sentence = "Hello, this is very strict";32.双感叹号有什么作用?
!!true // true !!2 // true !![] // true !!"Test" // true !!false // false !!0 // false !!"" // false这是可行的,因为 JavaScript 中的任何东西本质上都是“Truthy”或“Falsy”。
var student = {name: "John", age:20};
delete student.age;
console.log(student);
输出:{name: "John"}
34. 如何检查 JavaScript 中变量的类型?typeof "John Abraham" // Returns "string" typeof 100 // Returns "number"35. JavaScript 中的 null 是什么?
var name = null; console.log(typeof(name))36. Null 与 undefined的区别
37. 你能用 JavaScript 访问历史记录吗?
这是可以的,您可以通过包含浏览器历史记录的 window.history 访问历史记录。要检索上一个和下一个 URL,可以使用以下方法:
window.history.back() window.history.forward()38.什么是全局变量?
x = 100; // Creates a global variable.此外,如果在任何函数之外使用 var 创建变量,则会创建一个全局变量。
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>堆代码- duidaima.com </title>
<script>
function sayHi() {
alert('Hi, how are you?');
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button type="button" onclick="sayHi()">Click here</button>
</body>
</html>
41. preventDefault() 方法有什么作用?document.getElementById("link").addEventListener("click", function(event){
event.preventDefault()
});
42.什么是setTimeout()方法?setTimeout(function() {
console.log("Good day");
}, 1000);
43.什么是setInterval()方法?setInterval(function() {
console.log("Good day");
}, 1000);
44. 什么是 ECMAScript?{
'name': 'Matt',
'address': 'Imaginary Road 22',
'age': 32,
'married': false,
'hobbies': ['Jogging', 'Tennis', 'Padel']
}
JSON 的语法规则是:var dataJSON = {name: "Matt", age: 51};
var dataString = JSON.stringify(dataJSON);
console.log(dataString);
输出:'{"name":"Matt","age":51}'
const a = b || c;这使得如果 b 是假的,那么 c 将被分配给 a。(Falsy 表示 null、false、undefined、0、空字符串或 NaN。)
let func = function(x) {
};
func.property1 = "Hello there";
console.log(func.property1);
输出:Hello there